Hyphenating Your Documents
You can improve the appearance of your document by hyphenating words at the ends of the lines. Once hyphenated, text that is not justified will be less ragged at the margin, and justified text will have more uniform spacing between the characters. You can hyphenate text in one of three ways.
- You can have Word automatically hyphenate your entire document.
- You can have Word hyphenate text but allow you to confirm the placement of each hyphen.
- You can manually insert various types of hyphen characters.
NOTE
You should hyphenate your document after you finish editing, formatting, and using the other proofing tools, because these operations can change the position of line breaks. Also, if you later change features of the page design that affect line breaks, such as the margins, you might need to hyphenate your document again.
Hyphenating Your Document Automatically
You can let Word hyphenate the document in the active window by pointing to Language on the Tools menu and then choosing Hyphenation to open the Hyphenation dialog box:
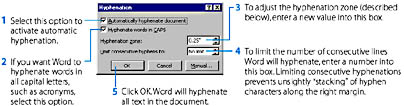
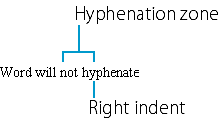
The hyphenation zone controls the number of hyphenations that Word performs. It works as follows: When Word encounters a word that extends beyond the right indent, it must decide whether it can wrap the word (that is, move the entire word down to the next line) or whether it should hyphenate the word. If wrapping the word would leave space at the end of the line that is narrower than the hyphenation zone (.25 inch wide by default), Word wraps it:
CAUTION
When you select the Automatically Hyphenate Document option, Word will hyphenate your entire document even if you have selected only a portion of the document.
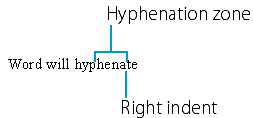
If, however, wrapping the word would leave a space wider than the hyphenation zone, Word hyphenates it:
SEE ALSO
For information on applying the Don't Hyphenate and other paragraph formatting features, see "Applying Paragraph Formatting Directly." For information on applying the Do Not Check Spelling Or Grammar feature to a block of text, see "Marking the Language."
Choosing a wide hyphenation zone reduces the number of hyphenations that Word must perform, but it increases the raggedness of the margin (or makes the intercharacter spacing less uniform in justified text).
TIP
You can assign a paragraph the Don't Hyphenate paragraph formatting to exclude it from automatic hyphenation or hyphenation with confirmation (discussed in the next section). In contrast, applying the Do Not Check Spelling Or Grammar language formatting, mentioned near the beginning of the chapter, blocks all proofing (spelling, grammar, and hyphenation).
Hyphenating Your Document Using Confirmation
If you want Word to hyphenate your document but allow you to confirm the placement of each hyphen, do the following:
- If you want to hyphenate your entire document, place the insertion point anywhere in the document. If you want to hyphenate only a portion of your document, select that portion.
- Point to Language on the Tools menu, and then choose Hyphenation to open the Hyphenation dialog box:
- In the Hyphenation dialog box, set the hyphenation options you want, but make sure that the Automatically Hyphenate Document option is deselected. These options were explained in the previous section.
- Click the Manual button. Word activates Print Layout view and begins looking for possible hyphenations. When Word is finished hyphenating, it returns you to your original document view.
- Whenever Word encounters a word that requires hyphenation, it displays the Manual Hyphenation dialog box, which shows the word and the proposed position of the hyphen, together with all other possible hyphen positions in the word:
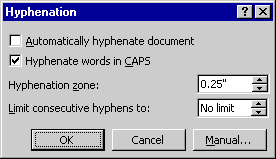
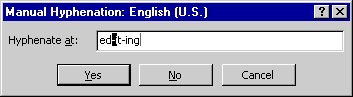
Each possible hyphenation position is marked with a hyphen. The proposed hyphenation position is marked with a blinking highlight in addition to the hyphen. The position of the right indent is marked with a vertical line. Word also carries out the proposed hyphenation in the document and highlights the hyphen character.
You should now do one of the following:
- To hyphenate the word at the proposed position, just click Yes.
- To hyphenate the word at a different position (say, to avoid a hyphen after only the first two letters of a long word, as in the example), use the Left or Right arrow key to move the blinking highlight to that position, and then click Yes.
- To skip hyphenating the word, click No. The word will be wrapped rather than hyphenated.
Inserting Hyphen Characters Manually
When Word hyphenates a word, it inserts a special character known as an optional hyphen. If a word containing an optional hyphen is shifted so that it no longer falls at the end of a line, the hyphen is not printed. However, the optional hyphen remains within the word, and it will reappear and allow the word to be broken if the word shifts back to the end of a line.
You can manually insert optional hyphens, as well as several other related special characters, as shown in Table 10-2.
TIP
If you click the Show/Hide ¶ button on the Standard toolbar, Word displays on the screen all the characters listed in Table 10-2. To display optional hyphens only, choose Options from the Tools menu, click the View tab, and select Optional Hyphens in the Formatting Marks area.