8.6. Asynchronous Transfer Mode
| < Day Day Up > |
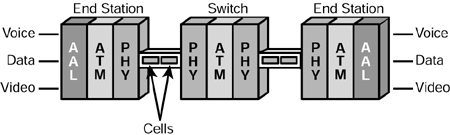
| Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) is a method of digital communication that is capable of very high speeds. It is used to transport voice, video, data, and images. ATM can be used as the basis for both LAN and WAN technologies. Separate networks are often used to carry voice, data, and video information, largely because these traffic types have different characteristics. With ATM, separate networks are not required. ATM is the only standards-based technology designed from the beginning to accommodate the simultaneous transmission of data, voice, and video. In an effort to combine LAN communications with telecommunications, ATM is gaining increasing favor. ATM, which is also the prevailing wide area backbone technology in public data networks, provides the potential for creating a single set of hardware and communications protocols for both. Standard ATM communication was based on a small (53-byte) packet size that posed a significant technical challenge when used to transfer data files. Additionally, ATM packet dropping, which had no serious consequences when transferring voice or video data, was not acceptable for data communication. To address these issues, a variation of ATM Asynchronous Adaptation Layer 5 was designed to provide scalable system-to-system communication for computer data. A gateway interface connects Fibre Channel switches to an ATM network to extend the distance of the fabric between local and remote sites. ATM is available at various speeds from megabit to gigabit. ATM is illustrated in Figure 8-18. Figure 8-18. Asynchronous Transfer Mode.
|
| < Day Day Up > |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 278