2.8 Fleet Management
2.8 Fleet Management2.8.1 IntroductionA large corporation wants to track all its vehicles in use. It therefore sends out an RFP to fleet management companies to introduce a new service for automatic vehicle detection systems, in order to make sure that employees do not misuse the cars. Part of the new service requires a tight integration into a satellite navigation system, connection to all gas stations , and a fleet management system that is able to track the use of the cars . In the past, employees used company cars for private excursions, and used the company gas card to refill their private cars. It was never clear which car was used by whom and for how long. The new system is designed to cut down on employee abuse. Additionally, in case of emergencies, accidents, and breakdowns, fleet management would be able to react quickly and efficiently . 2.8.2 The PresentIf we look at the possibilities today, it becomes quite clear that the required technology is available. GPS, mobile Internet, and fleet management software packages can track the location and the use of the car. Due to the different technologies used for all these components , it is quite expensive to integrate them and make them work efficiently. The problem becomes apparent if you look at the number of vehicles that need to be tracked. If we talk about five or ten cars, it would be almost possible to track them manually, but fleet management service companies often have thousands of vehicles in operation and rented out to many different companies by a fleet management service provider. In order to make this system work, the information would need to flow from the car via the satellite to the fleet management service provider, which in turn offers an extranet that allows the company to check the status of each car. Although not very common yet, telemetric data could also be sent with the location to make sure that the fleet management service provider is able to track repairs and mileage of the cars out in the field. This would require adding lots of technology to the cars, as very few support this type of integrated information exchange today. To realize such a fleet management service, it would be necessary to create an online service where companies can register all cars they use. There are several problems with this approach. First, there is no standard way to describe vehicles. Every manufacturer uses a similar, but not identical way of providing a description of a car. Therefore, the company needs to create its own vocabulary to describe the vehicles in use. This vocabulary can be used to build a catalogue , where one could be sure that every item is described in a very precise way. Such a system could be very expensive, even for a large corporation, which may outsource the whole operation to reduce the cost significantly. Once all cars are registered, employees can book vehicles based on a set of specifications provided by the company. This could range from car transportation between two offices to doing a roadshow with large trucks . The system would check which vehicles are available and their proximity to the desired location. It does not really help if a car in South Africa is available and you need one at the airport in Milan, Italy. The Web site could provide not only a set of vehicle specifications, but add a different view by providing use cases, meaning that an employee does not select the type of car, but the type of situation he or she is in, and the Web site will select the vehicle accordingly . Once the employee has decided what he needs the vehicle for, the exact route can be specified by an online route planner. This would enable the employee to calculate gas costs and provide the duration of the travel. Today, the information can be stored on a PDA or printed out, for the convenience of the driver. If the vehicle has a built-in navigation system, the employee can re-enter the data and be guided by that system. Today, it is not possible to transfer the data between an online system and a car navigation system automatically. The employee picks up the car and sets off on the journey. With GPS tracking enabled, the vehicle can be tracked. This way, fleet management could offer additional help if the driver hits a traffic jam or has a breakdown. En route, drivers would be able to refill the fuel tank using a gas card, with the money being deducted automatically from the account of the company. In theory, this works very well, because it is limited to the car that the employee is using. In reality, this means that the drivers may use the card to buy fuel for something other than the company car. Although the cashier at the gas station should check the license plate, this is often not done thoroughly; hence, the high rate of fraud. It is difficult to overcome this problem today. Once the vehicle has arrived at the destination, telemetric data could be sent back to the fleet management for statistical reasons. Imagine lots of employees travel from Milan to Florence every day for business reasons. You would like to know which time is the best to get there, how long it takes at a certain time of day, and how much it costs to get there. By collecting this telemetric data and creating the statistics, it would be possible to determine that it is not a good idea to leave Milan at nine o'clock in winter, because the motorway is often very foggy. In summer, it is okay to leave at nine, because most people are already at work and the motorway is free. Many other statistics can be created, to make the use as efficient as possible. Another example could be that ten people are driving from Milan to Florence in the morning, but all use their own cars. If you can find three people that leave at the same time and return at the same time, you could have them car pool, thus reducing costs heavily. The complexity of this scenario makes it impossible to introduce such a solution today, although most components are available and could be interconnected . 2.8.3 The FutureThe solution in the near future will look quite different. Several companies are working on introducing new technologies to make life easier for fleet management. New cars will all include an online connection either to the Internet or to a dedicated wireless connection to a server. The technology to do so is becoming cheaper every day. All vehicles need to be equipped with mobile connectivity that connects them securely to a telemetrics service. This service collects data and provides the information to the fleet management service. The telemetrics service is responsible for maintaining the connection between the vehicles and the fleet management within the company. This includes operating the satellites and transforming the data that comes from the car. As companies often have cars from different manufacturers, and no standard has been set on how the information should be transmitted, the data is structured differently for every car type or manufacturer. The role of the telemetrics service is to convert the data from the car and present it in a unified way to the fleet management. The gasoline payment service is an automated gas station that detects which car is filling up. This can be done via a camera that takes a picture of the number plate and compares it to the database of the fleet management service and makes sure that only the cars that are eligible can pay through the corporate gasoline card. More advanced systems will include a Bluetooth service that enables the gas station to communicate with the car, meaning that the car can tell what type of gas it requires and send the company credit card information electronically . The Fraunhofer Gesellschaft [10] in Germany is even a step ahead by providing robots that fill up the gas automatically. By combining these new technologies, vehicles could be served faster and more efficiently.
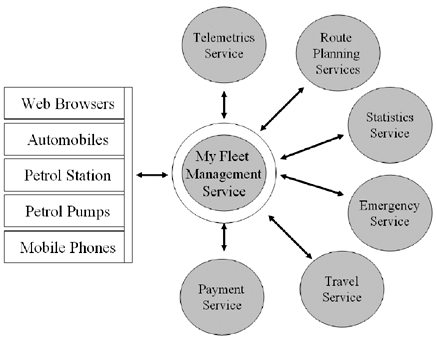
The central fleet management service consists of an employee Web front-end, which allows employees to perform the required transaction for booking a vehicle and for getting more information about the service. Employees can register for the service or can be automatically eligible for the service because of the role the employee has in the company. More importantly, the fleet management service provides many administrative functions for managing the fleet and providing information to the users. Tightly connected to the fleet management service is the route planning service that will not only help employees find their way easily, it is also the basis for statistics. The statistics service takes all the data, puts it into a data warehouse, and provides management statistics to the fleet management service. The travel service provides the fleet management service with information about delays, traffic jams, important news, and other related information. This would mean a huge reduction in effort and lower the entry barrier significantly, if the fleet management service portal ensures that the information is securely stored and only authorized systems and people are allowed to see it. Multiple access for the employees to the fleet management portal needs to be guaranteed . This means that employees can use the service via the Web, the phone, fax, or any other means of communication. The same is true for the information that comes from the fleet management system. Depending on where the employee is, the information should be sent as e-mail, SMS, voicemail, fax, or any other means of communication. 2.8.4 SummaryLet's take a look at the me-centric features of this scenario. Broadband access is not a requirement here. Although everything needs to be connected, the amount of data that is flowing back and forth is minimal compared to the other scenarios. Telematics data can be easily transmitted in XML files over low-bandwidth networks. The biggest issue to solve is coordinating a large number of vehicles and their users (see also Figure 2.9). While the company does not need a car for each employee, it can reduce the number of vehicles drastically with good fleet management. Therefore, agents needs to collaborate and find out who should use which car when. Each employee who needs a car should also have an agent that makes car pool reservations on his or her behalf based on the schedule of the employee. Figure 2.9. Fleet Management Ecosystem To make sure that employees use the cars only for the intended business travel, the route can be planned by the coordination agent, which allows the user to predict the time of the journey and when the next person can use the car. By using the GPS to track the car, it is also possible to see if the employee is taking the shortest route to the business meeting or if the employee is going some other routes to do some other things. This can also be used for filling up the car with gas. The telemetrics system sends back information about gas usage and allows an intelligent agent to look out for gas stations in the vicinity. The prices are prenegotiated, and the driver can stop at the gas station and fill up the car. The driver does not have to pay personally . As soon as he leaves , the company pays for the amount of fuel that was bought. This ensures that only company cars are filled up. |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 88