5.1 Lossless compression
5.1 Lossless compression
The JPEG standard specifies two classes of encoding and decoding, namely lossless and lossy compression. Lossless compression is based on a simple predictive DPCM method using neighbouring pixel values, and DCT is employed for the lossy mode.
Figure 5.1 shows the main elements of a lossless JPEG image encoder.
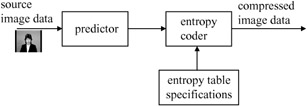
Figure 5.1: Lossless encoder
The digitised source image data in the form of either RGB or YCbCr is fed to the predictor. The image can take any format from 4:4:4 down to 4:1:0, with any size and amplitude precision (e.g. 8 bits/pixel). The predictor is of the simple DPCM type (see Figure 3.1), where every individual pixel of each colour component is differentially encoded. The prediction for an input pixel x is made from combinations of up to three neighbouring pixels at positions a, b and c from the same picture of the same colour component, as shown in Figure 5.2.
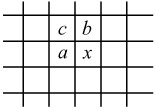
Figure 5.2: Three-sample prediction neighbourhood
The prediction is then subtracted from the actual value of the pixel at position x, and the difference is losslessly entropy coded by either Huffman or arithmetic coding. The entropy table specifications unit determines the characteristics of the variable length codes of either entropy coding method.
The encoding process might be slightly modified by reducing the precision of input image samples by one or more bits prior to lossless coding. For lossless processes, sample precision is specified to be between 2 and 16 bits. This achieves higher compression than normal lossless coding, but has lower compression than DCT-based lossy coding for the same bit rate and image quality. Note that this is in fact a type of lossy compression, since reduction in the precision of input pixels by b bits is equivalent to the quantisation of the difference samples by a quantiser step size of 2b.
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 148