Developing the Implementation Plan
In this part of the deployment process, the IT and Media departments divide the deployment into tasks and define the phases. Even if your deployment is comparatively simple, you should go through a similar process to make sure you have considered every angle.
The original objective of the Windows Media deployment was to replace tape distribution and enable one-to-many broadcasting. The system that the IT and Media departments designed achieved those objectives. It also anticipated future objectives that did not incur additional cost in material and time. For example, a Windows Media server is required to do broadcasting. For no extra cost, the server also supports server-side playlists, streaming over a wireless network, and authorization and authentication.
Phases of Development
Fabrikam managers decided to divide deployment into three phases. At the end of each of the following phases a complete, working system will be in place:
-
Phase I: Base system. Users in Toronto will be able to create and stream on-demand content, and they can locate content with the Media Guide portal site.
-
Phase II: Extended system. Users worldwide will be able to stream on-demand content. Live unicast broadcasting will be available on a limited, local basis.
-
Phase III: Enhanced system. Users worldwide will be able to stream broadcast content; a kick-off series of training programs will be available on-demand; and usage reports and a user feedback system will be in place.
At the end of the last phase, the system will be fully operational according to the original plan. In addition, hundreds of popular videotapes will be available online, as well as the kick-off training series.
In your plan, you may want to start with a pilot phase in which you build and test representative samples of the full deployment. For example, you could build one production workstation and provide streaming media to a subset of the entire network. In this way, you could gather baseline information and receive useful feedback from end users. The pilot program would enable technical support personnel to learn about the system before they attempt to answer user questions, and would enable IT personnel to test configurations before opening up the system companywide. A pilot program can help you manage risks and ultimately help ensure success with less cost. In this scenario, however, Fabrikam jumps ahead to full deployment.
Establishing a Timeline
Figure 14.3 shows the proposed timeline for completion of Fabrikam’s streaming media deployment.
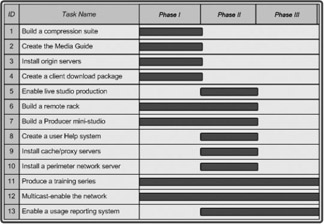
Figure 14.3: A timeline helps schedule deployment tasks.
Because our focus is on Windows Media deployment, we will not go into system planning in depth. A complete deployment plan would require more detail in the schedule, and of course an understanding of the availability of personnel, resources, and budget. A deployment such as the one we are describing could run anywhere from three months to two years, depending on available resources. You would also have to include requirements, content identification and prioritization, and other business-specific needs, and it would follow the basic deployment process: gathering requirements, designing, testing, building a pilot, deploying, operating the system, and gathering usage data for evaluation.
The Fabrikam timeline consists of the following tasks:
-
Build a compression suite. A production facility for creating and converting audio and video content to Windows Media files. The suite integrates with the existing facility that handles production and post-production of videos.
-
Create the Media Guide. A Web site for users to locate and access Windows Media-based content.
-
Install origin servers. The Windows Media server farm that originates the distribution of content.
-
Create a client download package. Users can download the package and install Windows Media Player.
-
Enable live studio production. Upgrading an existing facility for live broadcasting over the intranet.
-
Build a remote rack. A portable equipment rack used for encoding on location.
-
Build a Producer mini-studio. A small production facility intended for use by any employee to record and edit presentations for on-demand delivery.
-
Create a user Help system. A system to explain how to use the Producer mini-studio.
-
Install cache/proxy servers. The system of servers used to decentralize the distribution of Web and Windows Media-based content.
-
Install a perimeter network server. The Windows Media server from which users on the company’s extranet can stream content.
-
Produce a training series. A series of training videos intended to kick-off the new streaming media system.
-
Enable multicasting on the network. The ability to deliver multicast streams where possible throughout the corporate network.
-
Enable a usage reporting system. A system that combines logging data from all servers and creates reports showing client usage.
As you can see in the timeline, several of the tasks overlap. At the same time that the Media Guide, compression suite, and origin server are to be deployed, work is to begin on the Producer mini-studio, the training series, and making sure all routers in the company are multicast-enabled. Also, development of a usage tracking system would be started during the second phase.
The tasks identified on the chart were divided between the Media and IT departments, both of which developed plans for completion of their portions. Representatives of both departments planned to meet regularly to make sure the deployments were coordinated.
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 258