Study Approach
|
| < Day Day Up > |
|
A set of sampling criteria was initially determined in order to identify the studies that formed the foundation for our research endeavor. First, we decided to include only those studies that have been published in major journals within the IS domain. Second, only studies published between 1995 and 2002 were included for further consideration. Third, we limited our focus to those electronic commerce studies that were conducted at the individual level unit of analysis. Hence, consumers or users of web technologies were the main subjects in these studies. Fourth, for a study to be included, it had to be based on empirical (quantitative) analysis. This allowed us to focus on empirically tested constructs and relationships rather than those that have only been conceptualized.
Based on the stated criteria, we conducted a thorough search of the following major IS journals: Communications of the ACM; Decision Sciences; Decision Support Systems; IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics; Information Systems Research; Information Technology and Management; Information and Management; International Journal of Electronic Commerce; Journal of End User Computing; Journal of Management Information Systems; and MIS Quarterly. These journals were considered to be mainstream IS journals that are appropriate outlets for research on online consumer behavior. Studies were located via computer searches of large bibliographic databases (UMI-Proquest and ScienceDirect) and by manually scanning the journals. For search of electronic databases, a list of keywords (e-commerce, electronic commerce, web site, technology acceptance model, World Wide Web, online, B2C, Internet, theory of planned behavior, consumer behavior, trust, etc.) in combination with the name of the journal was used for identification of the articles. Upon completion, a total of 42 nonredundant papers were identified for inclusion.
As shown in Table 1, the most popular outlets for online consumer behavior research were Information Systems Research (11 articles), International Journal of Electronic Commerce (11 articles), and Information and Management (nine articles). Two recent special issues on e-commerce metrics were the main sources of the Information Systems Research articles. As shown in Figure 1, the analysis of the studies published in those IS journals over time confirmed a recent surge of research interest on this subject. While the number of articles published each year was increasing over time, most articles were published in 2000 and thereafter (seven articles before 2000, seven articles in 2000, seven articles in 2001, and 21 articles in 2002).
| Journals | Count |
|---|---|
| Information Systems Research | 11 |
| International Journal of Electronic Commerce | 11 |
| Information & Management | 9 |
| Communications of the ACM | 3 |
| MIS Quarterly | 2 |
| IEEE Transactions on Systems Man and Cybernetics | 2 |
| Journal of Management Information Systems | 1 |
| Information Technology and Management | 1 |
| Decision Support Systems | 1 |
| Journal of End User Computing | 1 |
| Total | 42 |
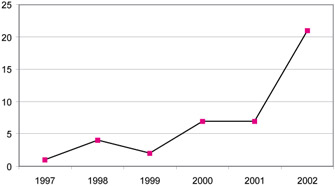
Figure 1: Yearly Number of Online Consumer Behavior Studies Published in IS Journals
Two researchers read each of the papers and independently coded and tabulated the following items in independent tables: methodology, sample size, sample source, independent and dependent variables, task, theory basis, and study findings. The coders then met to compare the tables and resolve the discrepant cases in order to reach a consensus in their categorization and tabulation, as shown in Table 2. The overall inter-rater agreement between the two coders for the categorization of study methodology, sample source, theory basis, and task was 94%. Analysis showed that the most common research method is survey (23 studies), followed by laboratory experiments (15 studies), combined approaches (three studies), and secondary data analysis (1 study). Half of the studies used consumers and the other half used student (including undergraduate and graduate) subjects as the source of samples. A total number of 27,202 individuals participated in the studies that were included in the final set. Laboratory experiment-based studies either used actual web sites (web sites for books, airline tickets, legal services, automotives, car rental, etc.) or resorted to simulated replicas of actual web sites. Books were the most popular product type used in the studies. Other product types included CDs, airline tickets, used laptop computers, videos, and flowers. In terms of virtual products, legal services, e-banking services, financial products, and news services were employed by the studies. Subjects were typically asked to respond to the instrument based on their immediate prior experience or their general impression regarding behavior in an online environment. The tasks ranged from rating web site attributes that may influence their behavior to making purchases for a specific product.
| No. | Year | Cite | Method | N | Sample Source | IV | DV | Task | Theory Basis | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1997 | Jarvenpaa & Todd | Experiment | 220 | Primary household shoppers | Product perceptions, shopping experience, customer service, & consumer risk | Attitude and intentions toward electronic shopping | N/A | Retail patronage (Arnold et al., 1978) | Product perceptions, shopping experience, and customer service were found to affect consumer behavior. |
| 2 | 1998 | Agarwal & Parsad | Survey | 175 | Part-time MBA students | Computer playfulness & personal innovativeness | Acceptance behavior | N/A | TAM (Davis, 1989) & Innovation diffusion theory (Rogers, 1983) | Personal innovativeness construct was developed and validated and was proposed to affect individual perceptions about a new IT. |
| 3 | 1998 | Liang & Huang | Survey | 85 | Internet users | Uncertainty, asset specificity & transaction cost | Perceived acceptance of electronic channel | Product purchase: books, shoes, toothpaste, microwave & flower | Transaction cost economics (Williamson, 1979, 1985) | Experienced shoppers were found to be more concerned about the uncertainty in electronic shopping, which subsequently increased transaction costs and reduced acceptance of electronic channels. |
| 4 | 1998 | Parthasarathy & Bhattacherjee | Survey | 145 | Consumers | External influence, interpersonal influence, utilization, usefulness, ease of use, compatibility, & network externality Time of adoption, external influence, interpersonal influence, & utilization | Discontinuers and continuing adopters Discontinuer type: replacement Vs disenchantment | Evaluation of an online service | Innovation diffusion theory (Rogers, 1983; Brancheau & Wetherbe 1990) | External influence, interpersonal influence, utilization, usefulness, compatibility and network externality were found to be the distinguishing factors between discontinuers and continuing adopters. Time of adoption, interpersonal influence and utilization explained whether discontinuation results from replacement or disenchantment. |
| 5 | 1998 | Westland & Au | Experiment | 116 | Under-graduate students | Catalog look up interface, bundles (pre-selected assortment or kits) and virtual reality based store fronts | Money spent, time spent & number of items | N/A | Virtual reality shopping behavior (Burke, 1996) | No difference was found in the amount of money spent or item purchases by customers interacting with three different types of Web interfaces, but subjects did spend much more time while interacting with a virtual reality interface. |
| 6 | 1999 | Bellman, Lohse, & Johnson | Survey | 10,000 | Household shoppers | Looking for product information, wired lifestyle, discretionary time, email use, demographic variables (gender, education, age, income) & privacy | Online purchase & annual online spending | N/A | Shopping behavior life cycle (Rich, 1968) | Wired life style and time starvation were found to be the most important predictors of online purchase behavior. Privacy and security issues were important but were becoming increasing less important predictors of online shopping. |
| 12 | 2000 | Limayem, Khalifa, & Frini | Survey | 705 | Web shoppers | Personal innovativeness, subjective norms, behavioral control, perceived consequences, & intention | Internet shopping | N/A | Theory of planned behavior (Ajzen, 1991) | Shopping behavior was found to influence intentions and behavioral controls. Intentions were determined by attitudes and were also moderately affected by perceived consequences, personal innovativeness and subjective norms. Attitudes were strongly influenced by perceived consequences and moderately by personal innovativeness |
| 13 | 2000 | Liu & Arnett | Survey | 119 | Webmasters | Information quality, learning capability, playfulness, system quality, system use, & service quality | Web site success | N/A | TAM (Davis, 1989) | Information service quality, system use, playfulness, and system design were found to impact Web site success. |
| 14 | 2000 | Otto, Najdawi, & Caron | Experiment | 60 | Under-graduate students | Download time | Web-user satisfaction, format, ease of use, graphics appeal, responsiveness | N/A | User information satisfaction (Doll & Torkzadeh, 1988, 1994) | Delays of 15 seconds or less did not impact a user's overall level of satisfaction. |
| 15 | 2000 | Vellido, Lisboa, & Meehan | Survey | 2,180 | Web users | Shopping experience, consumer risk perception, customer service & product perception | Propensity to buy online | N/A | Consumer's reaction to the Web (Jarvenpaa & Todd, 1997) | Shopping experience (compatibility), consumer risk perception (trust and security), affordability, ease of use (effort), and customer service (effort, responsiveness and empathy) were found to be the main predictors of online purchase behavior. Demographic variables such as age, income, and Web usage pattern did not add to the predictive power of the model. |
| 16 | 2001 | Barnes & Vidgen | Survey | 96 | Students | Tangibles, reliability, responsiveness, assurance, & empathy | N/A | Evaluation of Web site selling books | SERVQUAL (Parasuraman et al., 1988) | WebQual is developed and used to evaluate Internet bookshops' Web site quality. |
| 17 | 2001 | Griffith, Krampf, & Palmer | Experiment | 336 | Students | Consumer involvement with retailer's offerings, product evaluation, attitude change | Shopping intentions | Evaluation of Web based and print catalogs | Interface-involvement theory (Reeves & Nass, 1996) | A print physical-medium interface was found to be more effective than a Web-based physical-medium interface in stimulating consumer involvement with retailer offerings and a positive consumer response. |
| 18 | 2001 | Lee & Turban | Survey | 405 | Students | Trustworthiness of Internet merchant (ability, integrity and benevolence), trustworthiness of Internet shopping medium (technical competence, reliability, and medium understanding), & contextual factors (effectiveness of third party certification & effectiveness of security infrastructure) | Consumer trust in Internet shopping | N/A | Trust (Mayer et al., 1995) | Merchant integrity was found to be a major positive determinant of consumer trust in Internet shopping, and that its effect was moderated by the individual consumer's trust propensity. |
| 19 | 2001 | Liao & Cheung | Survey | 312 | Household members | Price (market participation and retail price), shopping experience, vendor quality, IT education Internet usage, & network speed | Willingness to shop online | N/A | IS and Marketing literature | Transaction security, retail price, and shopping experience were found to negatively impact willingness to purchase on the Internet. Vendor quality, IT education and training, and level of Internet usage were positively related to willingness to purchase. The network speed had no significant impact. |
| 20 | 2001 | Moon & Kim | Survey | 152 | Graduate students | Ease of use, usefulness, playfulness & attitude toward use | Behavioral intention to use the Web | N/A | TAM (Davis, 1989) | The study extended and validated the TAM within a Web context by introducing playfulness as a new factor that reflected the user's intrinsic belief in Web acceptance. |
| 21 | 2001 | Ramaswami, Stader, & Brett | Survey | 154 | Users of financial services | Agent performance (task and return performance) satisfaction, conflict, knowledge of financial products, confidence in decision making, & time availability | Willingness to use online channel, searches for financial information & online-purchase | Product purchase: financial products | Motivation-ability-opportunity framework (Macinnis et al., 1991) | Performance of the agent was related to higher levels of online information search, but did not impact online purchase. Disagreements between the client and the agent acted as an antecedent to use of online channel and online purchase. Knowledge and confidence were not related to information search or online purchases. Willingness to use the online channel was positively related to information search but not actual purchases. Time availability, money, age, and amount of advice by the agent were not found to be significant. |
| 22 | 2002 | Agarwal & Venkatesh | Survey | 1475 | Household consumers & investors | Content, ease of use, promotion, made for the medium, & emotion | Web site usability | Evaluation of Web sites: airline, bookstore, auto manufactures, and car rental | Human Computer Interaction literature and Microsoft usability guidelines | Content was found to be equally important across all industries and tasks. Customer deemed ease of use to be more important than investors. In contrast, investors found promotion to be more important than customers. |
| 23 | 2002 | Aladwani & Palvia | Survey | 101 127 | Students | Technical adequacy, specific content, content quality, appearance | N/A | Evaluation of Web site: banks, bookshops, car, and electronics | Web quality literature | Perceived Web quality is conceptualized as consisting of technical adequacy (security, navigation, search facilities), specific content (general information, contact information, policies), content quality (accuracy, completeness, clarity, currency, usefulness, and conciseness), and appearance (attractiveness, colors, multimedia). |
| 24 | 2002 | Ba & Pavlou | Experiment & Field Study | 393 | e-Bay's users | Feedback profile, trust in seller | Price premium | Product purchase: auction goods | Literature on trust & rating systems | Appropriate feedback mechanism induced calculus-based credibility trust without repeated interactions between two transacting parties. Trust mitigated information asymmetry by reducing transaction-specific risks, which eventually generated price premiums for reputable sellers. |
| 25 | 2002 | Bhattacherjee | Survey | 147 | Evening MBA students | Ability, integrity, benevolence & overall trust | Willingness to transact | Product purchase: books and bank account | Nomological model of trust | Scales for ability, integrity, benevolence, and overall trust dimensions were developed and validated within the Web context. |
| 26 | 2002 | Chau, Cole, Massey, Weiss, & O'Keefe | Experiment & Survey for each study | 119 (USA) 150 (Hong Kong) | Students | Culture and purpose of Internet use | Attitude toward Internet use | Evaluation of Web site: automobile (Ford) | Literature on culture | Subjects in the U.S. had a higher level of use of the Web for electronic commerce and information search, while subjects in Hong Kong used the Web more for hobby activities and social communication. |
| 27 | 2002 | Chen, Gillenson, & Sherrell | Survey | 253 | Web shoppers | Compatibility, perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, attitude toward use, & intention to use | Use (purchase or seek information) | Product purchase: multiple (Books, CDs etc.) | TAM (Davis, 1989) & Innovation diffusion theory (Rogers, 1983) | Compatibility, perceived usefulness and perceived ease of use were found to predict attitude toward using a Web site. Compatibility and perceived ease of use also impacted perceived usefulness. Attitude determined intention of use, which in return predicted actual use. |
| 28 | 2002 | Chen & Hitt | Secondary Data Analysis | 2902 | Investors | Demographics, Web site usage, change in usage, use of multiple brokers, Web site quality, product breadth, cost, personalization, ease of use, minimum deposit, & investment in retention | Switching & attrition | Product purchase: use of online brokerage services | Random utility modeling framework (McFadden, 1974) | Usage and change in usage were found to be good predictors of switching and attrition. Site quality, minimum balance requirement and costs also influenced customer behavior. The low minimum balance attracted customers but also subsequently increased their propensity to switch. |
| 29 | 2002 | Devaraj, Fan, & Kohli | Experiment | 134 | Consumers | Ease of use, usefulness, uncertainty, asset specificity, empathy, responsiveness, reliability, & assurance | Channel satisfaction & channel preference | Product purchase: books and CDs | TAM (Davis, 1989), Transaction cost economics (Williamson, 1979), & SERVQUAL (Parasuraman et al., 1988) | Technology acceptance and transaction cost economics variables were found to be good predictors of channel satisfaction. Empathy and assurance were the only variables in SERVQUAL that predicted channel satisfaction. It was found that the integrated model that combined the three models provided a better picture of factors that affected channel satisfaction, which impacted channel preference. |
| 30 | 2002 | Koufaris | Experiment | 280 | Web shoppers | Product involvement, Web skills, value and non-value added services, & challenges Perceived control, Shopping enjoyment, Concentration, Perceived usefulness, & Perceived ease of use | Unplanned purchases & intention to return | Product purchase: books (bookamillion.com) | TAM (Davis, 1989) & Flow theory (Csikszentmihalyi, 1988) | Product involvement, Web skills, and challenges impact concentration, while these factors along with value and non-value added services impacted shopping enjoyment. None of the variables in the model significantly predicted unplanned purchases. Shopping enjoyment and usefulness were found to be significant predictors of intention to return. It was concluded that the interface and Web functionalities might be equally important to retain a customer as compared with customer service and lower prices. |
| 31 | 2002 | Koufaris, Kambil, & LaBarbera | Survey | 332 | Consumers | Search mechanism used, positive challenges, shopping enjoyment, perceived control | Unplanned purchases & intention to return | Product purchase: video (Kozmo.com) | Theory of planned behavior (Ajzen, 1991) & Flow theory (Csikszentmihalyi, 1988) | Perceived control and shopping enjoyment impacted the intention of new Web customers to return, but did not influence repeat customers to return. It was also found that Web store that utilized value added search mechanisms and presented a positively challenging experience improved customer's shopping enjoyment. |
| 32 | 2002 | Liang & Lai | Experiment | 30 | Students | Motivators, hygiene factors, & media richness | Purchase from an online store, future visit, & future purchase | Product purchase: books | Online consumer behavior literature | Motivators (search engines, shopping carts), hygiene (security, risk), and media richness (feedback, chat channels) were found to be good predictors of channel choice. Motivators were found to be the most important factors followed by media richness and hygiene factors. |
| 33 | 2002 | Liao & Cheung | Survey | 323 | Consumers | Security, accuracy, speed of transaction, user involvement, convenience, ease of use, & experience | Willingness to use e-banking | Product purchase: e-banking | Literature on information technology use and cognitive analysis | Security, accuracy, speed of transaction, user involvement, and ease of use were found to play a significant role in predicting willingness to use Internet based e-banking. |
| 34 | 2002 | Lu & Lin | Experiment | 145 | Under-graduate students | Content belief, context belief, infrastructure belief, & customer attitude | Customer loyalty | Evaluation of an e-publishing Web site (news) | Rayport & Sviokla model & Theory of reasoned action (Fishbein & Ajzen, 1975) | Content belief, context belief, and infrastructure belief were found to predict consumer's attitude, which subsequently impacted their loyalty. Content belief also had a direct effect on customer loyalty. |
| 35 | 2002 | McKinney, Yoon, & Zahedi | Survey Experiment | 568 312 | Students consumers | Web information quality and Web service quality | Web customer satisfaction | Product search: airline tickets | End user satisfaction literature, IS use and success literature, and expectancy disconfirmation paradigm | The difference between information quality expectation and information quality perceived performance led to information quality disconfirmation. Similarly, the difference between service quality expectation and service quality perceived performance led to service quality disconfirmation. Both these factors impacted Web information quality and Web service quality and these factors then determined Web customer satisfaction. |
| 36 | 2002 | McKnight, Choudhury, & Kacmar | Experiment | 1403 | Students | Disposition to trust, (control for personal innovativeness), institution-based trust (control for general we experience), trusting beliefs, & trusting intentions (control for perceived site quality) | Trust related behavior | Evaluation of a Web site offering legal advice | Theory of reasoned action (Fishbein & Ajzen, 1975) | The trust construct is proposed and validated as a multi-dimensional construct (disposition to trust, institution-based trust, trusting beliefs, and trusting intentions). |
| 37 | 2002 | Palmer | Experiment | 35 30 35 | Undergraduate, graduate, executive MBA students | Download delay, navigation/organization, interactivity, responsiveness, & information/content | Web site success | Evaluation of 750 Web sites | Web site usability and design literature & Media richness theory | Results from three studies suggested that Web site success was significantly associated with Web site download delay, navigation, content, interactivity, and responsiveness. |
| 38 | 2002 | Ranganathan & Ganapathy | Survey | 214 | Online shoppers | Information content, design, security, & privacy | Intent to purchase | N/A | Literature on Web site characteristics and functionalities | Information content, design, security, and privacy were found to discriminate between shopper who had high intent to purchase and low intent to purchase. In terms of order of importance, security had the highest ranking followed by privacy, design, and information content. |
| 39 | 2002 | Slyke, Comunale, & Belanger | Survey | 511 | Students | Gender, full-time work experience, computer use, major, age, email use, word processing use, Web browser use, prior Web experience, access to credit card and access to the Web | Intention to shop on the Web | N/A | Innovation diffusion theory (Rogers, 1983) | Gender, computer use, email use, prior Web use, and access to credit card were found to be significant predictors of intent to shop on the Web. Men rated compatibility, relative advantage, result demonstrability, and trustworthiness of Web shopping higher, and its complexity lower than did women. It was argued that women viewed shopping as a social activity and were less technology oriented as compared to men. |
| 40 | 2002 | Stafford & Stern | Survey | 329 | Students | Affinity with the computer, intention to use, ease of use, perceived usefulness, & involvement | Bid behavior | Product purchase: auction goods | TAM (Davis, 1989), Affinity theory (Rubin, 1981, 1984), & Involvement theory (Zaichkowsky, 1985) | Propensity to bid in online auctions was influenced by acceptance of technology, involvement with auctions, and affinity for computers. |
| 41 | 2002 | Torkzadeh & Dhillon | Survey | 421 | Students | Online payment, Internet product choice, Internet vendor trust, shopping travel, & Internet shipping errors | N/A | N/A | Keeney's (1999) framework | Two sets of measures, means objectives and fundamental objectives, were developed in this study. Means objectives were measured in terms of Internet product choice, online payment, Internet vendor trust, shopping travel, and Internet shopping errors. Fundamental objectives were measured in terms of Internet shopping convenience, Internet ecology, Internet customer relation, and Internet product value. |
| 42 | 2002 | Zhang & von Dran | Survey | 67 | Graduate students | Up-to-date, accuracy, multiple sources, easy to navigate, & timely | N/A | Evaluation of a Web site providing news (CNN.com) | Kano model (Kano et al., 1984) | Kano model of quality was used in an exploratory investigation of customer quality expectations of a specific type of cite (CNN.com). It was found that customer's quality expectations changed over time, and thus no single quality checklist would be good for an extended time period. |
|
| < Day Day Up > |
|
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 191