Feature Selection
Cisco IOS Software supports many features for all types of IBM-type networking. Sometimes it is difficult to choose an IBM feature based on the function a router needs to provide. Refer to Figure 5-1 to find a simple network diagram that represents the problem you are trying to solve with routers. Then choose the IBM networking feature and refer to the appropriate section of this chapter for configuration information.
Figure 5-1. Basic Network Topologies to Consider Using with IBM Networking
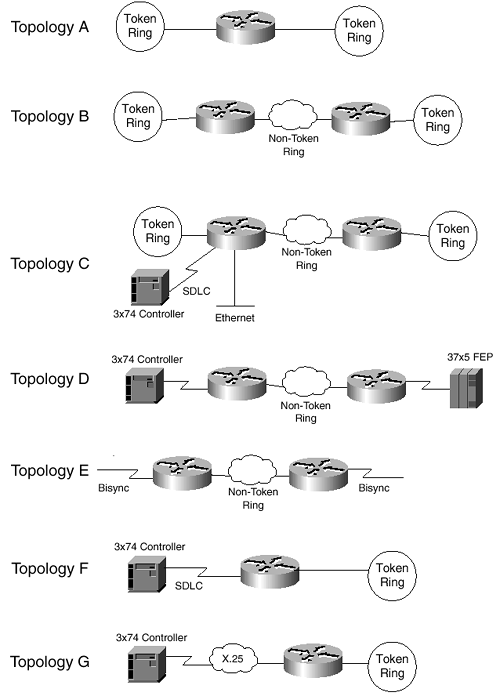
This chapter presents many of the most commonly used IBM networking features. Other features, such as QLLC and SDLLC, are not presented, because their functions can be performed by the more robust DLSw+ feature. In addition, features such as the Channel Interface Processor (CIP), Channel Port Adapter (CPA), Advanced Peer-to-Peer Networking (APPN), Native Client Interface Architecture (NCIA), and Airline Product Set (ALPS) represent much more complicated and specialized applications. These features are best left to the more detailed Cisco documentation on IBM Network Solutions. Figure 5-1 and Table 5-1 provide a series of basic network topologies as well as a guide to which IBM networking feature is appropriate, given a specific topology, and the benefits of that IBM networking feature.
Table 5-1. IBM Networking Features: Benefits and Where to Use
| Network Topology in Figure 5-1 | IBM Networking Feature to Use | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| A | Source-Route Bridging (SRB) | Bridging between physical Token Ring interfaces on a router. |
| B | Remote Source-Route Bridging (RSRB) | Source Route Bridging between routers across non-Token Ring media. |
| C | Data-Link Switching Plus (DLSw+) | Bridging of Token Ring, Ethernet, and serial via TCP, FST, and Direct Encapsulation. Supports SDLLC and QLLC media translation. Scalable and fault-tolerant. |
| D | Serial Tunnel (STUN) | Serial transport via TCP, FST, and Direct Encapsulation. |
| E | Block Serial Tunnel (BSTUN) (not presented) | Transport of asynchronous bisync data-link protocol via TCP, FST, and Direct Encapsulation. |
| F | SDLLC Media Translation (not presented; refer to DLSw+) | Translates SDLC device traffic to Token Ring SNA. |
| G | QLLC Media Translation (not presented; refer to DLSw+) | Translates X.25 device traffic to Token Ring SNA. |
EAN: N/A
Pages: 185