Cisco IDS Sensor Appliances
| [ LiB ] |
You must consider several factors when selecting a sensor. These factors include the overall size and number of networks you need to monitor, the speed at which those networks operate , and the option of using IDS modules instead of standalone IDS appliances.
Cisco offers several different sensors; this section discusses the latest appliances Cisco has to offer. Sensors come in one of two forms, a dedicated appliance or a module that inserts into a router or a switch. The sensors within the 4200 Series are all standalone appliances used to perform only one function, monitor traffic. Cisco offers the IDS-4215, IDS-4235, IDS-4250, and the IDS-4250-XL. Your network size will determine which sensor you need. The following sections describe each of the 4200-series sensor appliances in more detail.
| | Cisco's older tried-and-true sensors called the NetRangers are being discontinued and replaced with the newer slimmer profiles of the most recent 4200 series. |
IDS-4215 Appliance
The Cisco IDS-4215 appliance can monitor up to 80Mbps worth of traffic, and it is Cisco's smallest appliance. Like most sensors within the 4200 series, the IDS-4215 has only a 1RU form factor and runs on the Linux operating system. The base model IDS-4215 comes with only two interfaces, int0 (sensing) and int1 (command and control). You can expand this model with a four-port Fast Ethernet (4FE) card to host additional sensing interfaces.
Here are the standard IDS-4215 highlights:
-
80Mbps sensing performance
-
One sensing interface (a 10/100BASE-TX)
-
One control interface (a 10/100BASE-TX)
-
1RU form factor
-
Optional expansion card 4FE to enable support for four additional 10/100BASE-TX interfaces
| | The 4215 is intended for monitoring T1/E1 and T3 network connections but can be used anywhere . Just remember that it can handle only 80Mbps. |
Figure 6.4 shows a 4215 sensor with the 4FE expansion card installed.
Figure 6.4. IDS-4215 back panel.
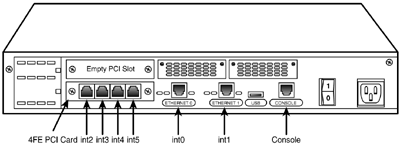
Table 6.1 lists and describes some of the important IDS-4215 interfaces.
Table 6.1. IDS-4215 Interfaces
| Interface | Description |
|---|---|
| int0 | Sensing (sniffing) interface |
| int1 | Command and control (management) interface |
| int25 | Optional sensing (sniffing) interface with the 4FE expansion card installed |
| Console | Serial console port for configuration |
| | Don't forget the sensing interface/port is always int0. Int1 is for the command and control interface. Also, notice that int0 is the first port on the left. |
IDS-4235 Appliance
The IDS-4235 sensor can monitor up to 250Mbps of traffic and is directed at the multiple T3 marketplace . In addition, the 4235 is capable of monitoring all sorts of traffic lines. It can monitor 10/100/1000Mbps networks, but is always limited by the 250Mbps performance capability. The 4235 also has monitor and keyboard ports to allow configuration without a remote management station.
Here are the standard IDS-4235 highlights:
-
250Mbps sensing performance
-
One sensing interface is 10/100/1000BASE-TX
-
One control interface is 10/100/1000BASE-TX
-
1RU form factor
-
Monitor and keyboard ports
-
Optional redundant power supplies
-
Optional expansion card 4FE to enable support for four interfaces
Figure 6.5 displays a 4235 sensor.
Figure 6.5. IDS-4235 back panel.
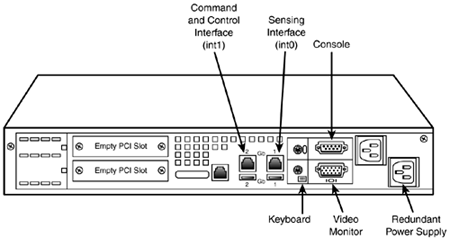
Table 6.2 lists and describes some of the important IDS-4235 interfaces.
Table 6.2. IDS-4235 Interfaces
| Interface | Description |
|---|---|
| int0 | Sensing (sniffing) interface |
| int1 | Command and control (management) interface |
| Console | Serial console port for configuration |
| USB | Universal Serial Bus (unused) |
| Mouse | For an external mouse (unused) |
| Keyboard | Uses a keyboard to configure the sensor |
| Monitor | Uses a monitor to manage the sensor |
| | On the 4235, notice that the int0 is in a different location than on the 4215; on the 4235, int0 is the port furthest to the right. |
IDS-4250 Appliance
The IDS-4250 can monitor twice the amount of traffic than can the IDS-4235, at a rate of 500Mbps. You can expand the 4250 with the optional interface 1000BASE-SX to monitor fiber lines or add the 4FE card to expand the number of 10/100BASE-TX network cards.
Here are the standard IDS-4250 highlights:
-
500Mbps sensing performance
-
One sensing interface (a 10/100/1000BASE-TX)
-
One control interface (a 10/100/1000BASE-TX)
-
1RU form factor
-
Monitor and keyboard ports
-
Optional redundant power supplies
-
Optional expansion card 4FE to enable support for four interfaces
Figure 6.6 displays an IDS-4250 sensor; Table 6.3 lists and describes some of the important IDS-4250 interfaces.
Figure 6.6. IDS-4250 back panel.
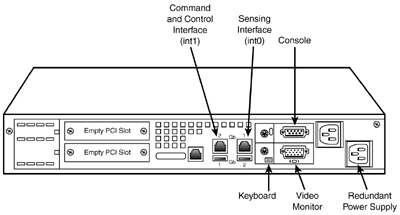
Table 6.3. IDS-4250 Interfaces
| Interface | Description |
|---|---|
| int0 | Sensing (sniffing) interface |
| int1 | Command and control (management) interface |
| Console | Serial console port for configuration |
| USB | Universal Serial Bus (unused) |
| Mouse | For an external mouse (unused) |
| Keyboard | Uses a keyboard to configure the sensor |
| Monitor | Uses a monitor to manage the sensor |
IDS-4250XL Appliance (Accelerator Card)
The IDS-4250-XL model is virtually the same as the IDS-4250 with the exception of the addition of the IDS Accelerator (XL) card. This card adds two sniffing interface slotsint2 and int3and gives you one full Gigabit line-rate performance. Once the IDS XL card is installed, the original int0 monitoring interface is converted to a dedicated TCP reset interface; int2 and int3 do not support this functionality.
| | For the exam, remember that the XL card only operates if installed in the upper Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) slot. |
| | If you have an IDS-4250 and you add the XL card, then you create an IDS-4250-XL. With the IDS-4250-XL sensor, Cisco just gives you the option of buying an IDS-4250 with the XL card already installed and preconfigured. |
Here are the standard IDS-4250-XL highlights:
-
1000Mbps sensing performance
-
One TCP reset interface, at 10/100/1000BASE-TX
-
One control interface, at 10/100/1000BASE-TX
-
One XL accelerator card
-
1RU form factor
-
Monitor and keyboard ports
-
Optional redundant power supplies
-
Optional expansion card 4FE to enable support for four interfaces
Figure 6.7 displays an IDS-4250-XL sensor.
Figure 6.7. IDS-4250-XL back panel.
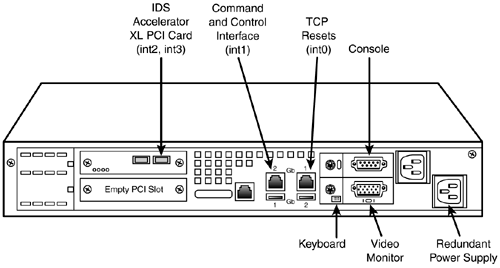
Table 6.4 lists and describes the important IDS-4250-XL interfaces.
Table 6.4. IDS-4250-XL Interfaces
| Interface | Description |
|---|---|
| int0 | TCP reset interface |
| int1 | Command and control (management) interface |
| int23 | Sensing (sniffing) interfaces |
| Console | Serial console port for configuration |
| USB | Universal Serial Bus (unused) |
| Mouse | For an external mouse (unused) |
| Keyboard | Uses a keyboard to configure the sensor |
| Monitor | Uses a monitor to manage the sensor |
| | The IDS-4250-XL has a dedicated TCP reset interface because it cannot send TCP resets on the normal monitoring ports. The TCP reset interface is int0 on the IDS-4250-XL. |
| | Other IDS 4200 series models can operate IDS version 4.0 software. Cisco has discontinued selling these models of sensors, however, and states that they have reached their end-of-sale status. Some of these models include the 4210, 4220, and the 4230. |
| [ LiB ] |