Learning About KDE Utilities
KDE comes with a number of bonus applications, accessible through the K Menu button. They fall into several categories: Accessories, Internet, Other, Preferences, Programming, Multimedia, and System Tools. This is not a comprehensive list of programs available through the K Menu button. GNOME utilities were covered in Chapter 16 ; we take a look at others in the following two chapters. While most of the utilities in this section are based on the work of the KDE project, we ve included a few third-party utilities as well.
| Note | The lists in this chapter may not reflect the options you see on your computer. Available menu options depend on the software that you have installed. |
Accessories
KDE includes a number of accessories that can help you with simple computing tasks . They re accessible through the K Menu ˜ Accessories submenu. Figure 17.33 shows the More Accessories submenu off the Accessories menu. Accessories that we do not cover here are primarily GNOME related and are addressed in Chapter 16 .
Figure 17.33: Accessories menus
Autorun The Autorun utility reads any currently installed CDs for autorun executable programs or audio CDs. They are run if found. If you want to allow regular users access to autorun programs, you ll need to add the user , exec options to the CD configuration line in /etc/fstab .
Character Selector The Character Selector, also known as KCharSelect, allows you to work with a number of non-English languages that still use roman-style alphabets. As you can see in Figure 17.34, it provides an interface where you can include a number of special letters and accented characters in your documents.
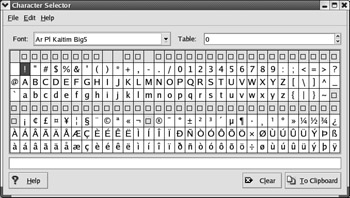
Figure 17.34: The KDE Character Selector
Clipboard Tool The Clipboard Tool opens the configuration options described earlier for the Klipper.
Floppy Formatter The Floppy Formatter (KFloppy) allows you to format standard floppy drives to the MS-DOS or ext2 filesystems. As shown in Figure 17.35, it has a straightforward interface that lets you customize the format.
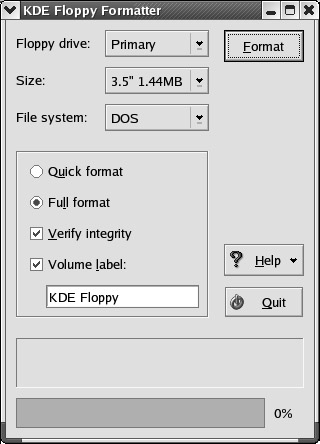
Figure 17.35: Floppy Formatter
Handheld PDA The Handheld PDA utility starts GNOME Pilot, described in Chapter 16 .
Kandalf s Tips The Kandalf s Tips utility opens the hints that you see when you first start KDE. An example is shown in Figure 17.36.
Figure 17.36: Kandalf s Tips
Kate You can use Kate, the KDE advanced text editor, to edit various text files. As shown in Figure 17.37, Kate also provides you with a convenient window to the command-line interface.
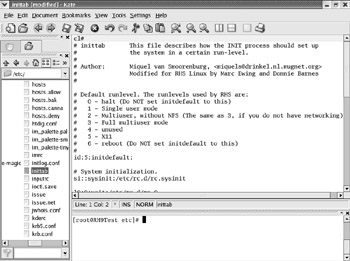
Figure 17.37: Using Kate on /etc/inittab
Kdict The KDE dictionary (Kdict) provides access to the online dictionary server at dict.org . It uses TCP/IP port 2628; as long as you re connected to the Internet, it s easy to use to find the definitions that you need. An example is shown in Figure 17.38.
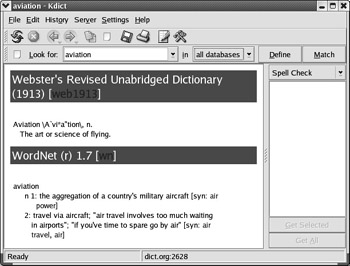
Figure 17.38: Online dictionary access
Kpager The KDE pager (Kpager) opens a small window that displays open workspaces; it is functionally equivalent to the desktop workspace view described earlier within the KDE panel.
Print Jobs The KJobViewer allows you to manage the current jobs in your print queue(s). Various functions allow you to hold, resume, delete, or move any current print jobs.
Print Manager This opens the GNOME Print Manager utility described in Chapter 16 .
Scientific Calculator The KCalc utility is a configurable calculator that can be controlled through the numeric keypad. You can set it up in Trigonometric or Statistical modes, each with different functions.
More Accessories
The other KDE accessories are, for the most part, applets with minor functionality. We ve described them briefly in Table 17.9.
| Accessory | Description |
|---|---|
| Address Manager | The KDE Address Book allows you to configure contact information for people in your address book. |
| JPilot | The JPilot utility is used for synchronizing data between KDE and handheld devices that conform to the PalmPilot and PalmOS standards; a sample view is shown in Figure 17.39. |
| KAlarm | With the KDE personal alarm message and command scheduler, you can set up reminders or administrative commands on a schedule. |
| Kandy | The Kandy utility allows you to synchronize the KDE address book with your mobile phone. |
| KArm | With the KArm utility, you can track the time that you spend on various tasks. |
| KdeprintFax | The KdeprintFax utility is an add-on to KDE Print; it allows you to view a file that you ve printed to a fax device. |
| KHexEdit | The KHexEdit utility is a customizable hex editor that can display and help you edit data in hexadecimal, octal, and binary modes. (That corresponds to base 16, base 8, and base 2 for the math majors.) It can also show files in text mode. |
| KJots | The KJots utility lets you jot down short notes in an organized fashion. Any books that you create can be added to a hotlist. |
| KNotes | The KNotes utility allows you to add some short notes to a list that you can print or e-mail. |
| KOrganizer | The KOrganizer is a handy scheduling utility, shown in Figure 17.39. 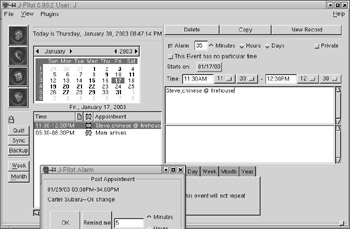 Figure 17.39: Syncing a handheld computer with JPilot |
| KPilot | The KPilot utility uses the latest version of Desktop HotSync software; it is intended to substitute for Palm desktop software. |
| KTimer | KTimer allows you to start a command after a given delay; the default is 100 seconds. |
| KWrite | KWrite is a text editor suitable for programmers. |
| Text Editor | Text Editor is a more basic editor; KEdit is the default KDE text editor. |
| VNC Viewer | Covered in Chapter 16 . |
| Word Translator | The Word Translator incorporates other dictionaries based on the server or that associated with Babylon ( www.babylon.com ). See Figure 17.40. 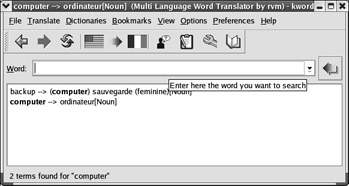 Figure 17.40: KDE Wind Translator |
Once begun, a number of these utilities, such as KOrganizer, KNotes, and KAlarm, place icons on the panel, next to the system clock.
Internet
KDE includes several network utilities that can help you work your way through the Internet. They range from IRC clients to modem connection utilities. They re accessible through the K Menu ˜ Internet More Internet Applications submenu, shown in Figure 17.41. Several GNOME applications, including Mozilla, gFTP, Instant Messenger, Video Conferencing, Balsa, exmh, Galeon, IRC Client, Sylpheed, and Evolution, were addressed in Chapter 16 . Ethereal is covered in Chapter 22 .
Figure 17.41: The More Internet Applications submenu
KGet KGet is a KDE download manager also known as Caitoo. When integrated with the default KDE web browser, Konqueror, it lists and allows you to monitor, pause, and resume downloads. A sample download is shown in Figure 17.42.
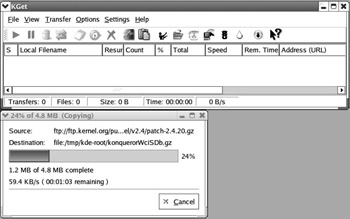
Figure 17.42: KGet monitors downloads.
Kisdndock This applet allows you to configure any installed ISDN devices. ISDN, the Integrated Services Digital Network, is an option for digital Internet connections that works nominally at about twice the speed of a regular telephone modem. As ISDN is popular in Europe, it is not surprising that KDE, which is mostly developed in Europe, provides solid ISDN support.
If you haven t yet set up an ISDN device, you ll need to configure one first via redhat-config-network- druid as described in Chapter 21 .
| Note | The redhat-config-network-druid utility was formerly known as internet-druid . |
Kit The Kit utility is currently the KDE Instant Messaging (IM) client for the AOL system. The first time you run Kit, you re taken through a wizard where you can set up an AOL IM account. Future versions of Kit may include support for other messaging systems.
KMail KMail is the default KDE e-mail client. It is highly customizable; you can configure it with shortcuts and actions on the toolbar. Of course, you can also set up the e-mail accounts that you use.
For example, you can set it up with shortcuts for a number of functions, such as using e-mail filters and marking messages, replies, and more. Over 100 different shortcuts are possible. You can configure the main toolbar with the actions of your choice.
It is not difficult to configure a new e-mail account. In KMail, click Settings ˜ Configure KMail. Naturally, this opens the Configure KMail dialog box. In the left-hand pane, click Network; you ll be able to configure sending and receiving accounts in the tabs shown in Figure 17.43.
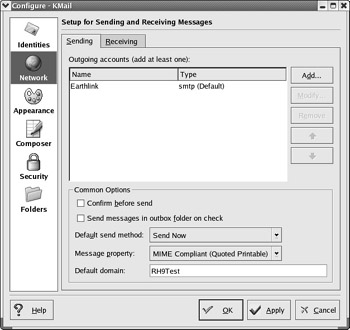
Figure 17.43: Configuring KMail
KNewsTicker You can set up a news ticker in the panel. KNewsTicker can access a number of different sources. The process for adding KNewsTicker is a little different; you don t use the K Menu but need to add it directly to the panel.
To add KNewsTicker, right-click on an open area of the panel. In the menu that appears, select Add ˜ Applet ˜ KNewsTicker.
KNode You can also use KNode as the default newsgroup reader. It s as straightforward to configure as KMail; once KNode is open, click Settings ˜ Configure KNode. This opens the Preferences - KNode dialog box. Click New to open up the New Account - KNode dialog box. As shown in Figure 17.44, KNode is highly configurable, and the entries for news accounts are straightforward.
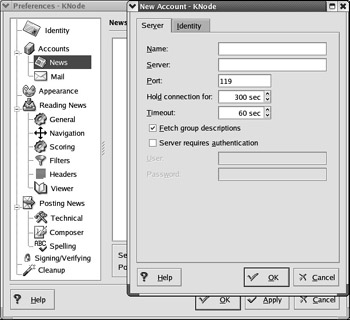
Figure 17.44: The KNode newsreader
Konqueror Web Browser Konqueror is the default KDE web browser. Like GNOME s Nautilus, it s also used to browse file folders. You ve already seen the Konqueror configuration options when we discussed the KDE Control Panel earlier in this chapter. You can configure these settings and more when you select Settings ˜ Configure Konqueror. The basic browser is shown in Figure 17.45, and the configuration options are shown in Figure 17.46.
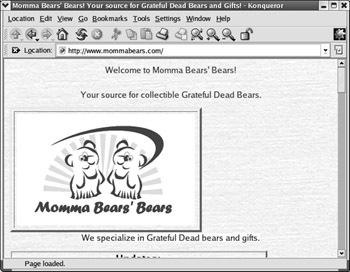
Figure 17.45: The Konqueror Web Browser
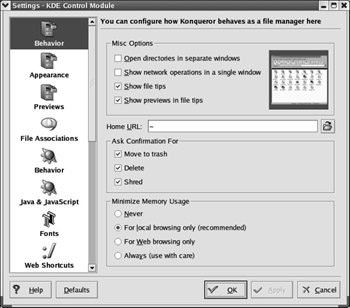
Figure 17.46: Configuring Konqueror through the KDE Control Module
Korn If you want a utility to monitor your mailbox, start Korn, the KDE mail checker. Once configured for the account of your choice (local, POP3, IMAP4, and more), start Korn. Once it s docked in the panel, it monitors configured mailboxes at fixed time intervals. The default is 5 minutes.
KPPP One of my favorite Linux GUI applications is KPPP, which is primarily used to connect to an ISP over a telephone modem. It is highly configurable; you can set up the accounts of your choice for different ISPs or locations. If you re having trouble configuring a modem, KPPP makes it easy to experiment with different devices. KPPP also includes logs and terminal screens that can help you track the performance of your connection. The main KPPP screen is shown in Figure 17.47.
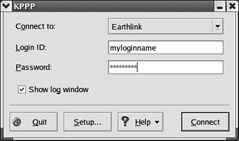
Figure 17.47: KPPP
KPPP Log Viewer The KPPP Log Viewer starts a connection log for the current month, which is especially useful if your connections incur costs per minute or byte. This is a common situation for some wireless and European telephone modem connections.
KSirc If you want to connect to an IRC chat room, you can use the default KDE chat client, KSirc. Once KSirc is open, you can configure a new connection by selecting Connections New Server. As shown in Figure 17.48, you can select from available chat server groups, choose a server, enter a password if required, and then click Connect. If the connection is successful, you ll see a new window with your chat room.
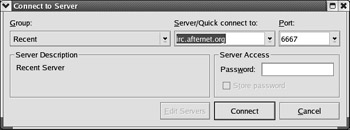
Figure 17.48: Configuring KSirc for chat
Licq Licq is another Internet chat client, with KDE support.
Other Utilities
KDE includes other utilities that generally do not easily fit into the other K Menu categories. Many of them can serve educational purposes. They range from Kalzium, which helps you learn the periodic table of the elements, to KVocTrain, which you use to enhance your vocabulary. These utilities are accessible through the K Menu ˜ Other submenu, shown in Figure 17.49. Some of the utilities in this menu that are not part of the KDE desktop are not covered in this chapter.
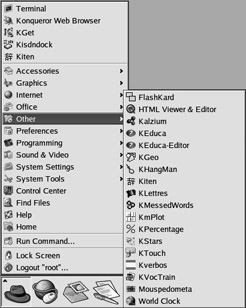
Figure 17.49: Other KDE utilities
FlashKard FlashKard is a KDE vocabulary builder. Once a vocabulary list is loaded, you can quiz yourself on the meanings of the words in the list. A sample list in German is available in sample-de.kvtml , in the /usr/share/apps/kvoctrain/examples directory.
Kalzium Kalzium is a KDE utility that presents a periodic table of the first 103 elements, shown in Figure 17.50. Each element includes a clickable button, which provides more information about each element, and a link to additional information from the Chemistry department of the University of Split, Croatia ( www.ktf-split.hr/en/index.html ).
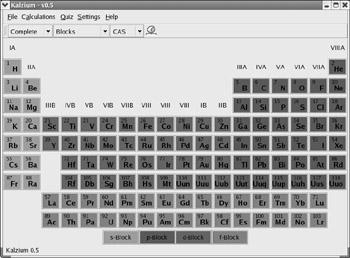
Figure 17.50: A KDE periodic table
KEduca KEduca supports the creation and revision of form-based exams. You can add questions with KEduca-Editor. More information is available at sourceforge .net/projects/keduca .
KGeo KGeo is an interactive KDE geometry program, which helps math teachers illustrate basic geometrical principles.
KHangMan KHangMan is a KDE version of the hangman game for guessing words.
Kiten Kiten is another interactive dictionary; by default, it works with Japanese (Kanji) and English. An example translation is shown in Figure 17.51.
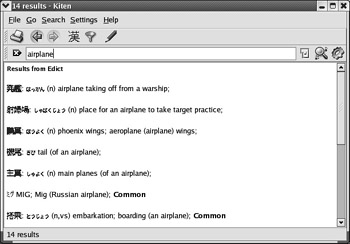
Figure 17.51: Kiten translating from English to Japanese
KLettres KLettres is a KDE utility that teaches the alphabet. It is currently configurable in Danish, Dutch, and French.
KMessedWords KMessedWords is a KDE anagram game.
KmPlot KmPlot is a KDE mathematical function plotter; it can help you graph various equations.
KPercentage KPercentage is a KDE utility that quizzes students on calculating percentages.
KStars KStars is a KDE planetarium utility that helps you identify different stars, based on a look at a clear night.
KTouch KTouch is a KDE program that helps you learn to touch type.
Kverbos You can use the Kverbos utility to learn different Spanish language verb forms.
KVocTrain KVocTrain is another flash card utility, similar to FlashKard. It also uses .kvtml databases.
Mousepedometa Also known as KOdometer, this utility tracks the mileage of your cursor across the desktop.
World Clock The KDE World Clock can display the current time in different locations, along with a view of where the sun should be visible on a clear day.
Preferences
KDE includes several utilities in the Preferences submenu (K Menu ˜ Preferences). Just a few of the utilities shown in Figure 17.52 are KDE utilities; see Table 17.10 for a brief description.
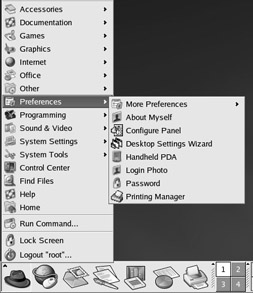
Figure 17.52: The Preferences menu
| Utility | Description |
|---|---|
| Configure Panel | This opens the Settings - KDE Control Module window, where you can set up the panel; described earlier in this chapter. |
| Desktop Settings Wizard | This wizard helps you configure KDE for your language, location, preferred system behavior, special effects, and style. |
| Note | Because none of the utilities in the More Preferences menu are based on KDE, we do not cover them here. |
More Programming Tools
KDE includes several utilities in K Menu ˜ Programming ˜ More Programming Tools submenu. Just a few of the utilities shown in Figure 17.53 are KDE utilities; we describe them briefly in Table 17.11.
Figure 17.53: More Programming Tools
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Cervista | A KDE tool for keeping track of different versions of source code, using CVS (Concurrent Versions System). |
| KBabel | Supports the use of other languages for comments and other guides in program code. |
| KBabel - Catalog Manager | Merges KBabel-based directories. |
| KBabel - Dictionary | Also known as PO Compendium; lists translation messages for a project. |
| KBugBuster | Supports bug management; by default, includes a connection to the KDE bug tracking system at bugs .kde.org. |
| Kompare | A KDE front end to the diff command for reviewing the differences between files. |
| Memory Profiler | For monitoring the memory behavior of programs , including leaks. |
| Quanta Plus | A web development tool for KDE. |
Multimedia
A number of KDE multimedia applications are available when you click Main Menu ˜ Sound & Video. As shown in Figure 17.54, these include various audio and CD players and sound control utilities.
Figure 17.54: Multimedia Menus
KsCD The KDE small/simple CD Player is an easy-to-use player for audio CDs. As shown in Figure 17.55, it has the standard buttons that allow you to play and move between CD tracks. It also includes access to the compact disc database (CDDB) described earlier. If you click on the name of the song, you ll be able to select the song of your choice from the CD tracklist.
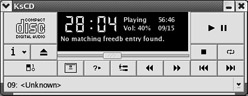
Figure 17.55: KDE CD Player
Sound Mixer The KDE Sound Mixer, also known as KMix, allows you to regulate sound input from a number of different sources.
aRts Builder As described earlier, aRts is the KDE sound server. aRts Builder is a graphical design tool that can help you configure connections for various sound characteristics.
aRts Control Tool This is a tool for controlling different settings of the aRts sound server.
Kaboodle Kaboodle is a media player for single files, such as those in .wav format.
KMid The KDE MIDI/Karaoke file player allows you to play .mid and .kar files if your sound card has hardware support for raw MIDI files.
KMidi KMidi is a front end to the TiMidity synthesizer (see Figure 17.56). If your sound card does not provide hardware MIDI support, you may be able to use KMidi to play .mid files. You ll also need an /etc/timidity.cfg configuration file; a sample is available in the /usr/share/apps/kmidi/config directory. If you see errors when you try to start KMidi, make sure you have the arts- devel -* RPM installed.
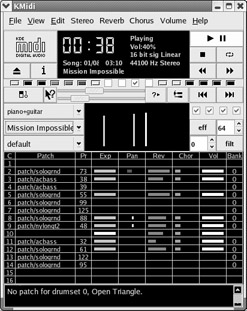
Figure 17.56: KMidi at work
Noatun The Noatun utility is a front end to the aRts sound server. When you start it, it may look like it s not working. In fact, it adds an icon to your panel. Right-click on the icon to open the basic Noatun menu. Similar to the XMMS audio player from Chapter 16 , Noatun includes an equalizer and playlist menu.
TiMidity Synth See KMidi.
System Tools
There are some KDE system tools that are not related to the redhat-config-* tools primarily covered in Chapter 19 . The menus are shown in Figure 17.57. We cover a wide variety of administrative tools in this section.
Figure 17.57: The More System Tools menu
Create A Boot Disk The Create A Boot Disk utility calls the qmkbootdisk command, which helps you create a boot disk for your installation on a 1.44MB floppy drive. For more information, see the discussion of mkbootdisk in Chapter 11 . The interface is simple, as shown in Figure 17.58.
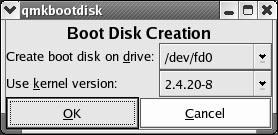
Figure 17.58: Making a boot disk
Desktop Sharing Desktop Sharing, formerly known as krfb , supports management of xinetd servers.
File Manager Opens the home directory for the current user in Konqueror.
KAudioCreator This utility is somewhat out of place; it really belongs with the other multimedia applications in the Sound & Video menu. With KAudioCreator, you can copy tracks from audio CDs for writing to the CDs of your choice. It also supports CDDB access to help you find more information on each track.
KDat KDat is a KDE tape archiver, based on the tar command.
KDE System Guard The KDE task manager and performance monitor is known as the KDE System Guard, or ksysguard for short. By default, it presents graphical views of system loads based on the top command. You can also set up graphs to monitor a number of other systems. A basic view of this tool is shown in Figure 17.59.
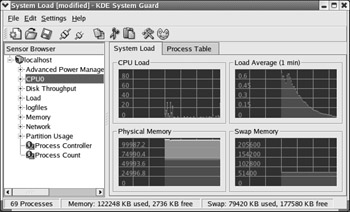
Figure 17.59: KDE System Guard
KDiskFree The KDiskFree utility illustrates available free space on all mounted partitions; it is essentially an illustrated front end for the df command described in Chapter 07 .
Kernel Tuning You can modify some of the settings associated with your kernel, which are stored in the /proc directory, described in Chapter 11 . For example, if your Linux computer is a gateway between networks, you ll want to enable IP Forwarding. One method is described in Chapter 21 . Alternatively, you can set it up through the Kernel Tuning utility, shown in Figure 17.60.
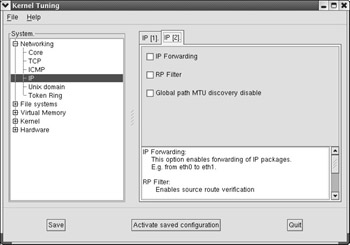
Figure 17.60: Kernel Tuning
KRec The KRec utility is a recording fron end to the KDE aRts sound server. It s a multimedia utility that actually belongs in the Sound & Video menu.
KSim The KSim utility is a system monitor that is a simple front end to the top command. KSim commands are docked in the KDE panel; right-click on the KSim menu bar to open the KSim Configuration menu, shown in Figure 17.61. As you can see, KSim is highly customizable.
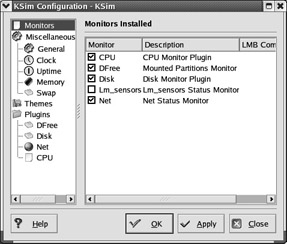
Figure 17.61: Configuring KSim
QTCups As of this writing, QTCups is still part of the Red Hat More System Tools submenu. It is obsolete and superseded by the KDEPrint utility, which you can start from a command-line interface with the kprinter command. KDEPrint serves as an interface between KDE utilities and the active print daemon on your computer. As noted in Chapter 25 , the default print service is CUPS.
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 220