Managing Mailboxes
When you create a new user by using the Add User Wizard from the Server Management console, an Exchange mailbox is created automatically for the new user. As a result, you don't usually have to create Exchange mailboxes separately. On occasion, though, you may need to modify some aspect of a user's Exchange configuration.
Several tabs in the user account Properties dialog box are useful for managing mailboxes. To summon this dialog box, choose Start ![]() All Programs
All Programs ![]() Administrative Tools
Administrative Tools ![]() Active Directory Users and Computers. Then drill down to the user account you need to modify and double-click it to bring up the Properties dialog box. The following sections describe the Exchange features that are available from the various tabs of this dialog box.
Active Directory Users and Computers. Then drill down to the user account you need to modify and double-click it to bring up the Properties dialog box. The following sections describe the Exchange features that are available from the various tabs of this dialog box.
The Exchange General tab
The Exchange General tab, as shown in Figure 11-2, lets you set these options:
-
Alias: The default name is the user's name, but you can change it if you want.
-
Delivery Restrictions: Set a message size limit for incoming and outgoing messages. You can also specify whom the user can receive messages from.
-
Delivery Options: Create a forwarding address and grant permission to other users to send on behalf of this account.
-
Storage Limits: Set the storage limits for the user's mailbox. You can have a warning message sent whenever the mailbox reaches one size limit and then prevent the user from sending or receiving mail after the mailbox reaches a second size limit.
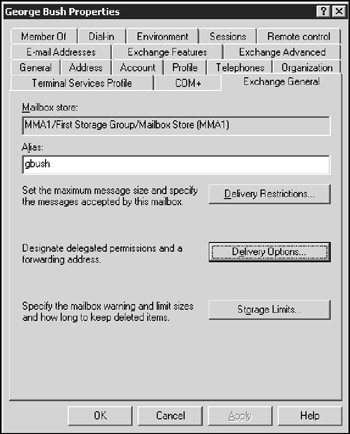
Figure 11-2: The Exchange General tab.
The E-mail Addresses tab
The E-mail Addresses tab of the User Properties dialog box, as shown in Figure 11-3, displays the e-mail addresses associated with a user account. If an e-mail address has been assigned incorrectly, you can use this dialog box to change it. Just select the incorrect e-mail address, click the Edit button, and enter the correct e-mail address. You can also add or remove an e-mail address from this dialog box.
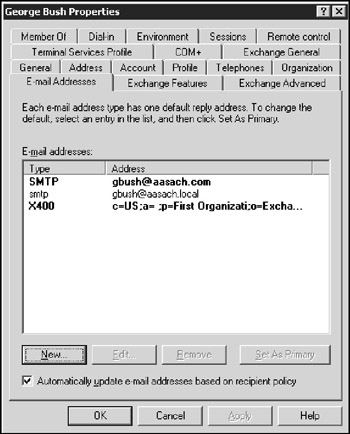
Figure 11-3: The E-mail Addresses tab.
The Exchange Features tab
Figure 11-4 shows the Exchange Features tab of the user Properties dialog box, which lets you configure optional Exchange features for the user.
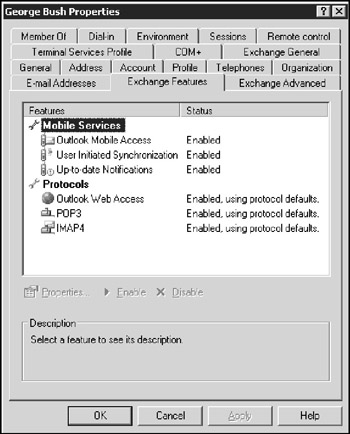
Figure 11-4: The Exchange Features tab.
The following list describes these features:
-
Outlook Mobile Access: The user can access Exchange data from a mobile device, such as a cellphone or PDA.
-
User Initiated Synchronization: The user can start a synchronization operation, to update the mobile device's data from the data on the Exchange server.
-
Up-to-Date Notifications: Enable automatic synchronizations.
-
Outlook Web Access: The user can access her Exchange mailbox from a Web browser rather than from an Outlook client. With this feature enabled, the user can read e-mail from any computer that has an Internet connection.
-
POP3: Enable Internet e-mail by using the POP3 protocol.
-
IMAP4: Enable Internet e-mail by using the IMAP4 protocol.
The Exchange Advanced tab
On the Exchange Advanced tab, as shown in Figure 11-5, you can configure various advanced features of Exchange.
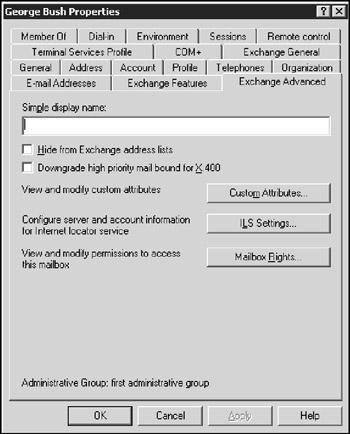
Figure 11-5: The Exchange Advanced tab.
The following list describes these features:
-
Simple Display Name: Specify a display name used by computers that can't display the full display name. You probably don't have to mess with this feature unless your computers can't display ASCII characters.
-
Hide from Exchange Address Lists: Check this option to prevent a user from appearing in address lists. This option is useful for mailboxes that you don't want to be widely known.
-
Downgrade High Priority Mail Bound for X.400: This option is compatible with the original X.400 standard, which was first released in 1984. If you exchange mail with old-style X.400 systems, you may need to use this option.
-
Custom Attributes: This button leads to a dialog box that lets you track up to 15 different custom attributes for a user. You can safely ignore this option.
-
ILS Settings: If you have an Internet Locator Service server installed, you can click this button to configure it. ILS lets online users find each other. It's used by applications, such as NetMeeting.
-
Mailbox Rights: The most frequently used feature on the Exchange Advanced tab, it lets you grant access to this user's mailbox to other users. For more information, see the section "Viewing Another Mailbox," later in this chapter.