The Need for Network Protection
|
| < Day Day Up > |
|
MPLS has been implemented primarily in the core of an IP network. Often, MPLS competes head to head with ATM networks; therefore, it would be expected to behave like an ATM switch in the case of network failure.
With a failure in a routed network, recovery could take anywhere from a few tenths of a second to several minutes. MPLS, however, must recover from a failure within milliseconds; the most common standard is 60 milliseconds. To further complicate the recovery process, an MPLS recovery must ensure that traffic can continue to flow with the same quality as it did before the failure. So, the challenge for MPLS networks is to detect a problem and switch over to a path of equal quality within 60ms.
Failure Detection and Tradeoffs
Two primary methods are used to detect network failures: heartbeat detection (or polling) and error messaging. The heartbeat method (used in fast switching) detects and recovers from errors more rapidly but uses more network resources. The error message method requires far less network resources but is a slower method. Figure 4.2 shows the tradeoffs between the heartbeat and error message methods of failure detection.
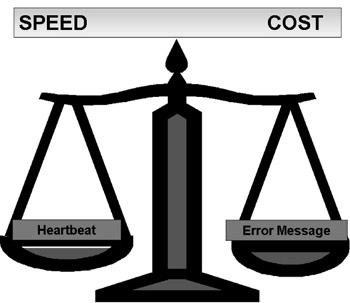
Figure 4.2: Heartbeat vs. Error Message Failure Detection
The heartbeat method (see Figure 4.3) uses a simple solution to detect failures. Each device advertises that it is alive to a network manager at a prescribed interval of time-hence the term heartbeat. If a heartbeat is missed, the path, link, or node is declared as being failed and a switchover is then performed. The heartbeat method requires considerable overhead functions-the more frequent the heartbeat, the higher the overhead. For instance, in order to achieve a 50ms switchover, heartbeats would need to occur about every 10ms.
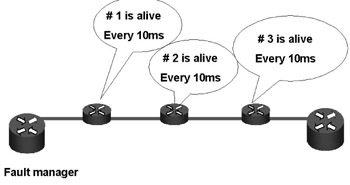
Figure 4.3: Heartbeat Method
In the other failure-detection system, the error message detection method (see Figure 4.4), when a device on the network detects an error, it sends a message to its neighbors, ordering them to redirect traffic to a path or router that is working. Most routing protocols use adaptations of this method. The advantage of the error message is that network overhead is low. The disadvantage is that it takes time to send the error-and-redirect message to the network components. Another disadvantage is that the error messages might never arrive at the downstream routers.
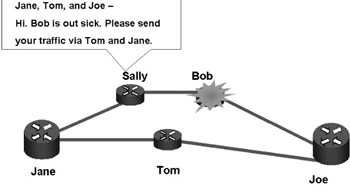
Figure 4.4: Error Messages
If switchover time is not critical (as it has historically been in data networks), the error message method works fine; however, in a time-critical switchover, the heartbeat method is often the better choice for optimal failure recovery.
|
| < Day Day Up > |
|
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 138