Hack 24 Enable Auditing
Log suspicious activity to help spot intrusions. Windows 2000 includes some very powerful auditing features, but unfortunately they are all disabled by default. Windows 2003 has corrected this by enabling some features by default, but it is still wise to check that you are tracking precisely what you want to audit. Using these capabilities, you can monitor failed logins, account management events, file access, privilege use, and more. You can also log security policy changes as well as system events. To enable auditing in any one of these areas, locate and double-click the Administrative Tools icon in the Control Panel. Now find and double-click the Local Security Policy icon. Expand the Local Policies tree node, and you should see something similar to Figure 2-1. Figure 2-1. Audit Policy settings in the Local Security Settings applet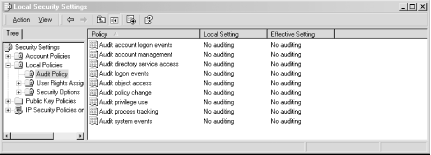 Now you can go through each of the audit policies and check whether to log successes or failures for each type. You can do this by double-clicking the policy you wish to modify, located in the right pane of the window. After double-clicking, you should see a dialog similar to Figure 2-2. Figure 2-2. The "Audit logon events" dialog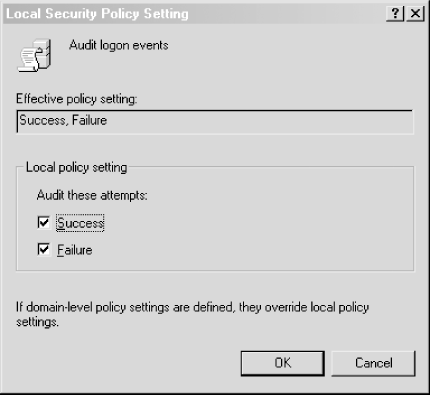 Leaving auditing off is akin to not logging anything at all, so you should enable auditing for all policies. Once you've enabled auditing for a particular policy, you should begin to see entries in the event logs for when a particular audit event occurs. For example, once you have enabled logon event auditing, you should begin to see entries for logon successes and failures in the system's security event log. |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 158