3 Energy needs
3 Energy needs
In order to find powering solutions, it is necessary to consider the instant power need P(t) and energy need E ie power consumption given by E = ˆ« P(t)dt.
The power of the communicated object is very variable. In fact, they frequently pass from active to standby mode to optimise the energy consumption. Standby consumption includes a minimum number of useful functions for fast restart, at commencement of radio reception etc.
From the energy consumption, one derives the autonomy that is an essential feature of wireless communicating objects; it must correspond to use, or the ergonomy of the object will be very bad.
Unfortunately, autonomy tends to decrease for with friendly function and with computing power on board (graphical colour interface, data compression, radio packet standard) as well as miniaturisation. Moreover, the objects offering more functions (data down-load, streaming), will be used for a longer time on average.
As an illustration, Figure 24.1 presents the autonomy of some objects related to their standby consumption (left scale) and in active mode (right scale). Some objects are only active when interacting with the user and their autonomy is, above all, limited by the self discharge of the energy source.
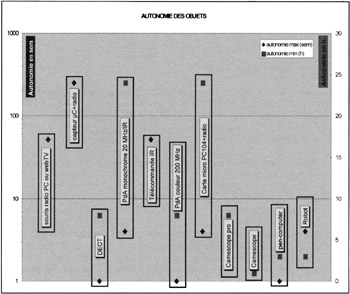
Figure 24.1: Standby and active autonomy of some objects
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 191