Cisco IOS Software Releases
Cisco IOS Software images for routers and access servers are released for use in the following fashion:
-
First Commercial Shipment (FCS) A Cisco IOS Software version that becomes commercially available to Cisco customers.
-
Major release A version number of Cisco IOS Software. It introduces a new set of features and functionality. This release begins as an FCS and is marked as Limited Deployment (LD) until it achieves General Deployment (GD) status.
-
Maintenance release A revision to a major release for bug fixes. No new functionality or platforms are added. This is introduced as a periodic release and is fully regression- tested .
-
Interim build release A special-circumstance revision to a maintenance release. It is not regression-tested.
-
Early Deployment (ED) release New functionality and hardware platforms are introduced for quick delivery. ED releases also receive regular maintenance releases.
-
ED Technology ("T") release A train of ED releases that contains new hardware and features. It is based on a major release and regular maintenance releases. One specific " T " release becomes the next major release.
-
General Deployment (GD) release A Cisco IOS Software version that is deemed to have stability and extensive market exposure and testing. A GD version is never based on an ED release.
Figure A-1 shows the basic flow of Cisco IOS Software releases. The process begins with a major release (12.1 in the figure). Major releases are always numbered as a dotted -decimal number with no other suffixes. Maintenance and interim build releases occur periodically or as needed, and all are based on the major release. These releases are shown proceeding across the figure to the right. At some point, a maintenance release receives General Deployment status.
Figure A-1. Cisco IOS Software Release Process
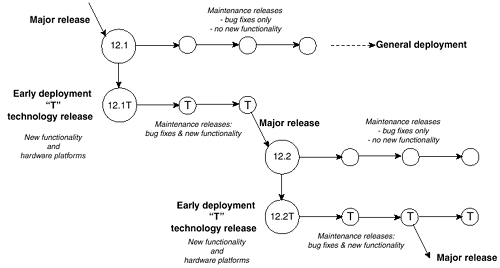
At the same time, a set of new technology and hardware features are added to the technology or "T" train of releases. This set of features is added to the major release, forming a release with a "T" suffix (12.1T in Figure A-1). Maintenance and interim build releases occur as needed, just as in the major release train. New features can be added to new maintenance releases. These releases are shown proceeding across the figure to the right, parallel to the major release train.
Major and technology trains occur in parallel. New major releases are formed from the previous technology train.
Other types of early deployment releases are also possible. Many of these introduce new features or bug fixes for specific platforms on a one-time-only basis. These releases are denoted with a suffix other than "T" and are rolled into a later maintenance release in the technology train.
Release Numbering
Cisco IOS Software releases follow a standard numbering convention, as shown in Figure A-2. The major release is given as a dotted decimal number, as in "12.1." A suffix is added in parentheses to specify the maintenance release. This number begins with 1 and is incremented with each successive maintenance build. If interim builds are released, these are referenced by adding a dot and the interim build number after the maintenance release number.
Figure A-2. Cisco IOS Software Release Numbering
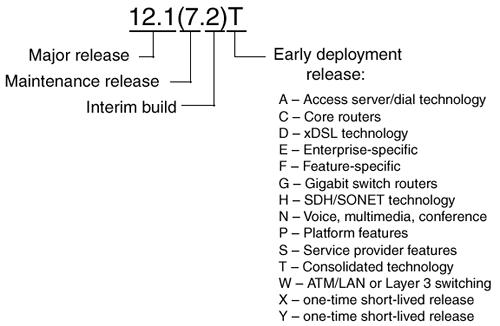
Early Deployment releases are identified by one or two additional letters and numbers at the end of the release number. Many types of ED releases can be produced. These are categorized as shown in the figure and are identified by the letter shown. For example, all technology train releases have the letter T as the ED suffix. Other short-lived ED releases have the letter X. If more letters and numbers follow, they serve only to differentiate the release from others that have a similar ED release status.
Choosing a Cisco IOS Software Release
Cisco offers a number of Cisco IOS Software image files, each containing a specific set of features and capabilities. Each image file supports a specific router hardware platform. The following list can help you cross-reference all of these variables to choose the correct Cisco IOS Software release.
NOTE
The URLs used in the following steps require a registered account on the Cisco CCO Web site. You might also need a valid service contract to gain access to the CCO Software Center for downloading Cisco IOS Software images. To register for a CCO account, go to www.cisco.com/register/.
-
Determine the features you need.
-
Use the Cisco IOS Feature Navigator tool on CCO:
http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/Support/FeatureNav/FN.pl
Select the Cisco IOS Software feature sets that are required for your network. To see the complete list of features, leave the "Search by full or partial feature name " field blank and click the Search button.
The list of features is very detailed, because various features were introduced in specific Early Deployment releases.
The Feature Navigator also allows you to match the list of features against a router platform and a Cisco IOS Software release if desired.
-
Use the Cisco Hardware-Software Compatibility Matrix tool on CCO:
http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/front.x/Support/HWSWmatrix/hwswmatrix.cgi
For a specific router platform, a table of the minimum (or earliest) software releases that offer full hardware support is shown. The platform is broken down into basic units and all possible hardware modules, referenced by Cisco part numbers. Select each module that you want to support in the platform, and click the "Display Intersection" button. The minimum supported IOS releases are listed for each hardware product.
-
-
Select a Cisco IOS Software release.
This selection can be based on many factors, including reliability, maturity, new technology, bug fixes, and so forth. Consider these basic release categories and their characteristics:
-
-
GD To reach GD status, an IOS release must be proven in the field, must be heavily tested, and must achieve a high customer satisfaction rating. You should choose a GD release if your requirements are for high reliability, maturity, and support for business-critical resources. Also remember that subsequent maintenance releases after the first GD release also retain the GD status.
-
LD Limited Deployment releases are simply major or maintenance releases that are introduced after FCS but before GD status is reached. LD maintenance releases are fully regression-tested and contain new bug fixes, but they do not include any new features or platforms until GD status. Choose an LD release if your requirements are based on stability rather than new features.
-
ED The technology or "T" release train provides up-to-date availability for new technologies. Maintenance releases within the "T" train also implement bug fixes and might introduce other new technologies and features. Choose a "T" release if you require support for specific new features, protocols, or technologies. The new features in the "T" release train will eventually be rolled into the next major release.
-
ED The "X" or other non-"T" releases implement new features and/or bug fixes for specific router platforms. These are one-time releases, introduced for quick availability, that get rolled into a later "T" release. Choose one of these ED releases if you require early access to new functionality for a new or specific hardware platform. Then consider migrating to the next available "T" release when it becomes available.
-
Interim These release builds are made available for special circumstances. Choose an interim release build if you are directed to do so by Cisco TAC or by the recommendations of a release note. Interim builds are not fully regression-tested. Therefore, you should make plans to migrate to the next maintenance release as soon as it becomes available.
-
-
-
Consider the minimum memory requirements.
Use the Cisco IOS Planner tool on CCO:
http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/Software/Iosplanner/Planner-tool/iosplanner.cgi?
You can select the router platform, Cisco IOS Software release, and software feature set in any order. The remaining choices are refreshed in the tool. As soon as you have selected a specific release, the minimum memory requirements are displayed for both RAM and Flash memory.
-
Consider the caveats present in the release.
-
Consult the list of bugs .
Use the Bug Navigator tool on CCO to search for known bugs:
http://www.cisco.com/support/bugtools/bugtool.shtml
You can search for bugs based on a description, feature set, IOS release, or general search. BugIDs are displayed, along with information about Cisco IOS Software release numbers with bug fixes.
-
Consult the release notes.
Begin by finding a specific major release number in the Cisco IOS Software Configuration section of CCO:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/
Then select either the Release Notes or Caveats link to read about resolved and open caveats with a Cisco IOS Software release number.
-
EAN: N/A
Pages: 185