1.4 A Reference Model for IT Systems
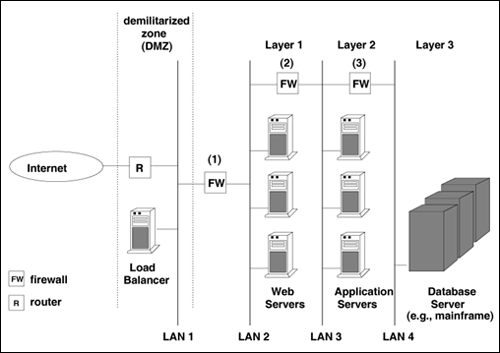
| IT systems do not exist in isolation. They are designed and built to serve the needs of and interact with human beings. This means that social systems and IT systems are usually integrated to form a "socio-technical" system [1]. Figure 1.7 shows a reference model for IT systems. System designers and developers depend on the social and business model that is to be supported by the system. The business model deals with the elements of the business that need to reflected in the design of an IT system. For example, the business model would include information on the number of branches, the number and location of ATMs, the number of accounts of each type, the number of executed banking transactions, as well as the bank's business evolution plans (e.g., mergers). The social model of the bank would include, for example, elements related to privacy policies to be enforced by the bank and its IT systems as well as accessibility policies of its systems to disabled people. Considerations at this level are vital to ensure that the high level requirements and constraints are satisfied by the system. Figure 1.7. A reference model for IT systems. The next layer in the reference model is the user interaction model, which describes the interactions between customers and the system. This model describes how users request services from the system, how often, and what is a typical sequence of submitted requests. An example of a user interaction model is the Customer Behavior Model Graph (CBMG) [11, 14] used to represent customer interactions with e-commerce and Web sites. The model captures the states a user may be in (e.g., searching, browsing, adding items to the shopping cart, checking out) as well as the transitions between these states. The model also includes the probability that these transitions take place as illustrated in Fig. 1.8. Figure 1.8. Example of a Customer Behavior Model Graph. Finally, the IT resources model deals with the elements of the IT infrastructure (e.g., processors, storage subsystems, networks, routers, firewalls) used to support the social and business model and the user interactions as depicted in Fig. 1.9. Figure 1.9. Example of an IT infrastructure. |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 166