Tool 32: Circles of Influence
| AKA | N/A |
| Classification | Team Building (TB) |
Tool description
The circles of influence tool allows a team to verify the extent of its self-management, decision-making authority, and problem-solving capability. Circles are used to display forces or problems that are within the team's influence or that are outside the team's influence.
Typical application
-
To evaluate problems and forces influencing a team's performance.
-
To identify a team's areas of responsibility and influence
-
To verify team management and authority.
-
To empower a team by increasing its influence and defining accountability.
Problem-solving phase
| Select and define problem or opportunity | |
| → | Identify and analyze causes or potential change |
| → | Develop and plan possible solutions or change |
| Implement and evaluate solution or change | |
| → | Measure and report solution or change results |
| Recognize and reward team efforts |
Typically used by
| Research/statistics | |
| 2 | Creativity/innovation |
| Engineering | |
| Project management | |
| Manufacturing | |
| Marketing/sales | |
| 4 | Administration/documentation |
| Servicing/support | |
| 3 | Customer/quality metrics |
| 1 | Change management |
before
-
Brainstorming
-
Consensus Decision Making
-
Team Process Assessment
-
Buzz Group
-
Team Mirror
after
-
Relationship Map
-
Sociogram
-
Delphi Method
-
Critical Dialogue
-
Multivoting
Notes and key points
-
Each participant takes no more than 10 minutes to list problems for consideration.
-
Use coding such as A-1, B-1, C-1, etc., to designate problems placed into circles of influence A-B-C.
Step-by-step procedure
-
STEP 1 The team's facilitator draws three circles of influence on a flip chart and explains the purpose and application of this tool. A team discussion follows.
-
STEP 2 The facilitator starts the team by providing an example problem for each circle of influence. Further clarification takes place to ensure that each participant understands the process.
-
STEP 3 Participants are asked to develop a list of existing and perceived problems that affect the team's present performance.
-
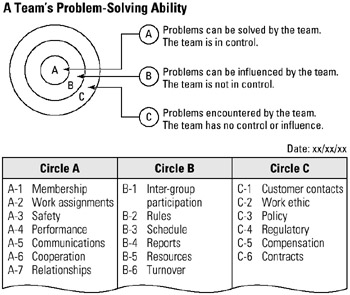
STEP 4 Once participants have completed their lists, the facilitator collects these lists for encoding and charting problems. See example A Team's Problem Solving Ability.
-
STEP 5 All listed problems are discussed and consensus is reached on where problems should be charted: circle A, B, or C. The first problem determined to be in circle A should be encoded as A-1.
-
STEP 6 All charted problems are recorded on flip charts titled Circle A, Circle B, and Circle C, as shown in the example. A discussion follows on the team's ability to control or influence problems.
-
STEP 7 Finally, the team explores ways to increase the team's influence, expand on its area of responsibility, and therefore, improve team performance.
Example of tool application
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 326