Components of a Data Warehouse
Inmon, Ralph Kimball, and Doug Hackney have published several books articulating traditional data warehouse architectures and construction processes (see Appendix A). Following are the four layers required to construct a data warehouse, which are critical to understanding SAP Business Information Warehouse architecture (see Figure 1-2).
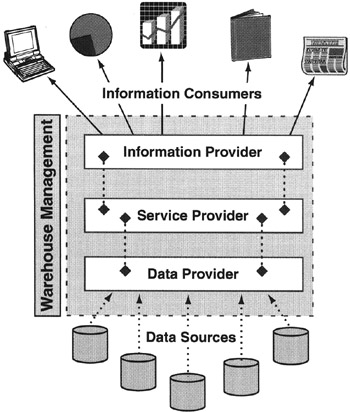
Figure 1-2: The Architectural Layers of a Data Warehouse.
-
Data Provider
-
Service Provider
-
Information Consumer
-
Data Warehouse Management
Data Provider Layer
The Data Provider layer is the primary gateway to the data sources (OLTP applications or other). Major tasks performed at this layer provide an environment in which to construct subject-oriented data analysis models. Metadata (data about the data) is pulled in to a data warehouse environment from its data sources. Extraction, Transformation, and Transport services fetch data from data sources, qualify, perform value-added data manipulation, and push data out to data warehouse data objects. Key services performed at this layer are the following:
-
Data Transport
-
Data Transformation
-
Data Cleansing
-
Data Extraction
-
Subject Models
Service Provider Layer
The Service Provider layer is responsible for managing and distributing data objects across the enterprise to support business intelligence activities in a controlled and secured fashion. At this layer, data is further transformed for specific data analysis tasks such as drill-down analysis and predefined reports integration with third-party subscribed data. Moreover, data/text-mining data services transform data into knowledge by applying analytical techniques or combining structured and unstructured data, such as building a Web-centric environment by authoring Web pages to merge product sales data, charts, graphs, and product images. This layer is very complex within the data warehouse architecture. Key services performed at this layer are the following:
-
Analytical Applications Integration
-
Data Distribution
-
Data Profiling
-
Data Partitioning
-
Information Authoring
-
Data Consolidation
-
Data Staging
-
Data Storage
Information Consumer Layer
The Information Consumer layer accesses information objects from a data warehouse. Information delivery services, provided by service providers, must be robust enough to handle large data volumes and multimedia objects. Keep in mind that not all end users have the same needs. Some users simply want to look at a list of numbers. Some may want to have push-button models to see charts and graphs, and analysts may need access to large volumes of data to do extensive data analysis. Data access and delivery services must be robust enough to handle all such scenarios. Key services performed at this layer are the following:
-
Information Presentation
-
Search Engines
-
End-User Data Synchronization
-
Data Conversions
-
Information Access APIs
-
Information Consumer Profiling
-
Global Catalogs
-
Information Delivery
Data Warehouse Management Layer
The Data Warehouse Management layer provides services to manage all data objects in all layers. Additional services at this layer include component installation, monitoring, tuning, scheduling, networking, database operations, and component problem tracking/analysis that can be performed globally. Key services performed at this layer are the following:
-
Governing Services
-
Track Resource Utilization
-
Audit and Controls
-
Scheduling
-
Client Profile
-
Multi-Tiered Models
-
Warehouse Operations
-
Source/Target Management
-
Data Dictionary
-
Development Management
-
Hardware/Software
-
Security
-
Metadata
| Team-Fly |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 174
- The Second Wave ERP Market: An Australian Viewpoint
- Context Management of ERP Processes in Virtual Communities
- Intrinsic and Contextual Data Quality: The Effect of Media and Personal Involvement
- A Hybrid Clustering Technique to Improve Patient Data Quality
- Relevance and Micro-Relevance for the Professional as Determinants of IT-Diffusion and IT-Use in Healthcare