| Java Number Cruncher: The Java Programmer's Guide to Numerical Computing |
| By Ronald Mak |
| | |
| Publisher | : Prentice Hall PTR |
| Pub Date | : October 29, 2002 |
| ISBN | : 0-13-046041-9 |
| Pages | : 480 |
| Supplier | : Team FLY |  | Copyright |
| |  | Preface |
| |  | How to Download the Source Code |
| |  | Part I. Why Good Computations Go Bad |
| | |  | Chapter 1. Floating-Point Numbers Are Not Real! |
| | |  | Section 1.1. Roundoff Errors |
| | |  | Section 1.2. Error Explosion |
| | |  | Section 1.3. Real Numbers versus Floating-Point Numbers |
| | |  | Section 1.4. Precision and Accuracy |
| | |  | Section 1.5. Disobeying the Laws of Algebra |
| | |  | Section 1.6. And What about Those Integers? |
| | |  | References |
 |
| | |  | Chapter 2. How Wholesome Are the Integers? |
| | |  | Section 2.1. The Integer Types and Operations |
| | |  | Section 2.2. Signed Magnitude versus Two's-Complement |
| | |  | Section 2.3. Whole Numbers versus Integer Numbers |
| | |  | Section 2.4. Wrapper Classes |
| | |  | Section 2.5. Integer Division and Remainder |
| | |  | Section 2.6. Integer Exponentiation |
| | |  | References |
 |
| | |  | Chapter 3. The Floating-Point Standard |
| | |  | Section 3.1. The Floating-Point Formats |
| | |  | Section 3.2. Denormalized Numbers |
| | |  | Section 3.3. Decomposing Floating-Point Numbers |
| | |  | Section 3.4. The Floating-Point Operations |
| | |  | Section 3.5. ±0, ± 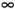 , and NaN , and NaN |
| | |  | Section 3.6. No Exceptions! |
| | |  | Section 3.7. Another Look at Roundoff Errors |
| | |  | Section 3.8. Strict or Nonstrict Floating-Point Arithmetic |
| | |  | Section 3.9. The Machine Epsilon 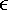 |
| | |  | Section 3.10. Error Analysis |
| | |  | References |
 |
 |
| |  | Part II. Iterative Computations |
| | |  | Chapter 4. Summing Lists of Numbers |
| | |  | Section 4.1. A Summing Mystery ”the Magnitude Problem |
| | |  | Section 4.2. The Kahan Summation Algorithm |
| | |  | Section 4.3. Summing Numbers in a Random Order |
| | |  | Section 4.4. Summing Addends with Different Signs |
| | |  | Section 4.5. Insightful Computing |
| | |  | Section 4.6. Summation Summary |
| | |  | References |
 |
| | |  | Chapter 5. Finding Roots |
| | |  | Section 5.1. Analytical versus Computer Solutions |
| | |  | Section 5.2. The Functions |
| | |  | Section 5.3. The Bisection Algorithm |
| | |  | Section 5.4. The Regula Falsi Algorithm |
| | |  | Section 5.5. The Improved Regula Falsi Algorithm |
| | |  | Section 5.6. The Secant Algorithm |
| | |  | Section 5.7. Newton's Algorithm |
| | |  | Section 5.8. Fixed-Point Iteration |
| | |  | Section 5.9. Double Trouble with Multiple Roots |
| | |  | Section 5.10. Comparing the Root-Finder Algorithms |
| | |  | References |
 |
| | |  | Chapter 6. Interpolation and Approximation |
| | |  | Section 6.1. The Power Form versus the Newton Form |
| | |  | Section 6.2. Polynomial Interpolation Functions |
| | |  | Section 6.3. Divided Differences |
| | |  | Section 6.4. Constructing the Interpolation Function |
| | |  | Section 6.5. Least-Squares Linear Regression |
| | |  | Section 6.6. Constructing the Regression Line |
| | |  | References |
 |
| | |  | Chapter 7. Numerical Integration |
| | |  | Section 7.1. Back to Basics |
| | |  | Section 7.2. The Trapezoidal Algorithm |
| | |  | Section 7.3. Simpson's Algorithm |
| | |  | References |
 |
| | |  | Chapter 8. Solving Differential Equations Numerically |
| | |  | Section 8.1. Back to Basics |
| | |  | Section 8.2. A Differential Equation Class |
| | |  | Section 8.3. Euler's Algorithm |
| | |  | Section 8.4. A Predictor-Corrector Algorithm |
| | |  | Section 8.5. The Fourth-Order Runge-Kutta Algorithm |
| | |  | References |
 |
 |
| |  | Part III. A Matrix Package |
| | |  | Chapter 9. Basic Matrix Operations |
| | |  | Section 9.1. Matrix |
| | |  | Section 9.2. Square Matrix |
| | |  | Section 9.3. Identity Matrix |
| | |  | Section 9.4. Row Vector |
| | |  | Section 9.5. Column Vector |
| | |  | Section 9.6. Graphic Transformation Matrices |
| | |  | Section 9.7. A Tumbling Cube in 3-D Space |
| | |  | References |
 |
| | |  | Chapter 10. Solving Systems of Linear Equations |
| | |  | Section 10.1. The Gaussian Elimination Algorithm |
| | |  | Section 10.2. Problems with Gaussian Elimination |
| | |  | Section 10.3. Partial Pivoting |
| | |  | Section 10.4. Scaling |
| | |  | Section 10.5. LU Decomposition |
| | |  | Section 10.6. Iterative Improvement |
| | |  | Section 10.7. A Class for Solving Systems of Linear Equations |
| | |  | Section 10.8. A Program to Test LU Decomposition |
| | |  | Section 10.9. Polynomial Regression |
| | |  | References |
 |
| | |  | Chapter 11. Matrix Inversion, Determinants, and Condition Numbers |
| | |  | Section 11.1. The Determinant |
| | |  | Section 11.2. The Inverse |
| | |  | Section 11.3. The Norm and the Condition Number |
| | |  | Section 11.4. The Invertible Matrix Class |
| | |  | Section 11.5. Hilbert Matrices |
| | |  | Section 11.6. Comparing Solution Algorithms |
| | |  | References |
 |
 |
| |  | Part IV. The Joys of Computation |
| | |  | Chapter 12. Big Numbers |
| | |  | Section 12.1. Big Integers |
| | |  | Section 12.2. A Very Large Prime Number |
| | |  | Section 12.3. Big Integers and Cryptography |
| | |  | Section 12.4. Big Decimal Numbers |
| | |  | Section 12.5. Big Decimal Functions |
| | |  | References |
 |
| | |  | Chapter 13. Computing p |
| | |  | Section 13.1. Estimates of p and Ramanujan's Formulas |
| | |  | Section 13.2. Arctangent Formulas That Generate p |
| | |  | Section 13.3. Generating Billions of Digits |
| | |  | References |
 |
| | |  | Chapter 14. Generating Random Numbers |
| | |  | Section 14.1. Pseudorandom Numbers |
| | |  | Section 14.2. Uniformly Distributed Random Numbers |
| | |  | Section 14.3. Normally Distributed Random Numbers |
| | |  | Section 14.4. Exponentially Distributed Random Numbers |
| | |  | Section 14.5. Monte Carlo, Buffon's Needle, and p |
| | |  | References |
 |
| | |  | Chapter 15. Prime Numbers |
| | |  | Section 15.1. The Sieve of Eratosthenes and Factoring |
| | |  | Section 15.2. Congruences and Modulo Arithmetic |
| | |  | Section 15.3. The Lucas Test |
| | |  | Section 15.4. The Miller-Rabin Test |
| | |  | Section 15.5. A Combined Primality Tester |
| | |  | Section 15.6. Generating Prime Numbers |
| | |  | Section 15.7. Prime Number Patterns |
| | |  | References |
 |
| | |  | Chapter 16. Fractals |
| | |  | Section 16.1. Fixed-Point Iteration and Orbits |
| | |  | Section 16.2. Bifurcation and the Real Function f ( x ) = x 2 + c |
| | |  | Section 16.3. Julia Sets and the Complex Function f ( z ) = z 2 + c |
| | |  | Section 16.4. Newton's Algorithm in the Complex Plane |
| | |  | Section 16.5. The Mandelbrot Set |
| | |  | References |
 |
| Top |