| As the most fundamental element of the document library, folders are the foundation of document management. You can help to ensure the greatest benefit from the workspace by carefully evaluating which folder features are needed and populating the workspace with the appropriate combination of folder types. 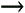 To refresh your familiarity with the various folder features, see Chapter 4, "Overview of Document Management." To refresh your familiarity with the various folder features, see Chapter 4, "Overview of Document Management." Folder Types As discussed in Chapter 3, there are two different types of folders available within the workspace: standard and enhanced. Enhanced folders provide support for all content management features. These include check-in and check-out functions, public and private (draft) views, document profiles, version history, and publishing approval processes. By default, all folders created in the document library have enhanced folder settings enabled. If you disable enhanced folder features, you change the folder to a standard folder. The following table shows a comparison of the SharePoint Portal Server features supported by each folder type. Table 10.1. Comparison of Folder Feature Support | Feature | Enhanced | Standard | | Categories |  |  | | Indexed documents |  |  | | Profile metadata |  |  | | Roles |  |  | | Approval Routing |  | X | | Check-in/check-out |  | X | | Version History |  | X | | Private Views |  | X | All folders within the document library support the categories, indexed documents, profile metadata, and roles features of SharePoint Portal Server. If you wish to enable or disable the enhanced features of a folder, you must first empty the folder. Enhanced folder settings can only be changed on an empty folder. You enable/disable enhanced folder settings on the General tab of the folder properties. If an enhanced folder is moved into a standard folder, it retains its enhanced features. A standard folder moved to an enhanced folder remains standard. Standard folders have some unique behaviors that are important to know. Multi-part or compound documents (documents with relative links to external documents, and so on) are only supported in standard folders. Also, any documents added to a standard folder are immediately published.  | Compound or multi-part documents are only supported in standard folders; see "Managing Compound Documents" in the "Troubleshooting" section at the end of the chapter. | Folder Properties and Settings All of the features available for a folder are visible in that folder's properties page. Folder properties are broken down onto four tabs: General, Security, Profiles, and Approval. General Tab The General tab (see Figure 10.1) displays basic bookkeeping information for the folder ”folder name , address, size and contents, and the date and time the folder was created and last modified. Also, the selection box to enable or disable enhanced folder features can be found here. Figure 10.1. General folder information is composed of system generated metadata. 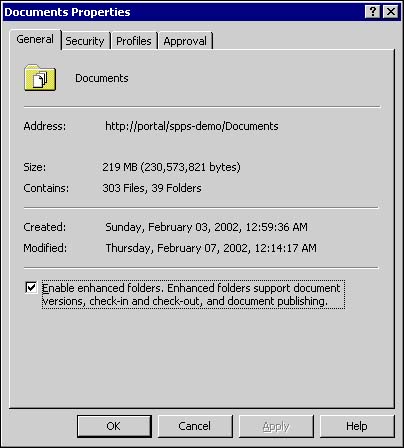 Security Tab and Roles The ability to restrict access to certain folders and the documents they may contain is important for document management. The Security Tab, see Figure 10.2, displays information pertaining to inheritance and access control for the contents of the folder. Two separate inheritance controls are available. The first, Use parent folder's security settings, is located toward the top of the window and blocks or allows setting inheritance for folders and documents within the folder. The second control, called Reset all subfolders to use these security settings, located at the bottom of the window, can be used to reset all the subfolders to the same settings as the current (parent) folder or as specified according to role-based settings. Figure 10.2. The default configuration of a folder's security settings. Note the Reset settings check box at the bottom of the properties window. 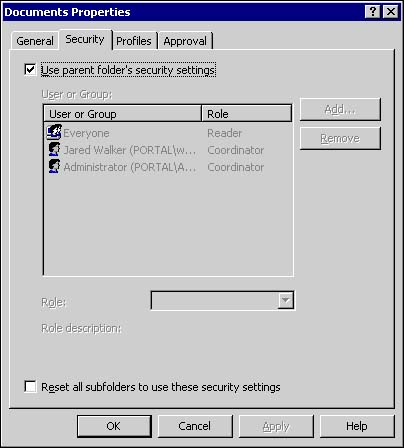 CAUITON Please note that applying this option will immediately change all of the folder's subfolders' settings! If any of the subfolders require special feature settings, you should avoid using this option, or you should document the subfolders' settings so that you can reapply them afterward.
If the folder is configured not to use its parent's security settings then you can configure security permissions by selecting either local or domain users or groups and assigning them a role. Users and groups can have multiple roles in the workspace, but only a single role in any given folder. In instances where users of a group are also specified independently in the security listing, the most permissive role assignment is enforced. There are three security roles: -
Reader ” A reader can read documents that have been published in the folder. CAUTION By default, the Everyone group is configured as a reader. If you wish to restrict universal access to published documents, be sure to remove the Everyone group from the security list.
-
Author ” An author can both create new documents and read and edit all documents in the folder. Figure 10.3. Role assignments are accessed on the Security tab of the folder's properties. 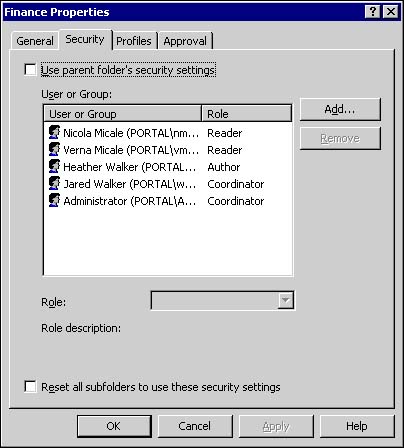 -
Coordinator ” A coordinator can assign roles to users and groups, select document profiles, and create and edit documents in the folder. TIP Don't be confused by roles. The role-based security model is merely a simplified representation of the traditional Windows security model. NT Groups are added to SharePoint Security roles to grant permissions. By combining normal access controls into easy to understand "roles," users who would not ordinarily be capable of administering security may be entrusted with administering access to their own folders.
Profiles Tab The Profiles tab (see Figure 10.4) displays the available list of document profiles and indicates which of the profiles can currently be applied to documents within the folder. You can enable a document profile for use in the folder by clicking the check box next to its name. By clicking on the name of an available document profile, you display its profile description in the Profile description area of the window. You may also change the default document profile for the folder by selecting your choice from the pull-down list at the bottom of the window. Figure 10.4. Selection of available document profiles and the default profile from the Profiles tab. 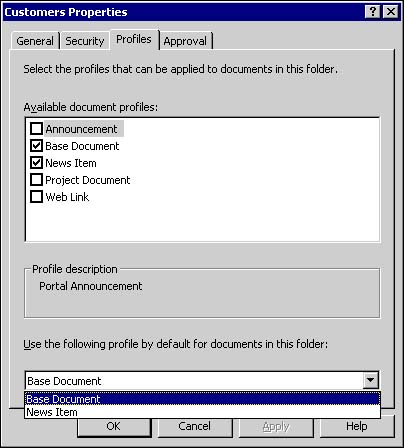 Once the document profiles are selected, the selected list could then be applied to documents within the folder. Approval Tab Often within document management, one or more people must review a document's content for accuracy or completeness before it can be approved for release or publication. SharePoint Portal Server's document approval routing feature provides a mechanism to enable and enforce that process. From the Approval tab, you can enable or disable document approval routing. If approval routing is enabled, documents must be approved by one or more people designated as approvers before they can be published and made available to readers. Both local and domain user accounts can be selected as approvers. Once selected, you have the option of including the approver's email address. If an email address is present, the user will receive an automatic email notification when a document is awaiting their approval. There is also a comments field at the bottom of the window, where you can enter text to be included in the notification email. One of two possible approval routes must also be chosen if approval is enabled: One after another or All at once. With One after another routing, also called serial approval routing , each person in the approvers list for that folder must approve the document in turn . Each person must approve the document before the next person in the list will receive an approval request notification. You can set the order of approval by using the up and down arrow buttons to the right of the Approvers section. If all of the approvers approve the document, SharePoint Portal Server publishes it. If any of the approvers reject the document, the approval process ends and the document returns to checked-in status. All at once, also called parallel approval routing , sends a notification to all listed approvers at the same time, indicating that the document is awaiting review. At any time, any approver can approve or reject the document. Figure 10.5. Serial approvers are ordered by number as shown in the Approvers box. That order can be changed by using the arrow buttons to the left of the box. 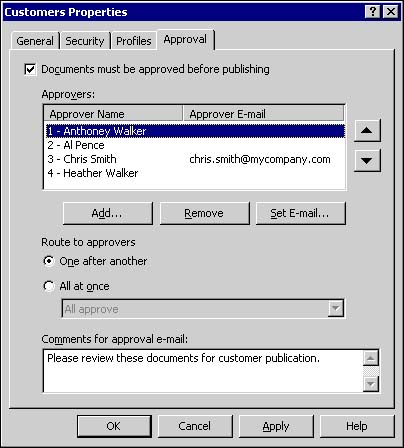 One of two approval scenarios must also be chosen. The first scenario, All approve, requires that all of the approvers approve the document before SharePoint Portal Server will publish it. If any of the approvers reject the document then the approval process ends and the document is returned to checked-in status, unpublished. The second approval scenario, "Only one approval required," sends a notification to each person on the approvers list. Once somebody on the list approves the document, it is published. Figure 10.6. Parallel approval notifies all selected approvers at the same time, requiring either one or all to approve or reject as selected. 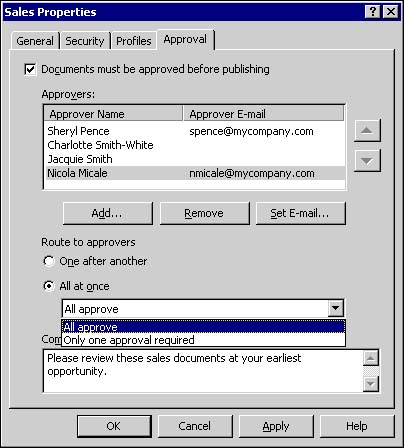 As you can see, the approval routing process allows you to plan and implement your approval strategy according to your business requirements. Folder Inheritance By default, all subfolders inherit folder settings from their parent folder. Since the Documents folder in the workspace is enhanced by default, any folders created or dragged into the Documents folder inherit its enhanced folder settings. Folders from outside the workspace that are dragged into any enhanced folder automatically become enhanced folders. Likewise, folders dragged into a standard folder in the workspace become standard folders. If you wish to break the folder inheritance setting before moving documents into the folder, simply create a new folder in the workspace and enable or disable inheritance on the Security tab within folder properties. Figure 10.7 provides an example of what happens when you try to change the enhanced settings of a folder that is populated with documents. Figure 10.7. Example of the error message that is generated when you attempt to change enhanced features of a folder. 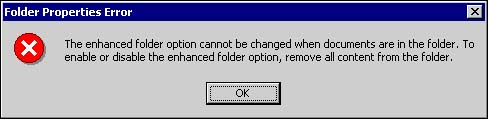 It is always best practice to plan your folder inheritance strategy prior to creating your folder hierarchy.  | 
 To refresh your familiarity with the various folder features, see Chapter 4, "Overview of Document Management."
To refresh your familiarity with the various folder features, see Chapter 4, "Overview of Document Management." 





