Lesson10.Troubleshooting
Lesson 10. TroubleshootingXsan will not mount any volume that has the same name as any existing volume or folder located at /Volumes/. Unlike some mounting mechanisms that automatically resolve name conflicts (for example, the Finder appends characters to each mounted volume name), the Xsan backend agent simply won't mount the volumes. To avoid this issue, create a unique name for each volume to be mounted. An Xsan volume can't be renamed in the Finder. You can't change the name of a mounted Xsan volume via the Finder. If you try, you get a message saying the name you've typed cannot be used, even if it is an acceptable Xsan volume name. To rename an Xsan volume, you must use Xsan Admin to reinitialize the volume. Mismatched optical transceivers (GBICs) can cause Fibre Channel communication errors and degrade SAN performance. To ensure good performance, use identical transceivers (same manufacturer and model number) on both ends of your Fibre Channel cables. cvadmin cannot list FSS. If you get the response "Cannot list FSS - reason -Bad file descriptor" when you run the cvadmin tool, make sure you are using the tool as the root user. Either log in as the root user or use the sudo command to run the tool. For example: $ sudo ./cvadmin After updating to 10.3.8, Xsan is disabled. If you're running Xsan and just installed Security Update 2005-002, you may come across an issue where the Xsan file system becomes disabled and won't start up. This happens because this security update overwrites the hostconfig file in the /etc directory, which removes the command to start the Xsan file system. To resolve this issue, modify the hostconfig file as follows:
Estimating metadata storage requirements To estimate the amount of space required for Xsan volume metadata, you can assume that 10 million files on a volume will require roughly 10 GB of metadata on the volume's metadata storage pool. LUNs can't be added to metadata and journaling storage pools. You can't add LUNs to a storage pool that is already being used to store journal data or metadata. This applies to any storage pool set to be used for "Journaling and metadata only" or "Any data." If you try to drag a LUN to a metadata or journaling storage pool, no insertion point appears. To check the data types a storage pool is used for, perform the following steps:
Xsan Admin lists duplicate LUNs. If you are using mismatched versions of Xserve RAID firmware and the RAID Admin application, you might see duplicate LUNs listed in the LUNs pane in Xsan Admin. To remove duplicate LUNs, perform the following step:
Store metadata on first or second storage pool. To avoid file system configuration problems, store volume metadata on only the first or second storage pool in a volume (the first two storage pools listed under the volume in the Storage pane of Xsan Admin). Otherwise, your controllers might fail over and you might see messages saying "A server you are using is no longer available" when a controller restarts. To see if a storage pool is used for metadata, perform the following steps:
Assigning affinities to subfolders on the SAN The cvmkdir command allows you to assign an affinity to a directory by typing the following: $ sudo cvaffinity -k pool path The instructions in the Xsan Administrator's Guide say you can use the storage pool name for the <affinity> parameter. This is true only if the storage pool name is eight characters or less, in which case the storage pool name and the affinity name are the same. If the storage pool name is longer than eight characters, the affinity name is an eight-character name that Xsan creates based on the storage pool name, and you need to use this shorter affinity name for the <affinity> parameter. This storage pool name can be found in the configuration file for the volume located in /Library/Filesystems/Xsan/config/<volume>.cfg. Upgrading Xsan controller software If your configuration includes a standby controller, you can upgrade the Xsan software without interrupting the SAN. Xsan controller software is always compatible with the preceding version of the client software. (Controllers can be one version ahead of clients.) So, you can upgrade your controllers first, and your client computers will continue to work until it is convenient to upgrade them to the same version.
To see a list of volumes hosted by the controller, type: $ sudo ./cvadmin select To see which controller is hosting a volume:
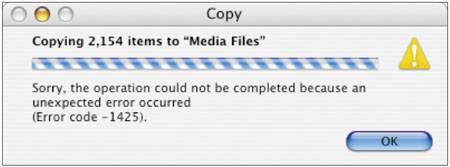
Now you can upgrade the standby controller. After slicing, some LUNs aren't listed in Xsan Admin. If you slice an array that was previously labeled for use with Xsan, you might need to remove the old label from the first slice. To see if the LUN is mounted using its old label, open Terminal and type the following: $ sudo cvlabel -l -s (The cvlabel tool is in /Library/Filesystems/xsan/bin.) This will show the old label. In the following sample output, the label is sanvol1. /dev/rdisk4/ [APPLE Xserve RAID 1.20] CVFS "sanvol1" To remove the old label, type the following: $ sudo cvlabel -u <label> where <label> is the old label (sanvol1 in the example). After you unlabel the LUN, it should appear in the LUNs pane in Xsan Admin. LUN doesn't have as much free space as expected. To make striping across LUNs possible, Xsan automatically adjusts LUN sizes to make all LUNs in a storage pool the same size as the smallest LUN in the pool. Xsan doesn't use the extra space on larger LUNs when you mix LUNs of different sizes in the same storage pool. Can't connect to a SAN computer from Xsan Admin If there is a firewall between the admin computer and the SAN computer, make sure TCP port 311 is open. User sees error code 1425 in finder when copying files to the SAN. The user is trying to occupy more space than allowed by his or her hard quota. New folders may have unexpected group ownership When creating folders on an Xsan volume, the group owner of a new folder is the primary group of the user who created itnot the group owner of the parent folder. Because of this, users who are members of a common group, but who have other primary groups, may create folders with varying ownership inside the folder of their common group. Members of this group may expect to have access to everything inside the common group's folder, but that won't be the case. To resolve the issue, log in as an administrator, select the affected folder, and Get Info. In the Ownership & Permissions section of the Info window, change the ownership to the desired group. New files and folders have read-only group ownership. When creating a new file or folder on the SAN, you will notice that the group permissions are set to "read only." This is due to the umask settings on the client computer. In order to change the setting so that file and folder creation allows the group to have read and write access, use the Terminal to alter the umask. In the Terminal, a per-user umask can be changed easily by typing the following: $ defaults write -g NSUmask -int 2 The above setting of 002 means that any new files or folders will have their group permissions set to "Read & Write." There are also third-party software applications available that will globally update the umask so that you don't have to enter the Terminal. Don't use mv command to move files to non-Xsan volumes. If you want to move files from an Xsan volume to a non-Xsan volume using the command line, don't use the mv command. Instead, use the cp command to copy the files and then delete the originals from the Xsan volume. Can't see storage via Fibre Channel connection Some Fibre Channel switches can suppress the generation of Registered State Change Notification (RSCN) messages on a port basis. This setting allows storage devices to inform hosts that it has entered the network. In some cases, if an Xsan client is restarted, a slight pause may occur throughout the entire Fibre network. This is unwanted in a video environment since it may cause dropped frames or other unexpected behavior. This suppression should be enabled only on ports connected to initiators (CPUs) and not targets (Xserve RAIDs). On Emulex switches, target ports should be set to "Targets with Stealth," and initiators should be set to "Initiators with Stealth." On QLogic switches, RSCN is disabled by enabling a feature known as I/O Stream Guard. In the following image, notice that the target port (14) is selected, and the I/O Stream Guard option is disabled. On initiator ports, also remember to disable Device Scan. QLogic-SANbox Manager 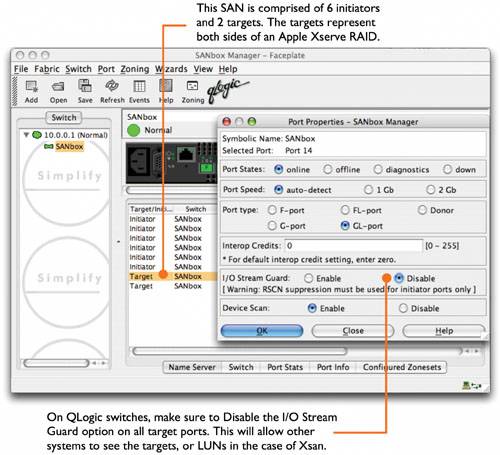 Emulex-Web Manager 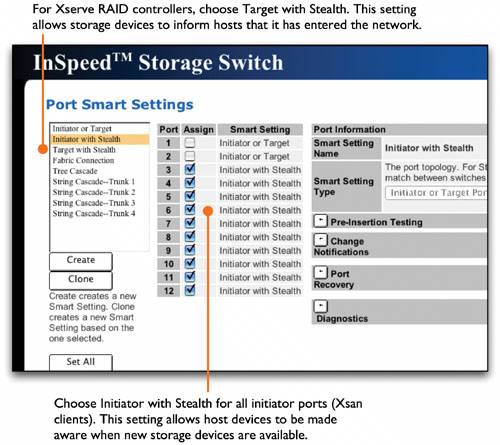 |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 120