AV Pair Example PPP Network
| In this section, you look at a very basic dial-in network using PPP. Numerous AV pairs are used in this section. You can guess that the service=ppp AV is used, and the protocol=ip is used as well. The purpose of this section is not to configure the PPP connection or the AAA configuration on the NAS device, rather to display the TACACS+ AV pair configuration in the ACS HTML interface. (See Figure 13-1.) Figure 13-1. PPP Dial-In Network with AV Pairs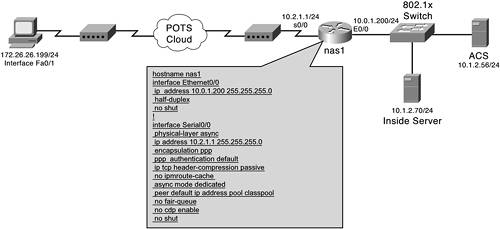 In this example, a dial-in user makes a connection into the NAS1 device and authenticates to ACS. In addition to authenticating to ACS, the user also has the ACS authorize the use of the PPP protocol. The configuration seen in Example 13-1 is the output from the show run command on the NAS device. Example 13-1. show run Command from NAS1! hostname nas1 ! ! aaa new-model aaa authentication login default group tacacs+ local aaa authentication enable default group tacacs+ none aaa authentication ppp default group tacacs+ local aaa authorization network default group tacacs+ ! username admin password cisco ! clock timezone gmt 0 ip subnet-zero no ip source-route no ip finger no ip domain-lookup ip host modem 2001 10.0.1.2 ! cns event-service server ! ! ! ! ! interface Ethernet0/0 ip address 10.0.1.200 255.255.255.0 half-duplex no shut ! interface Serial0/0 physical-layer async ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 encapsulation ppp ppp authentication default ip tcp header-compression passive no ip mroute-cache async mode dedicated peer default ip address pool classpool no fair-queue no cdp enable no shut ! interface Serial0/1 no ip address shutdown ! router rip version 2 network 10.0.0.0 no auto-summary ! ip local pool classpool 10.2.1.2 ip classless ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.0.1.3 ! access-list 101 permit icmp 10.2.1.0 0.0.0.255 any access-list 101 permit tcp 10.2.1.0 0.0.0.255 any ! ! tacacs-server host 10.1.2.56 tacacs-server key cisco123 default ! line con 0 exec-timeout 45 0 logging synchronous transport input none line 1 autoselect during-login autoselect ppp modem InOut modem autoconfigure type usr_sportster transport input all stopbits 1 speed 115200 flowcontrol hardware line aux 0 line vty 0 4 ! end Completing the ConfigurationOn the ACS, the user is already configured, as well as the group. For this situation, you assume that the group is already configured, with the exception of the PPP authorization. To configure ACS for authorization of the PPP session, you select the PPP IP TACACS+ option in the group configuration page of the HTML interface. By selecting this option, you are configuring the service=ppp and protocol=ip TACACS+ AV pairs. Follow these steps to complete the configuration:
This completes the configuration of PPP IP; however, your next action here might vary. As long as PPP is selected, the ACS authorizes the service. At this point, you might want to also assign an access list to the interface, configure an idle timeout value, or even push the IP address down to the dialing in user by utilizing other configuration sections of ACS, building an IP Pool, and assigning it to the user. Whatever you do in the ACS interface determines the TACACS+ AV pairs to be applied and used for the duration of the authenticated and authorized session. A key element to understand is that authentication must take place prior to authorization. If ACS has not already determined who the user requesting service is, ACS does not authorize the requested protocol. For more information on configuring AAA on the command-line interface of a Cisco IOS device, see Appendix A, "RADIUS Attribute Tables." Applying an ACL to the Dial InterfaceYou can further utilize AV pairs with this example by applying an ACL to the dial interface. You can actually do this in two ways. The first way is to define the numbered access list on the router and then reference the numbered access list on ACS. The second method is to create the entire ACL on ACS. For this example, you apply access list 101 to the interface. This is seen in Figure 13-2. Figure 13-2. Inbound ACL and PPP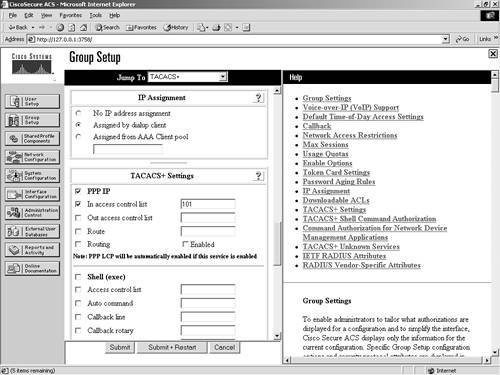 To perform this configuration, simply follow these steps on ACS:
In this configuration, a user dials in and is authenticated and authorized. An inbound ACL is applied as well. In the next section, "Understanding TACACS+ AV Pairs in the ACS Interface," you take a closer look at how the AV pairs appear in the HTML interface of ACS and are given the opportunity to determine what the AV pairs are in the given examples. |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 173