Cisco Wireless Bridges
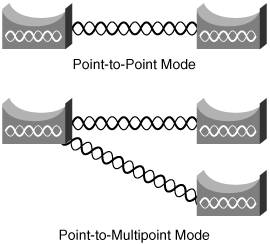
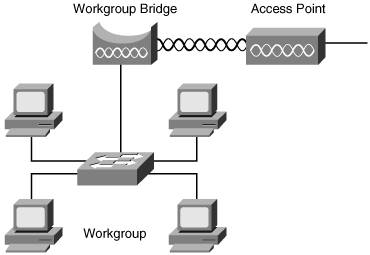
| In the past, connecting buildings on a campus or constructing a metropolitan-area network (MAN) required copper, fiber optic cabling, or expensive microwave equipment. Thanks to Wi-Fi technology, it is possible to unite geographically dispersed networks wirelessly. Cisco provides several options for wireless network connectivity. The ranges for these devices depend on a number of factors, especially the antenna. Antennas are explained in greater detail in Chapter 2. As you read through the product descriptions for APs and bridges (and later when client adapters are introduced), you might wonder why it is important to have an AP or bridge with a range of several thousand feet, or even a few miles, especially when client adapters can reach only a few hundred feet. It is important to understand that bridges and APs serve different functions. Although the job of an AP is to provide a point of connection to wireless clients, a bridge's main function is to connect with other bridges, and it serves as a link between two or more networks. APs, on the other hand, can also be added to enhance the range of a WLAN. Extending the network by adding APs can provide access to clients that are too far away from the WLAN to connect. As such, the greater ranges that APs and bridges afford are useful when bridges have to communicate with each other and when APs are placed to increase overall range. Enhancing your network's reach with additional APs is examined in Chapter 5. Cisco Aironet 1300 Series as a BridgeAs noted in the previous section, the Cisco Aironet 1300 can be used as an outdoor AP or it can be used to connect several LANs in a MAN or campus environmentor even mobile networks. For optimal results in this capacity, the AP must be configured with the proper antenna. The Aironet 1300 can serve as either a point-to-point or point-to-multipoint bridge. This is illustrated in Figure 1-12. Figure 1-12. Aironet Bridges Can Connect with One or Several Other Wireless Bridges The Aironet 1300 bridge can also perform double duty. While connecting with bridges at other sites, the Aironet 1300 can simultaneously perform the functions of a wireless AP, accepting wireless clients. If operating as a workgroup bridge, the Aironet 1300 connects wired Ethernet-enabled devices (laptops, network printers, and so on) to your WLAN. When the bridge is connected to an Ethernet switch, up to 255 devices can be added. Figure 1-13 illustrates this. Figure 1-13. Workgroup Bridging Connects Ethernet Devices to the WLAN The Aironet 1300 comes with either integrated antennas or it can be purchased with connectors for external antennas. As noted in the AP section, the Aironet 1300 bridge is capable of 802.11g. It offers a range up to 9 miles (in the United States) at 11 Mbps. For vehicle deployments, vehicles traveling over 60 mph (100 kph) with data rates at 12 Mbps and 24 Mbps and 128-byte packets experience a 1 percent packet error rate. Cisco Aironet 1400 SeriesLike the Aironet 1300, the 1400 seriesshown in Figure 1-14comes with either an integrated antenna or connectors for optional external antennas. Figure 1-14. Cisco Aironet 1400 Series Bridge Using the 802.11a protocol, the Aironet 1400 with a built-in antenna allows 54-Mbps data rates up to 8.5 miles for point-to-point links and up to 2.75 miles for point-to-multipoint links. Adding an upgradeable antenna, speeds of 9 Mbps can be achieved at a distance of 23 miles. The Aironet 1400 can be deployed in several ways, depending on your network's need. For example, it can be configured to be the singular connection between two geographically disparate networks. Alternately, it can be used as either the primary or the backup connection, in tandem with a second type of connection, such as a T1 line. The Cisco Wireless Security Suite manages security on both the Aironet 1300 and 1400 series. Centralized management is employed through a Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) server. Wireless Bridge Quick ComparisonEach model of Cisco Aironet device offers its own attributes including speeds, network standards, and protocols. Table 1-6 compares the two series.
|
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 126