Practical Applications: OPNET1
|
| < Day Day Up > |
|
Practical Applications: OPNET[1]
There are two parts to MPLS traffic engineering. The first part involves doing analysis, network discovery, and math. Second is putting traffic where you want it to be.
Network analysis can be a rather advanced subject. Some software designers have developed tools to make this job easier.
OPNET has designed a product line of software packages that will help your design and enhance your traffic planning. Cisco’s Tunnel Builder offers not only network discovery but also a method to guarantee bandwidth for high-priority circuits (e.g., voice).
This chapter has presented traffic engineering in an extremely simplified fashion for ease of learning. Mastering the art and science of traffic engineering—especially traffic planning and modeling—takes years of study, sophisticated algorithms, and specialized tools.
Throughout my travels, while teaching MPLS and interviewing networks designers, I have found that two key concerns of any network professional are traffic engineering and having the necessary tools to do the job right. Over the years, OPNET has earned a dominant presence in the network planning and design marketplace by developing products that combine ease of use with accurate algorithms. Tools such as OPNET SP Guru and its integrated support for both for Cisco and Juniper make OPNET a must-have tool for network designers.
As mentioned earlier, traffic engineering has four main aspects: measuring, characterizing, modeling, and directing the traffic to a desired location. OPNET MPLS solutions address three of these steps: measuring, characterizing, and modeling.
OPNET as a modeling tool is a twofold entity: dynamic and interactive. OPNET dynamically gathers data from operational networks. This data is compiled and processed to create a network model. From this operational model, planners can work with OPNET to perform “what-if?” analysis, traffic optimizing, peak busy-hour simulations, and other scenarios.
OPNET MPLS Capabilities and Features
OPNET offers an MPLS as part of its Specialized Model Library. Based on Internet standards and developed in collaboration with industry experts,[1] the OPNET MPLS model offers the most comprehensive and accurate performance predictions of networks that incorporate MPLS technology and traffic engineering policies.
OPNET’s MPLS model has broad appeal to those responsible for the functions outlined in Figure 5.10.

Figure 5.10: OPNET MPLS Uses
Combined with OPNET’s core products, the OPNET MPLS model benefits MPLS networks by providing the ability to perform the services outlined in Figure 5.11.
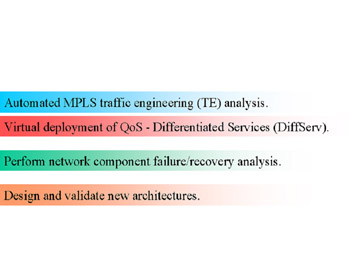
Figure 5.11: OPNET Services
-
Perform network component failure/recovery analysis: www.opnet.com/products/library/fail_recov.html. Quantify the performance impact of failure of specific links and devices.
-
Automate MPLS traffic engineering (TE): www.opnet.com/products/spguru/plan.html. OPNET automatically defines LSP explicit routes that minimize maximum link utilizations under normal conditions and secondary routes that will survive link and node failures. OPNET identifies link capacity that is unused during any failure, highlighting opportunities to reduce network capacity without impacting service levels.
-
Perform traffic engineering (TE) analysis: www.opnet.com/services/training/network_analysis_design.html. Make network operations more efficient and reliable while optimizing performance and resource utilization. Virtual deployment of QoS - Differentiated Services (DiffServ): Gain insight as to how Quality of Service (QoS) can be implemented to meet a Service Level Agreements (SLA).
-
Design and validate new architectures: www.opnet.com/services/training/network_analysis_design.html. For the R&D community, open control plane model architecture offers an opportunity to validate new approaches and test interoperability.
Key features include those shown in Figure 5.12.
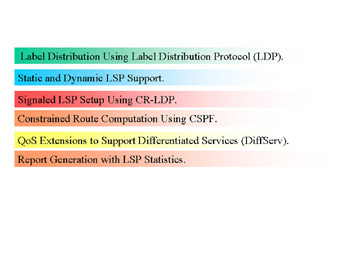
Figure 5.12: Key Features of OPNET MPLS Model
In an operational model, we first gather data from a network. Data is processed and performance software generates a top-view performance map, as shown in Figure 5.13. This figure shows a nonoptimized network using standard routing protocols.
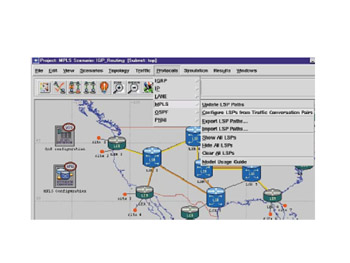
Figure 5.13: Nonoptimized Network
Through a process of network performance tuning using MPLS tunnels, we see in Figure 5.14 that OPNET generates a new network map and models showing several paths for traffic: a signaled LDP, a routed LDP, and an OSPF path.
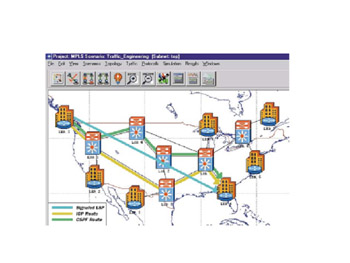
Figure 5.14: Optimized Network
Powerful networks require powerful tools for design, modeling, and testing. OPNET provides these programs in their suite of planning tools. For more information, contact OPNET Technologies, Inc., at www.OPNET.com or call (240) 497-3000.
[1]OPNET’s MPLS Model Development Consortium includes MPLS experts from Cisco, Ericsson, Hyperchip, Marconi, NEC, NTT, QoS Networks, and Qwest.
|
| < Day Day Up > |
|
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 138