Control of File and Folder Integrity
To conceal their presence in the affected system, intruders often change or substitute various programs in such a way that the replacement programs perform the same functions, except those that would reveal the intruder's presence. After such changes, some programs can perform other specific actions than those ones designed by the developer.
Quite often, intruders modify log files in order to delete the records containing information on unauthorized activity.
Furthermore, intruders can write new files to your disk - executable files, for example - that allow them to bypass existing access-control mechanisms. Besides programs, user files also often become the targets of attack targets. Unauthorized access to user files can result in the exposure of confidential information or, for example, the alteration of recipient data in a user-generated invoice.
Sometimes intruders are also interested in public information, such as Internet servers. The example illustrated in Fig. 5.2 is rather interesting. Take a look at the banner in the upper part of the window, which is the evidence that the site has been hacked. But wait … it was not the SecurityFocus site that was hacked, but rather the site of the Thruport company that places its advertising materials on the SecurityFocus site.
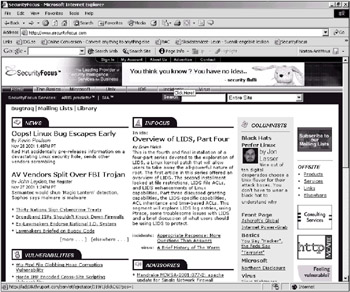
Fig. 5.2. The hacked www.securityfocus.com server
Of course, you can go further than simply controlling changes to files and directories. Sometimes it is useful to control specific fields within a file, such as database fields or system-registry keys. Most unauthorized programs (especially "Trojan horses") use various components of the system registry to start automatically during booting of the operating system. These keys include:
-
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
-
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunServices
-
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce
-
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunServicesOnce
-
HKEY_USERS\DEFAULT\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
-
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
-
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunServices
-
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce
-
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunServicesOnce
-
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnceEx
For example, the Donald Dick Trojan can be identified by the presence of the HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Service\VxD\VMLDR registry key (for Windows 9x), or the HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SessionManager registry key (for Windows NT). The BackOrifice Trojan can leave traces of its activity in HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunServices. This registry key, along with other keys, such as Run, RunOnce, RunServicesOnce, and RunOnceEx, is frequently used by various Trojans that need to load automatically at the system startup. For example, the NetBus Trojan can be detected by the presence of a key named after the Patch.exe file (Fig. 5.3).
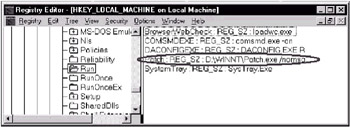
Fig. 5.3. Control over the Windows registry
The list of registry keys used by Trojans is constantly growing. For example, the Internet Scanner system, besides the keys that were already mentioned above, checks the following registry branches:
-
HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\currentVersion\App Paths
-
HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Controls Folder
-
HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\DeleteFiles
-
HKIM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer
-
HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Extensions
-
HKIM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\ExtShellViews
-
HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings
-
HKTM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\ModuleUsage
-
HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RenameFiles
-
HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Setup
-
HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\SharedDLLs
-
HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Shell Extensions
-
HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall
-
HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Compatibility
-
HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Drivers
-
HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\drivers.desc
-
HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Drivers32\0
-
HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Embedding
-
HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\MCI
-
HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\MCI Extensions
-
HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Ports
-
HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\ProfileList
-
HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\WOW
To minimize the possibility of "Trojan horses," just do not allow them to register themselves in the Windows registry. This can be done by means of editing the default access rights to the above-listed registry keys. In Windows NT/2000, this task is performed using the built-in Regedt32.exe utility, while, in Windows XP, the same task is performed using Regedit.exe (Fig. 5.4).
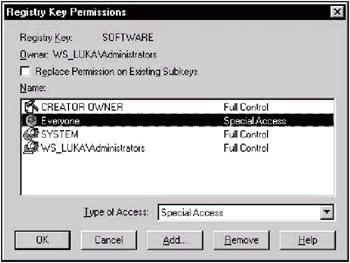
Fig. 5.4. Changing access rights to the system-registry keys
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 152