Monitoring and Troubleshooting
| Once file-sharing services are enabled, you'll need to monitor them from time to time and ensure they are functioning properly. If not, you should know how to take corrective action. Monitoring File-Sharing ProcessesYou can monitor file-sharing processes by using Activity Monitor and by examining the log files. For general troubleshooting of SMB or FTP service, use Activity Monitor to watch launchd start daemons. Choose All Processes Hierarchical from the pull-down menu in Activity Monitor. You might need to increase Activity Monitor's update frequency using the Monitor menu. The log files for nmbd, smbd, and ftpd are /var/log/samba/log.nmbd, /var/log/samba/log.smbd, and /var/log/ftp.log, respectively. You can get more output from ftpd, nmbd, or smbd by invoking any of them with the d option. You do that by editing the files under /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/. For example, if you change the ftp.plist ProgramArguments key from keyProgramArguments/key array stringftpd/string stringl/string /array to keyProgramArguments/key array stringftpd/string stringl/string stringd/string /array the next time ftpd executes, it will write more detailed output to /var/logs/ftp.log. The d options to nmbd and smbd allow you to specify a debug level by putting an integer after the d. A level of 3 should give you as much detail as you need. The following figure shows ftpd debug (d) output to ftp.log. 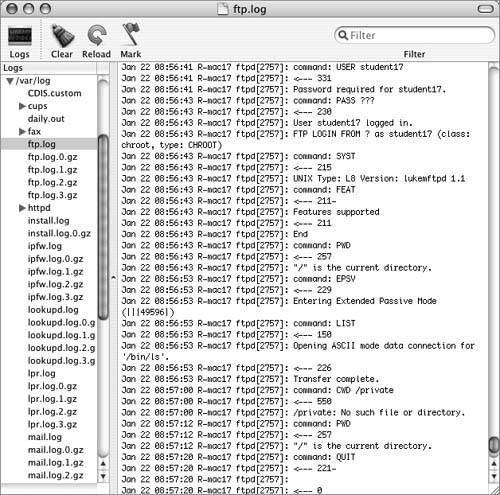 You can use the log files to debug AppleFileServer. Before it quits, AppleFileServer writes to the log /Library/Logs/AppleFileService/AppleFileService. In addition, configd writes messages to the system log when it starts AppleFileServer. Troubleshooting Connection FailuresIf users cannot connect to your system, you can take several steps to troubleshoot the problem. First, determine whether the problem is specific to one protocol. If more than one protocol is affected, you should troubleshoot your network connection as described in Lesson 25, "Resolving Network System Issues." If the problem is specific to AFP, determine how many other users are already connected. Mac OS X allows up to ten users to connect to your computer simultaneously using Personal File Sharing. If you need to let more users connect, you can upgrade to the unlimited-client version of Mac OS X Server. If you click the Firewall button in the Sharing pane of System Preferences, you can add other ports and control their firewall settings. For any of the file-sharing protocols, if users cannot connect, verify that the protocol's port is enabled in com.apple.sharing.firewall.plist. You can also get a real-time view of the current firewall settings by typing sudo ipfw list. SMB-Specific TroubleshootingIf Windows File Sharing (SMB) clients cannot connect to your computer after you upgrade to a newer version of Mac OS X, change the password on each account on your computer. You should also verify that their account is enabled for Windows File Sharing in Sharing preferences. It might take nmbd a few minutes to stop when you stop Windows File Sharing using the Sharing pane of System Preferences. The testparm command checks the smb.conf file and reports errors. If you then press Return, it lists all configuration parameters, including defaults not specified in smb.conf, as shown in the following text. testparm Load smb config files from /private/etc/smb.conf Processing section "[printers]" Loaded services file OK. Invalid combination of parameters for service printers. Level II oplocks can only be set if oplocks are also set. Server role: ROLE_STANDALONE Press enter to see a dump of your service definitions # Global parameters [global] dos charset = CP437 unix charset = UTF-8-MAC display charset = UTF-8-MAC workgroup = RECOVERY server string = instructor auth methods = guest, opendirectory map to guest = Bad User passdb backend = opendirectorysam, guest guest account = unknown client NTLMv2 auth = Yes client lanman auth = No client plaintext auth = No defer sharing violations = No os level = 8 local master = No wins server = 10.0.1.25 brlm = Yes printer admin = @admin, @staff vfs objects = darwin_acls [printers] path = /tmp printable = Yes browseable = No The workgroup name is case-sensitive. If, for example, some of your computers are assigned to Workgroup and others are assigned to WORKGROUP, you will see two workgroups in your browser window. On some versions of Windows, a user who connects to a remote computer using SMB must have the same short name on the remote computer as on the local computer. Mac OS X supports these Windows network authentication methods:
|
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 258