The Telnet Utility
|
|
Telnet is an acronym formed from Terminal EmuLation for NETworks and was originally developed to open terminal sessions from remote Unix workstations to Unix server. Although still used for that purpose, it has evolved into a troubleshooting tool. Figure 4.13 shows the basic Telnet interface as it is being used to start a terminal session on a remote Unix host.
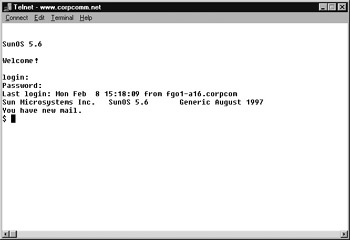
Figure 4.13: The Windows 95/98 and NT Telnet utility
In today’s Windows 95/98 and NT environments, Telnet is a basic GUI tool for testing TCP connections. You can telnet to any TCP port to see if it is responding, which is especially useful when checking SMTP and HTTP (web) ports. If you’ll remember from Chapter 3, “TCP/IP Fundamentals,” each upper-layer service in a TCP stack has a number for its address. Each network service that uses a particular address will respond to a TCP request on this port (if the defaults are used). Table 4.6 lists the most commonly referenced port numbers and their associated services.
| Port | TCP/IP Service |
|---|---|
| 21 | FTP |
| 23 | Telnet |
| 25 | SMTP |
| 80 | HTTP Session Start |
| 110 | POP3 Mail Transfer Protocol |
| Note | This list is by no means comprehensive. For a complete list, go to www.microsoft.com/support/ or support.novell.com. |
To find out if a TCP service is responding, follow these steps:
-
Choose Start Ø Run.
-
Enter telnet and click OK to open the Telnet utility.
-
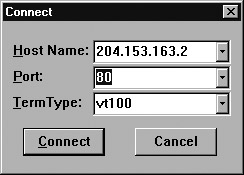
Choose Connect Ø Remote System to open the Connect dialog box:
-
In the Host Name field, type the IP address or DNS host name of the host running the TCP service to which you want to connect.
For example, to find out if a web server is responding to TCP port 80 (its default port), enter the IP address or DNS host name of the web server (204.153.163.2, in this case).
-
In the Port field, enter the number from Table 4.6 that corresponds to the service you want to check.
-
Click Connect.
If you successfully connect to the web server, you won’t be notified that this is the case. If the web server doesn’t respond, you’ll receive a Connect Failed message.
If you’re attempting to connect to an SMTP server, telnet to port 25, and you’ll see a screen similar to that in Figure 4.14. Theoretically, you could send an e-mail message using Telnet to see if your SMTP system is functioning.
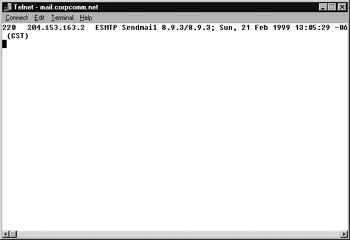
Figure 4.14: Using Telnet to find out if your SMTP mail system is responding
|
|