Project Processes
As we discussed earlier, PMI defines project management as a series of processes that are executed to apply knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to project activities to meet project requirements. These processes have been organized into five groups.
The process groups are tightly linked, as the outputs from one group are the inputs to another group . Figure 1.1 shows the links between the groups. The process groups may overlap. You may begin planning the project before all of the initiation activities are complete.
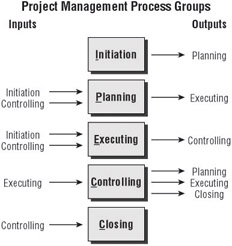
FIGURE 1.1 PMI Process Groups
As we discuss each group, notice the correlation between the process groups and the domains covered in the CompTIA Project+ exam. The process groups are the foundation of project management. You need to understand each group and how it contributes to the completion of the project.
Initiation Processes
Initiation processes include all of the activities that lead up to the authorization to start the project. These activities include such items as business need identification, high-level requirement definition, and cost justification. Because the Initiation process is an integral part of Domain 1.0 on the Project+ objective blueprint, we will take a more detailed look at the initiation process in Chapter 2, 'Project Initiation.'
Planning Processes
Planning processes are where the project goals and objectives are refined and broken down into manageable pieces of work. Project managers create time and cost estimates, and determine resource requirements for each activity.
Several other critical areas of managing a project require up-front planning. These areas include communication, risk, quality, and procurement.
| Note | The Planning process group, which is included in both Domains 1.0 and 2.0 of the exam, is undoubtedly one of the most critical stages of managing a project. For that reason Planning will be covered in detail in Chapters 3-7. |
Executing Processes
Executing processes are where the work to complete the project is done. The project manager must coordinate all the project team members as well as other resources assigned to the project.
Executing processes include the actual execution of the project plan, team development, quality assurance, and information distribution. We will examine this more closely in Chapter 8, 'Project Execution.'
Controlling Processes
Controlling processes are the activities that monitor the progress of the project to identify any variances from the project plan. Requests for changes to the project scope are included in this process. This area is also where any corrective action will be taken.
Other areas of the Controlling process group are cost control, quality control, performance reporting, and risk control. In Chapter 9, we will spend considerable time discussing the various methods for monitoring progress, specifically change control and quality control.
Closing Processes
The closing processes drive the formal acceptance of the project work and provide a means to fold the product into the ongoing organization structure.
Closing processes include sign-off, archive of project documents, turn over to a maintenance group, release of project team members, and review of lessons learned. Although some of these activities may seem fairly straightforward, several areas deserve close attention. Chapter 10, 'Project Closure,' will explore the last stages of an IT project and how they can differ from other projects.
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 156