DHCP Overview
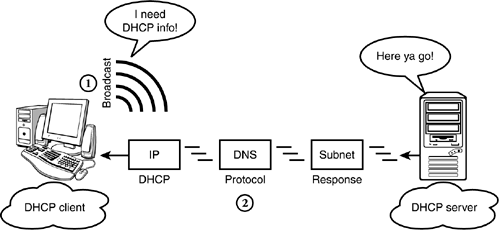
| The next step in our elegant IP management ballet is communication. If you want a computer (or some other device) to function on a TCP/IP network, you must first configure it with a number of IP options. These "options" are small, but important, tidbits of data that helps network devices communicate such as a client's own domain name, a client's IP address, the DNS server's IP address, the subnet mask, and so on. All computers must be aware of these facts in order to coexist peacefully on a TCP/IP network. As you can see in Figure 4.13, DHCP is built on the client/server model. In this model, the server is a host that provides initialization parameters to clients using the DHCP protocol. Similarly, the client is an Internet host that requests parameters from the DHCP server. In this scenario, the DHCP server delivers host-specific configuration parameters and assigns network addresses. Figure 4.13. The DHCP client/server model.
So, how does it work? In Figure 4.13, the DHCP client initiates a broadcast request by saying, "I need DHCP info!" In response, the DHCP server examines the request broadcast to determine which network segment it came from. If the DHCP server is configured to respond to that segment, it sends IP configuration data to the client. In this model, IP addresses can be allocated to DHCP clients in one of three ways:
Fortunately, NetWare 6 uses eDirectory to help automate DHCP allocation. With eDirectory integration, IP addresses are stored in the central database for automatic or dynamic allocation. This prevents single-point-of-failure problems experienced with other DHCP implementations. Thanks to NetWare 6, eDirectory ensures that DHCP provides managed IP addresses throughout the enterprise. Even more importantly, you can administer DHCP configurations as objects in the eDirectory tree. Speaking of objects, let's continue our NetWare 6 DNS/DHCP review with a description of NetWare 6's 11 DNS/DHCP eDirectory objects. |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 128