202.
| [Cover] [Contents] [Index] |
Page 28
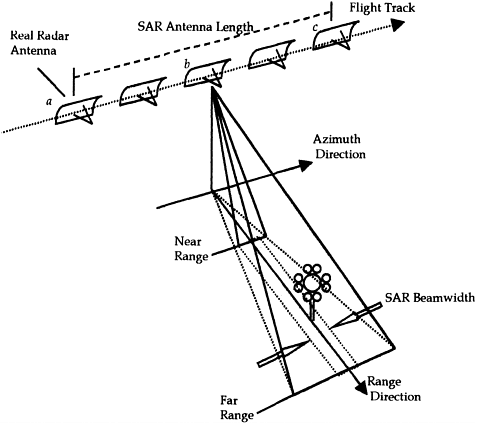
Figure 1.14 Concept of the synthetic aperture.
compute frequency shifts and thus determine the location and scattering properties of the target.
1.6.2 Geometric effects on radar images
A radar image is generated from the timing data for transmitted energy to be returned to radar antenna. This timing delay is dependent on the distance between the radar antenna and the target. This distance is the slant range (Figure 1.13), which is the path along which the microwave energy travels. Therefore, every target located on the terrain being observed by the radar will be mapped on to the slant range domain. Because of this slant range mapping, radar imagery is likely to be affected by geometric distortions. The most common distortions are those of layover, foreshortening and shadow.
The ‘layover’ effect results when the top of an illuminated target is ‘seen’ by the radar as the bottom, and the bottom of the target is recorded by radar as the top. This phenomenon occurs when the time for the microwave energy to travel from the antenna to the top of an object is less than the
| [Cover] [Contents] [Index] |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 354