47.
| [Cover] [Contents] [Index] |
Page 14
gram offset as a measure of atmospheric path radiance, as shown in Figure 1.7.
The empirical line method is described and evaluated by Smith and Milton (1999). The method requires that ground measurements of surface reflectance of dark and bright areas in the image are taken simultaneous with the overflight, though if the areas are spectrally stable then the measurements need not be simultaneous (though they must be taken under similar atmospheric and illumination conditions). The image data are converted to radiance using the standard calibration, and surface reflectance R is regressed against sensor radiance L to give a relationship of the form 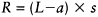 . The term a represents atmospheric radiance, which is then subtracted from apparent radiance L before conversion to reflectance. Other descriptions of the empirical line method are Farrand et al. (1994) and Teillet (1986).
. The term a represents atmospheric radiance, which is then subtracted from apparent radiance L before conversion to reflectance. Other descriptions of the empirical line method are Farrand et al. (1994) and Teillet (1986).
1.3.2 Modelling techniques
The methods described in Section 1.3.1 above involve the subtraction of the same pixel value from the whole image. They are easy to apply, but only provide an approximate correction. If the magnitude of the ground-leaving reflectance for each pixel is required, a more sophisticated method based on modelling techniques is necessary (e.g. Tanré et al., 1986, 1990). These methods attempt to model atmospheric interactions, through which one can retrieve estimates of true target reflectance.
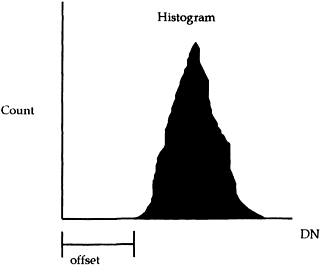
Figure 1.7 An estimate of path radiance is the image histogram offset from zero.
| [Cover] [Contents] [Index] |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 354