10.7 A Class for Solving Systems of Linear Equations
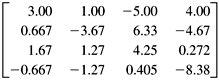
10.7 A Class for Solving Systems of Linear Equations We've covered a lot of ground so far in this chapter. We began by solving a system of linear equations with the Gaussian elimination algorithm, which involved forward elimination followed by back substitution. Then we recast the problem as the matrix equation Ax = b, and we used LU decomposition (forward elimination with scaled partial pivoting) to factor matrix A into matrices L and U. We used the equation Ly = b and forward substitution to solve for y, and then we used the equation Ux = y and back substitution to arrive at the solution x for the original system. With matrices L and U, we can quickly solve for x, given any new b. We can do iterative improvement on x. Listing 10-0 shows class LinearSystem in package numbercruncher.matrix , which is a subclass of SquareMatrix . A LinearSystem object represents a coefficient matrix A. Its methods can perform LU decomposition and solve for x when given b, where x and b are represented by ColumnVector objects. The class uses a couple of tricks. Instead of storing matrices L and U separately, it stores them together into a SquareMatrix object LU , which contains the elements of U in its upper triangle and the elements of L (without the ones on the diagonal) in its lower triangle. Thus, our matrices L and U from our example system would be stored in LU as The class does partial pivoting not by actually exchanging rows of the matrix but, instead, by keeping track of the exchanges in a permutation vector, implemented as the integer array permutation of row indices. Instead of exchanging rows, the class exchanges elements of permutation , and later, instead of indexing the rows directly, it goes through permutation . Thus, permutation also keeps a record of the row exchanges. The class computes the scaling factors, but it does not actually scale the rows by multiplying them by the factors. It uses the scaling factors only to decide whether or not a row exchange is needed to choose the best possible pivot element. Listing 10-0 The LinearSystem class. package numbercruncher.matrix; import java.util.Random; import numbercruncher.mathutils.Epsilon; import numbercruncher.mathutils.AlignRight; /** * Solve a system of linear equations using LU decomposition. */ public class LinearSystem extends SquareMatrix { private static final float TOLERANCE = Epsilon.floatValue(); /** max iters for improvement = twice # of significant digits */ private static final int MAX_ITER; static { int i = 0; float t = TOLERANCE; while (t < 1) { ++i; t *= 10; } MAX_ITER = 2*i; } /** decomposed matrix A = LU */ protected SquareMatrix LU; /** row index permutation vector */ protected int permutation[]; /** row exchange count */ protected int exchangeCount; /** * Constructor. * @param n the number of rows = the number of columns */ public LinearSystem(int n) { super(n); reset(); } /** * Constructor. * @param values the array of values */ public LinearSystem(float values[][]) { super(values); } /** * Set the values of the matrix. * @param values the 2-d array of values */ protected void set(float values[][]) { super.set(values); reset(); } /** * Set the value of element [r,c] in the matrix. * @param r the row index, 0..nRows * @param c the column index, 0..nRows * @param value the value * @throws matrix.MatrixException for invalid index */ public void set(int r, int c, float value) throws MatrixException { super.set(r, c, value); reset(); } /** * Set a row of this matrix from a row vector. * @param rv the row vector * @param r the row index * @throws matrix.MatrixException for an invalid index or * an invalid vector size */ public void setRow(RowVector rv, int r) throws MatrixException { super.setRow(rv, r); reset(); } /** * Set a column of this matrix from a column vector. * @param cv the column vector * @param c the column index * @throws matrix.MatrixException for an invalid index or * an invalid vector size */ public void setColumn(ColumnVector cv, int c) throws MatrixException { super.setColumn(cv, c); reset(); } /** * Reset. Invalidate LU and the permutation vector. */ protected void reset() { LU = null; permutation = null; exchangeCount = 0; } /** * Solve Ax = b for x using the Gaussian elimination algorithm. * @param b the right-hand-side column vector * @param improve true to improve the solution * @return the solution column vector * @throws matrix.MatrixException if an error occurred */ public ColumnVector solve(ColumnVector b, boolean improve) throws MatrixException { // Validate b's size. if (b.nRows != nRows) { throw new MatrixException( MatrixException.INVALID_DIMENSIONS); } decompose(); // Solve Ly = b for y by forward substitution. // Solve Ux = y for x by back substitution. ColumnVector y = forwardSubstitution(b); ColumnVector x = backSubstitution(y); // Improve and return x. if (improve) improve(b, x); return x; } /** * Print the decomposed matrix LU. * @param width the column width * @throws matrix.MatrixException if an error occurred */ public void printDecomposed(int width) throws MatrixException { decompose(); AlignRight ar = new AlignRight(); for (int r = 0; r < nRows; ++r) { int pr = permutation[r]; // permuted row index ar.print("Row ", 0); ar.print(r+1, 2); ar.print(":", 0); for (int c = 0; c < nCols; ++c) { ar.print(LU.values[pr][c], width); } ar.println(); } } /** * Compute the upper triangular matrix U and lower triangular * matrix L such that A = L*U. Store L and U together in * matrix LU. Compute the permutation vector permutation of * the row indices. * @throws matrix.MatrixException for a zero row or * a singular matrix */ protected void decompose() throws MatrixException { // Return if the decomposition is valid. if (LU != null) return; // Create a new LU matrix and permutation vector. // LU is initially just a copy of the values of this system. LU = new SquareMatrix(this.copyValues2D()); permutation = new int[nRows]; float scales[] = new float[nRows]; // Loop to initialize the permutation vector and scales. for (int r = 0; r < nRows; ++r) { permutation[r] = r; // initially no row exchanges // Find the largest row element. float largestRowElmt = 0; for (int c = 0; c < nRows; ++c) { float elmt = Math.abs(LU.at(r, c)); if (largestRowElmt < elmt) largestRowElmt = elmt; } // Set the scaling factor for row equilibration. if (largestRowElmt != 0) { scales[r] = 1/largestRowElmt; } else { throw new MatrixException(MatrixException.ZERO_ROW); } } // Do forward elimination with scaled partial row pivoting. forwardElimination(scales); // Check bottom right element of the permuted matrix. if (LU.at(permutation[nRows - 1], nRows - 1) == 0) { throw new MatrixException(MatrixException.SINGULAR); } } /** * Do forward elimination with scaled partial row pivoting. * @parm scales the scaling vector * @throws matrix.MatrixException for a singular matrix */ private void forwardElimination(float scales[]) throws MatrixException { // Loop once per pivot row 0..nRows-1. for (int rPivot = 0; rPivot < nRows - 1; ++rPivot) { float largestScaledElmt = 0; int rLargest = 0; // Starting from the pivot row rPivot, look down // column rPivot to find the largest scaled element. for (int r = rPivot; r < nRows; ++r) { // Use the permuted row index. int pr = permutation[r]; float absElmt = Math.abs(LU.at(pr, rPivot)); float scaledElmt = absElmt*scales[pr]; if (largestScaledElmt < scaledElmt) { // The largest scaled element and // its row index. largestScaledElmt = scaledElmt; rLargest = r; } } // Is the matrix singular? if (largestScaledElmt == 0) { throw new MatrixException(MatrixException.SINGULAR); } // Exchange rows if necessary to choose the best // pivot element by making its row the pivot row. if (rLargest != rPivot) { int temp = permutation[rPivot]; permutation[rPivot] = permutation[rLargest]; permutation[rLargest] = temp; ++exchangeCount; } // Use the permuted pivot row index. int prPivot = permutation[rPivot]; float pivotElmt = LU.at(prPivot, rPivot); // Do the elimination below the pivot row. for (int r = rPivot + 1; r < nRows; ++r) { // Use the permuted row index. int pr = permutation[r]; float multiple = LU.at(pr, rPivot)/pivotElmt; // Set the multiple into matrix L. LU.set(pr, rPivot, multiple); // Eliminate an unknown from matrix U. if (multiple != 0) { for (int c = rPivot + 1; c < nCols; ++c) { float elmt = LU.at(pr, c); // Subtract the multiple of the pivot row. elmt -= multiple*LU.at(prPivot, c); LU.set(pr, c, elmt); } } } } } /** * Solve Ly = b for y by forward substitution. * @param b the column vector b * @return the column vector y * @throws matrix.MatrixException if an error occurred */ private ColumnVector forwardSubstitution(ColumnVector b) throws MatrixException { ColumnVector y = new ColumnVector(nRows); // Do forward substitution. for (int r = 0; r < nRows; ++r) { int pr = permutation[r]; // permuted row index float dot = 0; for (int c = 0; c < r; ++c) { dot += LU.at(pr, c)*y.at(c); } y.set(r, b.at(pr) - dot); } return y; } /** * Solve Ux = y for x by back substitution. * @param y the column vector y * @return the solution column vector x * @throws matrix.MatrixException if an error occurred */ private ColumnVector backSubstitution(ColumnVector y) throws MatrixException { ColumnVector x = new ColumnVector(nRows); // Do back substitution. for (int r = nRows - 1; r >= 0; --r) { int pr = permutation[r]; // permuted row index float dot = 0; for (int c = r+1; c < nRows; ++c) { dot += LU.at(pr, c)*x.at(c); } x.set(r, (y.at(r) - dot)/LU.at(pr, r)); } return x; } /** * Iteratively improve the solution x to machine accuracy. * @param b the right-hand side column vector * @param x the improved solution column vector * @throws matrix.MatrixException if failed to converge */ private void improve(ColumnVector b, ColumnVector x) throws MatrixException { // Find the largest x element. float largestX = 0; for (int r = 0; r < nRows; ++r) { float absX = Math.abs(x.values[r][0]); if (largestX < absX) largestX = absX; } // Is x already as good as possible? if (largestX == 0) return; ColumnVector residuals = new ColumnVector(nRows); // Iterate to improve x. for (int iter = 0; iter < MAX_ITER; ++iter) { // Compute residuals = b - Ax. // Must use double precision! for (int r = 0; r < nRows; ++r) { double dot = 0; float row[] = values[r]; for (int c = 0; c < nRows; ++c) { double elmt = at(r, c); dot += elmt*x.at(c); // dbl.prec. * } double value = b.at(r) - dot; // dbl.prec. - residuals.set(r, (float) value); } // Solve Az = residuals for z. ColumnVector z = solve(residuals, false); // Set x = x + z. // Find largest the largest difference. float largestDiff = 0; for (int r = 0; r < nRows; ++r) { float oldX = x.at(r); x.set(r, oldX + z.at(r)); float diff = Math.abs(x.at(r) - oldX); if (largestDiff < diff) largestDiff = diff; } // Is any further improvement possible? if (largestDiff < largestX*TOLERANCE) return; } // Failed to converge because A is nearly singular. throw new MatrixException(MatrixException.NO_CONVERGENCE); } } Public method solve() returns a solution ColumnVector for a ColumnVector parameter b , assuming there were no exceptions, such as singularity. It calls method decompose() , forwardSubstitution() , and backSubstitution() . It calls method improve() to iteratively improve the solution vector x if the boolean parameter improve is true , and then it returns x . Method decompose() computes the values of the decomposed matrix LU . This matrix is not recomputed unless any coefficient value of matrix A was changed by a call to method set() , setRow() , or setColumn() . Method decompose() calls method forwardElimination() . Method improve() uses double-precision arithmetic to compute the residual values, whose accuracy is crucial to ensure convergence. It iterates at most MAX_ITER times, which is statically computed to be twice the number of significant digits. |
| |
| Top |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 141