11.7 Services Provided in the IEEE 802.11 Family
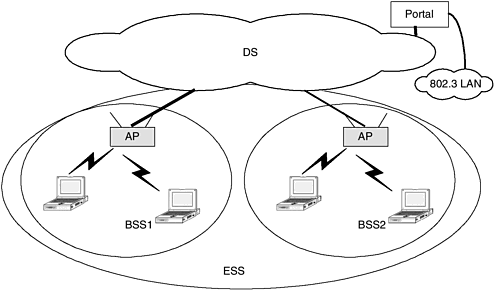
| In this section, we shall provide an overview of the various services expected of an IEEE 802.11 system. Some services are required in all stations , including the access point, and a few of them are very specific to the infrastructure mode. There are two categories of services provided in an IEEE 802.11 system. The first category is called station services, and the second category is the distributed station services (DSS). 11.7.1 Station ServicesServices that are common to all stations are referred to as station services. All IEEE 802.11 family devices, including the access point, will execute these services, and it does not matter whether it is the infrastructure mode or independent mode. Stations services support establishing basic connectivity to wireless LANs, which helps provide functions similar to that of plugging into a wired LAN port. There are four station services defined in IEEE 802.11 systems. Authentication and deauthentication are two station services similar to the function of physically connecting to the wired network like the LAN. These two services allow the IEEE 802.11 user to be authorized to use the WLAN services, and unauthorized users can be deauthenticated to preclude any services. Two other station services are privacy and data delivery. Privacy provides the security of using a wired LAN network within a building by encrypting data over the air. Data delivery services ensure that data are transported reliably over the wireless medium. 11.7.2 Distributed Station ServicesThe other category of services provided in the IEEE 802.11 family has no equivalent in wired LANs. This is known as the distribution system services (DSS). There are five different services, and these services are provided across a distribution system mentioned earlier. This requires the presence of an access point as one of the key elements, which communicates with the distributed system. The five different DSSs are association, disassociation, distribution, integration with wired network like LANs, and reassociation. The wireless station uses the association and disassociation services to gain access and remove access to WLAN services. Distribution is the process of using the backbone distributed system to update information about wireless stations and deliver packets to the appropriate destination. Integration with wired network like LANs is a feature to connect the wireless systems to the wired network. For example, users may be using an IEEE 802.11 family system and may send messages to their colleagues who are connected to the wired LAN like the Ethernet. Special functions called portals may exist as part of the access point. These portals are used to convert between IEEE 802.11 frames and the wired LAN frames and vice versa. A representation of the portals along with the IEEE 802.11 family network is shown in Figure 11-7. Figure 11-7. The entire IEEE 802.11 architecture, including connectivity to IEEE 802.3 network. |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 164