Lesson 3: Configuring Account Policies
In Chapter 4, "Managing User Accounts," you learned about assigning user account passwords and how to unlock an account that was locked by the system. In this lesson, you learn how to improve the security of users' passwords and how to control when the system locks out a user account.
After this lesson, you will be able to
- Configure Account Policies
Estimated lesson time: 35 minutes
Configuring Password Policy
Password Policy allows you to improve security on your computer by controlling how passwords are created and managed. You can specify the maximum length of time a password can be used before the user must change it. Changing passwords decreases the chances of an unauthorized person breaking into your computer. If a hacker has discovered a user account and password combination for your computer, forcing users to change their passwords regularly will cause the user account and password combination to fail and lock the hacker out of the system.
Other settings are available in Password Policy that you can use to improve your computer's security. For example, you can specify a minimum password length. The longer the password, the more difficult it is to discover. You can also maintain a history of the passwords used and block users from reusing their most recently used passwords. This prevents a user from having only a few passwords and alternating between them.
You can configure Password Policy on a computer running Windows 2000 Professional by using Group Policy or Local Security Policy.
Follow these steps to configure Password Policy using Group Policy:
- Use the MMC to create a custom console, add the Group Policy snap-in, and save it with the name Group Policy.
- Expand Local Computer Policy. Then, under Computer Configuration, expand Windows Settings, expand Security Settings, expand Account Policies, and then click on Password Policy.
- Select the setting you want to configure, and then, on the Action menu, click Security.
The console displays the current Password Policy settings in the details pane, as shown in Figure 7.4.

Figure 7.4 Current Password Policy settings using Group Policy
Table 7.4 describes the settings available in Password Policy.
Table 7.4 Password Policy Settings
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Enforce Password History | The value you enter in this setting indicates the number of passwords to be kept in a password history. A value of 0 indicates that no password history is being kept. This is the default. You can set the value from 0 to 24, indicating the number of passwords to be kept in password history. This value indicates the number of new passwords that a user must access before he or she can reuse an old password. |
| Maximum Password Age | The value you enter in this setting is the number of days a user can access a password before he or she is required to change it. A value of 0 indicates that the password will not expire. The default value is 42 days. You can set the range of values from 0 to 999 days. |
| Minimum Password Age | The value you enter in this setting is the number of days a user must keep a password before he or she can change it. A value of 0 indicates that the password can be changed immediately. This is the default. If you are enforcing password history, you should not set this value to 0. You can set the range of values from 0 to 999 days. This value indicates how long the user must wait before changing his or her password again. Use this value to prevent a user who was forced by the system to change his or her password from immediately changing it back to the old password. The minimum password age must be less than the maximum password age. |
| Minimum Password Length | The value you enter in this setting is the minimum number of characters required in a password. The value can range from 0 up to 14 characters inclusive. A value of 0 indicates that no password is required. This is the default value. |
| Passwords Must Meet Complexity Requirements | The options are Enabled or Disabled. The default is Disabled. If enabled, all passwords must meet or exceed the specified minimum password length; must comply with the password history settings; must contain capitals, numerals or punctuation; and cannot contain the user's account or full name. |
| Store Password Using Reversible Encryption For All Users In The Domain | The options are Enabled or Disabled. The default is Disabled. This enables Windows 2000 to store a reversibly encrypted password for all users in the domain—for example to be used with the Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP). This option is only applicable if your computer running Windows 2000 Professional is in a domain. |
The Local Security Policy Setting dialog box appears for the selected policy. Figure 7.5 shows the Local Security Policy Setting dialog box for the Maximum Password Age policy.
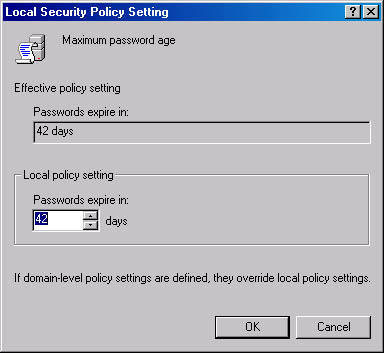
Figure 7.5 The Local Security Policy Setting dialog box for the Maximum Password Age policy
By carefully planning and configuring your Password Policy options, you can improve the security of your computer by decreasing the chances of an unauthorized user gaining access to it.
Configuring Account Lockout Policy
The Account Lockout Policy settings also allow you to improve the security on your computer. If no account lockout policy is in place, an unauthorized user can repeatedly try to break into your computer. If, however, you have set an account lockout policy, the system will lock out the user account under the conditions you specify in Account Lockout Policy.
You access Account Lockout Policy using either the Group Policy snap-in or the Local Security Settings window, just as you did to configure Password Policy. The Group Policy console displaying the current Account Lockout Policy settings in the details pane is shown in Figure 7.6.
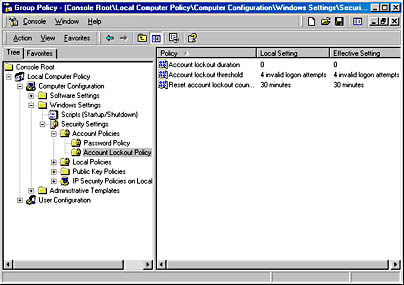
Figure 7.6 Current Account Lockout Policy settings using Group Policy
Table 7.5 explains the settings available in Account Lockout Policy.
Table 7.5 Account Lockout Policy Settings
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Account Lockout Duration | This value indicates the number of minutes that the account is locked out. A value of 0 indicates that the user account is locked out indefinitely until the Administrator unlocks the user account. You can set the value from 0 to 99999 minutes. (The maximum value of 99999 minutes is approximately 69.4 days.) |
| Account Lockout Threshold | The value you enter in this setting is the number of invalid logon attempts it takes before the user account is locked out from logging on to the computer. A value of 0 indicates that the account will not be locked out, no matter how many invalid logon attempts are made. You can set the range of values from 0 to 999 attempts. |
| Reset Account Lockout Counter After | The value you enter in this setting is the number of minutes to wait before resetting the account lockout counter. You can set the range of values from 1 to 99999 minutes. |

Practice: Configuring Account Policies
In this practice, you configure the account policies for your computer and then test your Account Policy to make sure it is correctly configured.
Exercise 1: Configuring Minimum Password Length
In this exercise, you configure a Password Policy setting, Minimum Password Length, for your computer. You then test the password length you configured to confirm that it was set.
To configure the Minimum Password Length setting
- Log on to your computer as Administrator.
- Use the MMC to create a custom console containing the Group Policy snap-in.
- In the Group Policy console, expand Local Group Policy, expand
- Computer Configuration, expand Windows Settings, expand Security Settings, and then expand Account Policies.
- Click Password Policy in the console tree.
- In the details pane, right-click Minimum Password Length and then click Security.
- Type 6 in the Characters box, and then click OK.
- Close the Local Security Settings window.
To test the Minimum Password Length setting
- Press Ctrl+Alt+Delete, and in the Windows Security dialog box, click Change Password.
- In the Old Password box, type password and type water in the New Password and Confirm Password boxes.
- Click OK.
A Change Password message box appears indicating that your new password must be at least six characters long. This means the Minimum Password Length setting in Password Policy is working.
- Click OK, and then click Cancel.
- Click Cancel to close the Windows Security dialog box.
Exercise 2: Configuring and Testing Additional Account Policies Settings
In this exercise, you configure and test additional Account Policies settings.
To configure Account Policies settings
- Use the Group Policy snap-in to configure the following Account
- Policies settings:
- A user should have at least five different passwords before he or she accesses a previously used password.
- After changing a password, a user must wait 24 hours before changing it again.
- A user should change his or her password every three weeks.
Which settings did you use for each of the three listed items?
Answer
- Close the Group Policy snap-in.
To test Account Policies settings
- Log on as User4 with a password of User4.
NOTE
If you get a Logon Message dialog box indicating that your password will expire in a specified number of days and asking whether you want to change it now, click No. - Change your password to waters.
Were you successful? Why or why not?
Answer
- Change your password to papers.
Were you successful? Why or why not?
Answer
- Close all windows and log off.
Exercise 3: Configuring Account Lockout Policy
In this exercise, you configure the Account Lockout Policy settings, and you then test them to make sure they're set up correctly.
To configure the Account Lockout Policy settings
- Log on to your computer as Administrator.
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Group Policy.
- In the Group Policy console tree, if necessary, double-click Local Computer Policy, then Computer Configuration, then Windows Settings, then Security Settings, and then Account Policies.
- Click Account Lockout Policy.
- Use Account Lockout Policy settings to do the following:
- Lock out a user account after four failed logon attempts.
- Lock out user accounts until the administrator unlocks the user account.
Which Account Lockout Policy settings did you use for each of the two conditions?
Answer
- Log off as Administrator.
To test the Account Lockout Policy settings
- Try to log on as User4 with a password of papers. Try this four times.
- Try to log on as User4 with a password of papers for the fifth time.
A message box appears, indicating that the account is locked out.
- Click OK and then log on as Administrator.
Lesson Summary
In this lesson, you learned that the Windows 2000 Local Security Settings window allows you to improve the security on your computer by making it more difficult for an unauthorized user to gain access to it. Using the Password Policy settings is one method you can use to improve the security on your computer. Setting Password Policy allows you to manage the passwords used on your computer. For example, Password Policy includes settings that allow you to force users to change their passwords regularly and to control the minimum length of a password.
You also learned about using another method of improving security on your computer: Account Lockout Policy. If no Account Lockout Policy settings are in place, an unauthorized user can repeatedly try to break into your computer. Using Account Lockout Policy, you can determine how many invalid logon attempts must be made before a user account is locked out of the computer. Account Lockout Policy also allows you to determine how long the account will be locked out; you can even set Account Lockout Policy to require that an administrator manually unlock the user account. In the practice portion of the lesson, you set and tested various account settings.
EAN: N/A
Pages: 244
- ERP System Acquisition: A Process Model and Results From an Austrian Survey
- Enterprise Application Integration: New Solutions for a Solved Problem or a Challenging Research Field?
- Context Management of ERP Processes in Virtual Communities
- Data Mining for Business Process Reengineering
- Healthcare Information: From Administrative to Practice Databases