Certification Objective 2.04: Customizing Your Installation
|
| < Day Day Up > |
|
Before we install Red Hat Enterprise Linux on a computer, we'll look at some of the critical decisions that you'll need to make during the Red Hat exams. Time is of the essence on these exams. While you could just install everything, that could easily cost you 15 minutes or more. That may be the time that you need to configure the critical services required to pass the exam. By the time you're done with this section, you'll have the tools to select just the software that you need.
Red Hat Enterprise Linux includes its own installation program, known as Anaconda. RHEL 3 Workstation and RHEL 3 Server include different sets of default RPM packages. With Fedora Core 1 or Red Hat Linux 9, you can simulate these installations using the Workstation or Custom installation options. Naturally, RHEL Workstation is associated with the RHCT exam; RHEL Server is associated with the RHCE exams.
As the RHCE exam includes RHCT components, you may also need to configure your computer as a workstation. Don't be surprised if you install applications associated with the X Window System and GNOME or KDE desktop environments.
| Exam Watch | Even RHCEs need to know how to configure the X Window, as they are often expected to configure workstations for users who need graphical applications. |
Depending on your needs, you can set up a system with anywhere from about 600MB to 4GB of files. In the real world, you'll need lots of additional room for user files, log files, and any additional applications that you may want to install in the future.
The essence of each installation is in the installed package groups. As you examine each of the options, focus on the associated package groups. First, there are basic package groups that are included with every installation. Then, there are the package groups that you can select during the installation process.
Baseline Packages
Every installation of Red Hat Enterprise Linux gets a series of packages, organized into the Core and Base package groups. You can find a list of these on the first Red Hat Enterprise Installation CD-ROM in /RedHat/base/comps.xml, at the top of this text file. I've modified this file slightly, as shown in Figure 2-3, to list the first few base packages specified in this file.

Figure 2-3: Red Hat Enterprise Linux base packages
Default Packages
The RHEL 3 server installation process installs about 1.4GB of software by default. This includes several package groups that are suitable for some uses. If this is good enough for the requirements as presented on your particular exam, activate the Accept The Current Package List option and click Next to continue. In most cases, you'll want to select the Customize The Set Of Packages To Be Installed option.
As shown in Figure 2-4, they include the package groups described in Table 2-2. They actually include three other package groups, Graphical Internet, Text Internet, and Printing Support. I include a basic description of these Package Groups in Table 2-2 as well.
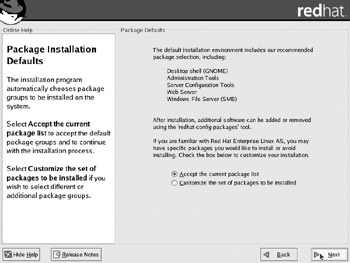
Figure 2-4: Red Hat Enterprise Linux default package groups
| Package Group | Description |
|---|---|
| Desktop shell (GNOME) | The default Red Hat Enterprise Linux GUI desktop. While it may not be required on the job for many servers, it is very likely that you'll need to install GNOME during the Red Hat exams. |
| Administration Tools | Includes Red Hat's basic GUI administration tools. Useful if you're going to configure Red Hat from the GUI. |
| Server Configuration Tools | Adds Red Hat's basic GUI configuration tools for many major servers. |
| Web Server | Installs basic packages associated with the Apache Web Server. Includes the Tux Web Server. |
| Windows File Server (SMB) | Includes the Samba client and server packages. |
| Graphical Internet | Graphical tools for connections and communication on TCP/IP networks. |
| Text Internet | Text-based tools for connections and communication on TCP/IP networks. |
| Printing Support | Basic software required to connect this computer to a printer and set it up as a print server. |
There are actually more default package groups, which you can review in the aforementioned comps.xml file. They include the following package groups: Printing Support, Dialup Networking Support, and Text-based Internet.
| On The Job | When you install RHEL 3, the Dialup Networking Support package group is automatically installed during the regular installation process. You're not even allowed to deselect it through the default version of Anaconda. |
Customizing Package Installation
In most cases, it will be best to customize the packages that you'll install during the Red Hat exams. Alternatively, you can use the redhat-config-packages (Red Hat Package Management) tool, described in more detail in Chapter 4. This section focuses on package groups. If you see requirements on your exam for a mail server, graphics applications such as The GIMP, and to recompile the kernel, you'll want to select the Mail Server, Graphics, and Kernel Development package groups.
| On The Job | The general option to select individual RPM packages during the Linux installation process is no longer available in RHEL (or in Fedora Linux). However, you can select some individual RPM packages as part of RHEL package groups during the graphical installation process. |
Red Hat package groups are organized logically; for example, all of the packages associated with the GNOME desktop environment belong to one Red Hat package group. It's important to pick only the package groups you need. Fewer installed packages means more room for personal files for you and your users, as well as the log files you need to monitor your system and actually get some use from your applications. On the exam, fewer installed packages leaves more time to configure the required services.
| On The Job | Understanding how these package groups work is important in a Kickstart installation, which is described in more detail in Chapter 3. |
Package Groups
This section includes the briefest possible overview of each of the packages you can select during the RHEL installation process. Remember, some of these packages depend on others; for example, if you want to install the GNOME Desktop Environment package group, the Red Hat installation program will make sure that you install the X Window System package group as well.
For complete details of the RPMs associated with each package, go to the first RHEL installation CD, and read the comps.xml file in the /RedHat/base directory in the text editor or Web browser of your choice.
These packages, as well as the order in which they are presented, are based on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 3. If you're using Fedora, some other version of Red Hat Linux, or even one of the third-party rebuilds, the packages may vary. In any case, the best way to study what's in each package group is through the graphical installation.
For example, Figure 2-5 illustrates the RHEL 3 installation, with a focus on the Mail Server package group. As you can see, two major mail servers, sendmail and postfix, are both installed by default when you select this package group.
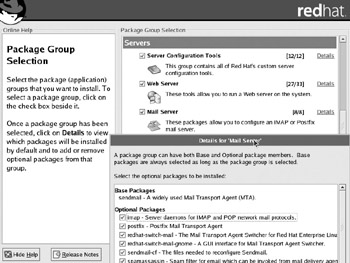
Figure 2-5: Red Hat Enterprise Linux Mail Server package group details
Take some time with this screen. Examine the packages within each package group. You'll learn about the kinds of packages that are installed by default. If you don't add them during the installation process, it isn't the end of the world. You can still add them with the rpm commands described in Chapter 3, or the redhat-config-packages (Red Hat Package Management) tool described in Chapter 4. What you learn here can help you select the package groups to install during the RHCE or RHCT exam.
In the following sections, I describe each package group in more detail, based on what you see during the RHEL ES 3 Server graphical installation process. You won't see all of these package groups during a RHEL 3 Workstation or Red Hat Professional Workstation installation.
During the Installation Exam
Even if you're taking the RHCE exam, pay attention to the software associated with the Linux desktop environment. The RHCE exam includes RHCT components, which means that you'll also be tested on setting up Linux as a workstation.
That means you'll be installing a number of package groups that you would not install on a computer that's just being used as a server. When you take the exam, read the configuration requirements carefully. I would not be surprised if you see a requirement to install software such as sound software and the OpenOffice.org suite.
But don't install everything. If you don't need to install the OpenOffice.orgsuite, you can save several minutes during the Installation and Configuration exam. The time you save could allow you to configure a few more services, which could determine whether you pass the exam.
And if you make a mistake during the installation process, don't panic. You can use the redhat-config-packages tool after installation to add any package groups that you missed.
X Window System
This package group includes a number of basic Linux GUI fonts, libraries, and critical tools such as the Red Hat GUI Display Settings tool, which you can start with the redhat-config-xfree86 command. It's required if you install the GNOME or KDE desktop environments.
As a Linux administrator, you may have confidence in your ability to configure Linux from the command line. In practice, you may install Linux on a number of computers without the GUI. However, even the RHCE exam includes an RHCT component, which tests your ability to create a Linux workstation for your users, which almost invariably includes a GUI.
| Exam Watch | Since the RHCT exam requires you to configure a workstation, and you have to meet all RHCT requirements during the RHCE exam, expect to install the GUI during the Installation and Configuration exam. |
GNOME Desktop Environment
The GNOME group includes the basic packages required to install the GNOME Network Object Model Environment. While GNOME is the default GUI for RHEL 3, read the instructions on your exam carefully. It's possible that you'll be asked to install the other major GUI, the K desktop environment.
When you choose to install the GNOME Desktop Environment package group, all GNOME packages are installed by default.
KDE Desktop Environment
The KDE group includes the basic packages required to install the K Desktop Environment, which is the main alternative GUI for RHEL 3. It is the default GUI for a number of other Linux distributions.
When you choose to install the KDE Desktop Environment package group, not all of the KDE packages are installed by default. However, unless you're familiar and feel that you can use the KDE Administrative tools to help you configure RHEL, you won't need to change the defaults associated with this package group.
| Exam Watch | Read the instructions on the RHCE and RHCT installation exam carefully. As an example, if it requires you to set up only KDE, it's a waste of time to accept the default GNOME desktop environment! |
Editors
These include the basic text editors associated with Linux: vi and emacs. It also includes nedit, a Macintosh-style text editor. While it's essential that you know vi to use the Linux rescue mode, the emacs text editor may be the most popular text editor in the world of Linux and Unix. It also requires an extensive series of packages, which makes it impossible to include emacs on a rescue floppy that is limited to 1.44MB.
Engineering and Scientific
RHEL includes a group of packages for mathematical and scientific purposes, such as gnuplot, pvm, and units.
Graphical Internet
Linux now includes a number of different GUI clients for Internet access, including the Mozilla Web browser, the xchat and gaim instant message utilities, and the Evolution personal information manager.
Text-Based Internet
Linux includes a number of different text-based clients for Internet access, including the elinks Web browser, and the fetchmail and mutt e-mail readers. This is closely related to the Graphical Internet package group.
Office/Productivity
This group includes the emerging standard for Linux office suites, OpenOffice.org, as well as related packages such as PDF viewers. It includes about 300MB of software. If you don't need these tools on your Linux computer, you should consider leaving this out of the installation.
| Exam Watch | Time is of the essence on the Red Hat exams. Unless specifically required on your exam, don't install the Office/Productivity package group. This can save you several minutes which you could use to meet other requirements on your exam. |
Sound and Video
Not surprisingly, the Sound and Video group installs the packages required to allow you to use sound cards and interconnect the basic components of your sound and video system: sound card, speakers, microphone, and CD/DVD drive.
Don't dismiss this package group out of hand; I've heard that some people are asked to configure a sound card during the RHCE exam. Therefore, it's possible that you'll want to install this package group when you configure the Linux desktop environment.
Authoring and Publishing
The Authoring and Publishing group includes support for several documentation systems, such as DocBook and TeX.
Graphics
This package group automatically incorporates the X Window package and a number of graphical applications. This includes the most prominent Linux graphics application, The GIMP. Depending on whether you also install GNOME and/or KDE, this also installs graphical packages associated with each of these GUIs.
Games and Entertainment
Be careful with this package group. Do you really want to install games on a business computing system? Some believe that computer games are useful to help newer users become comfortable with Linux. While I doubt that you'll ever have to install this package group during the RHCE or RHCT exams, read the instructions that come with your exam.
Server Configuration Tools
Red Hat has developed a series of GUI server configuration tools. For expert users, it's faster to configure most services from the command line interface. In fact, I encourage you to learn to configure all Linux services in this way; you'll be a better administrator.
However, these tools are installed by default in RHEL 3. As the RHCE exam requires you to configure servers, I encourage you to install this package group. It includes about 6MB of files, so the time penalty during the installation process is trivial. If you're less certain about your skills in one or more of these services-or if nerves affect your skills during an exam-these GUI tools can be a lifesaver:
-
redhat-config-bind Domain Name Service (DNS) configuration tool
-
redhat-config-httpd HTTP (Apache) configuration tool
-
redhat-config-network Network Configuration tool
-
redhat-config-nfs NFS Server Configuration tool
-
redhat-config-printer Printer Configuration tool
-
redhat-config-samba Samba Server Configuration tool
-
redhat-config-securitylevel Security Level Configuration tool
-
redhat-config-services Service Configuration tool
Web Server
The Web Server group installs Apache, Squid, and the extensive array of supporting modules and configuration files. It's installed by default for RHEL 3. It's quite possible that you'll have to configure at least a Web server for the RHCE exam.
Mail Server
This group includes the packages required to configure a sendmail-based IMAP or a postfix mail server. While it is not installed by default, it is quite possible that you'll have to configure a mail server such as sendmail or postfix during the RHCE exam.
Windows File Server
This group includes the Samba packages required to set up Linux as a client and as a server on a Microsoft Windows-based network. It is installed by default, and it's quite possible that you'll have to configure Samba during both the RHCT and RHCE exams. RHEL 3 includes the Samba 3.0 file server; if you're using Red Hat Linux 9 to study for your exam, you'll have to upgrade accordingly from the RPM source code, using the techniques described in Chapter 4.
While I haven't seen any Microsoft Windows computers at Red Hat, it is possible to configure and test Samba clients and servers, using a second Linux computer as a client.
DNS Name Server
The DNS Name Server group includes the tools you need to configure and maintain a Domain Name System server on the local Linux computer. In the Linux world, a DNS server is also known as a nameserver, based on the Berkeley Internet Name Domain (bind). While it is not installed by default, it is quite possible that you'll have to configure a DNS server during the RHCE exam.
FTP Server
This includes the default Red Hat FTP server, the Very Secure FTP Daemon (vsftpd). While it is not installed by default, it is quite possible that you'll have to configure an FTP server during the RHCE exam. It also happens to be the server that Red Hat uses for its own FTP sites.
SQL Database
The Structured Query Language (SQL) is one of the basic database languages. This group includes support for the PostgreSQL database system. It is not installed by default. As there is no reference to SQL or databases in any materials related to the RHCT or RHCE exams, I don't believe that you'll have to install this package group during either exam.
MySQL Database
The Structured Query Language (SQL) is one of the basic database languages. This group includes support for the MySQL database system. It is not installed by default. As there is no reference to SQL or databases in any materials related to the RHCT or RHCE exams, I don't believe that you'll have to install this package group during either exam.
News Server
This is a simple group, incorporating the inn (Internet Network News) server. It is not installed by default, and there is no reference to a News Server in the Red Hat Exam Prep guide.
Network Servers
This package group includes a number of smaller servers that are useful for running a network, including those associated with DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) and NIS (Network Information Service). It is not installed by default. When you select this package group during the RHEL 3 installation process, Red Hat installs DHCP and the NIS server.
However, if you're asked to install other components of this package group during the RHCE Installation and Configuration exam, you may want to customize details during the Anaconda installation process. You can then select the required servers as shown in Figure 2-6. Alternatively, you can just use the rpm command as described in Chapter 4 to install the appropriate packages after RHEL is installed. Servers with similar functionality are included in the Legacy Network Servers package group.
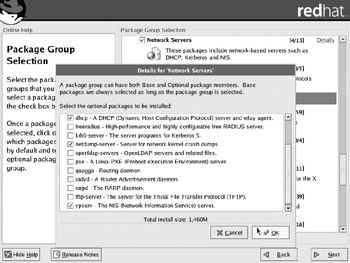
Figure 2-6: Network Servers package group
Legacy Network Servers
There are several legacy network servers. While some Linux gurus discourage their use due to security concerns, they remain popular. They include packages that allow you to install an RSH (Remote Shell), Telnet, and TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) server.
Development Tools
This group includes a large number of development tools. Additional development tools are included when you install other packages such as GNOME Development, Graphics, Web Server, News Server, and more. As there is no reference to Development Tools packages in any materials related to the RHCT or RHCE exams, I don't believe that you'll have to install this package group during either exam.
Kernel Development
This group includes the very large Kernel source packages, which currently require over 500MB of disk space. There is no longer a specific requirement to recompile the Linux kernel during the Red Hat exams. As this group requires over 500MB of software, don't install this package group unless required on your specific exam.
X Software Development
The X Software Development group includes the basic packages such as XFree86-devel required to develop additional GUI applications. As there is no reference to X Software Development packages in any materials related to the RHCT or RHCE exams, I don't believe that you'll have to install this package group during either exam.
GNOME Software Development
The GNOME group includes the basic packages required to develop additional GTK+ and GNOME GUI applications. As there is no reference to GNOME Software Development packages in any materials related to the RHCT or RHCE exams, I don't believe that you'll have to install this package group during either exam.
KDE Software Development
The KDE group includes the basic packages required to develop additional QT and KDE GUI applications. As there is no reference to KDE Software Development packages in any materials related to the RHCT or RHCE exams, I don't believe that you'll have to install this package group during either exam.
Legacy Software Development
Red Hat makes it possible to develop software on RHEL 3 for older versions of Red Hat Linux. The Legacy Software Development group includes support for older C and C++ language compilers. As there is no reference to these software development packages in any materials related to the RHCT or RHCE exams, I don't believe that you'll have to install this package group during either exam.
Administration Tools
Red Hat has developed a series of GUI administration tools. For expert users, it's faster to configure most services from the command line interface. In fact, I encourage you to learn to configure all Linux services in this way; in the long run, you'll be a better administrator.
However, these tools are installed by default in RHEL 3. For the purposes of the RHCE and RHCT exams, I encourage you to install this package group. If you're less certain about your skills in one or more of these services-or if nerves affect your skills during an exam-these GUI tools can be a lifesaver:
-
redhat-config-authentication Supports configuration of NIS and Samba clients and more; also known as the Authentication Configuration tool.
-
redhat-config-date Allows you to configure the time and date of your system; also known as the Date/Time Properties tool.
-
redhat-config-keyboard Lets you select a different keyboard; also known as the Keyboard configuration tool.
-
redhat-config-kickstart Opens a GUI for customizing a Kickstart file; also known as the Kickstart Configurator.
-
redhat-config-language Supports configuration of the GUI in different languages; also known as the Language Selection tool.
-
redhat-config-nfs Allows configuration of an NFS server; also known as the NFS Server Configuration tool.
-
redhat-config-packages Lets you install packages after RHEL is installed. Very important; also known as the Package Management tool.
-
redhat-config-proc Opens a GUI for customizing the kernel. Functionally similar to Microsoft's Registry Editor; also known as the Kernel Tuning tool.
-
redhat-config-rootpassword Allows you to change the root password (no special name).
-
redhat-config-soundcard Automatically configures most sound cards (no special name).
-
redhat-config-users Supports creating and modifying users and groups; also known as the Red Hat User Manager.
-
redhat-logviewer Provides a GUI for viewing standard log files; also known as the System Logs configuration tool.
System Tools
This package group includes a varied array of tools, from the ethereal network traffic reader to the zsh shell. This package group is not installed by default, and I believe it's unlikely that you'll have to install this package group during either exam. While the Samba client is part of this package group, you can also install it through the Windows File Server package group.
However, it's a good idea to review the details of this package group during your studies, just in case you need one of these packages during your exam.
Printing Support
Red Hat Enterprise Linux currently includes support for the Common Unix Printing System (CUPS). It supports the next-generation printing protocol, known as IPP. Once installed, it can help detect network printers, with the help of the redhat-config-printers (Printer Configuration) tool.
| On The Job | Red Hat no longer includes the Line Print Daemon (LPD) in the latest Linux distributions (RHEL 3 and Fedora Linux). |
|
| < Day Day Up > |
|
EAN: N/A
Pages: 194