Chapter 16: BIND Configuration
|
The configuration of the Domain Name Service is a large topic — indeed, entire books have been devoted to the subject. This chapter is not an exhaustive guide to DNS or BIND; it is assumed that you have a basic knowledge of both. Rather, the chapter explains the use of the Red Hat Linux BIND Configuration Tool to create BIND server zone files. The BIND Configuration tool creates the /etc/named.conf configuration file and the zone configuration files in the /var/named directory each time you apply your changes.
| Note | Do not edit the /etc/named.conf configuration file. The BIND Configuration Tool generates this file after you apply your changes. If you want to configure settings that are not configurable using the BIND Configuration Tool, add them to /etc/named.custom. |
The BIND Configuration Tool requires the X Window System and root access. To start the Bind Configuration Tool, go to the Main Menu Button (on the Panel) > Server Settings > Domain Name Service or type the command redhat-config-bind at a shell prompt (for example, in an XTerm or GNOME terminal).
The BIND Configuration Tool configures the default zone directory to be /var/named. All zone files specified are relative to this directory. The BIND Configuration Tool also includes basic syntax checking when values are entered. For example, if a valid entry is an IP address, you are allowed to type only numbers and the dot (.) character into the text area.
The BIND Configuration Tool allows you to add a forward master zone, a reverse master zone, and a slave zone. After adding the zones, you can edit or delete them from the main window as shown in Figure 16-1. After adding, editing, or deleting a zone, you must choose File > Apply in order to write the /etc/named.conf configuration file and all the individual zone files in the /var/named directory. Applying your changes will also cause the named service to reload the configuration files. You can also choose File > Quit and click Save and quit.
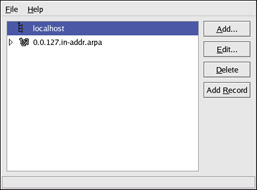
Figure 16-1: Adding a forward master zone
Adding a Forward Master Zone
To add a forward master zone (also known as a primary master), click the Add button, select Forward Master Zone, and enter the domain name for the master zone in the Domain name text area. A new window as shown in Figure 16-2 will appear with the following options:
-
Name — Domain name that was just entered in the previous window.
-
File Name — File name of the DNS database file, relative to /var/named. It is preset to the domain name with .zone appended to it.
-
Contact — Email address of the main contact for the master zone.
-
Primary Nameserver (SOA) — State of authority (SOA) record. This specifies the nameserver that is the best resource of information for this domain.
-
Serial Number — The serial number of the DNS database file. This number must be incremented each time the file is changed, so that the slave nameservers for the zone will retrieve the latest data. The BIND Configuration Tool increments this number each time the configuration changes. It can also be incremented manually by clicking the Set button next to the Serial Number value.
-
Time Settings — The Refresh, Retry, Expire, and Minimum TTL (Time to Live) values that are stored in the DNS database file.
-
Records — Add, edit, and delete record resources of type Host, Alias, and Name server.
The configuration shown in Figure 16-2 creates the following entry in /etc/named.conf:
zone "forward.example.com" { type master; file "forward.example.com.zone"; }; 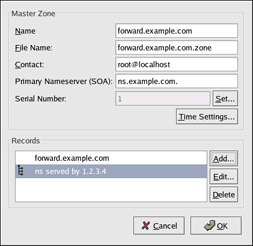
Figure 16-2: Adding a reverse master zone
It also creates the file /var/named/forward.example.com.zone with the following information:
$TTL 86400 @ IN SOA ns.example.com. root.localhost > 2 ; serial
28800 ; refresh 7200 ; retry 604800 ; expire 86400 ; ttl ) ns IN NS 1.2.3.4
After configuring the forward master zone, click OK to return to the main window as shown in Figure 16-1. From the pull-down menu, choose File > Apply to write the /etc/named.conf configuration file, write all the individual zone files in the /var/named directory, and have the daemon reload the configuration files.
|
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 278