187.
| [Cover] [Contents] [Index] |
Page 266
6.5.3 Maximiser of posterior marginals
Maximiser of the posterior marginals (MPM) is an alternative optimisation algorithm (Marroquin et al., 1987). It is based on minimising a criterion called the loss function describing the segmentation error. The MPM algorithm is similar to SA, but without the application of any cooling schedule. MPM will therefore be much faster than the SA algorithm in terms of computation time. MPM requires that the posterior distribution of w given observations d be a MRF. The pixel labelling scheme that minimises segmentation error can be shown to maximise the marginal posterior distribution so the new label w′r for pixel r is chosen based on the comparison of all possible labels to satisfy:
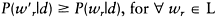 |
(6.53) |
The practical application of the MPM algorithm relies on an important assumption: that a Markov chain exists over wm states, where wm is the number of possible configurations, w is the number of classes or grey levels, and m is the number of pixels. Once this Markov chain has reached steady state, the marginal posterior probability can be approximated by counting the number of times each label is present at each pixel in a series of configurations. This approximation can be expressed by:
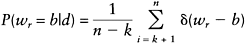 |
(6.54) |
where b represents the possible label belonging to label set L. Function δ(a −b) is defined as
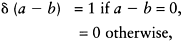 |
(6.55) |
which is equivalent to counting the times that pixel r is labelled as b during the process interval (n−k).
The parameters k and n are chosen heuristically; k is the number of iterations needed for the Markov chain to reach a steady state and n is selected for accurate estimation at acceptable computational cost. For example, in the case of a two-label classification problem, if one chooses k=10, n=110, and if pixel r is labelled 1 on twenty occasions and labelled 2 on eighty occasions, then the probability P(wr=Label 1|dr) will be 20/(n −k)=0.2, and P(wr=Label 2|dr)=0.8. The pixel r will then be classified as label 2 according to Equation (6.53). It can be inferred that the compu
| [Cover] [Contents] [Index] |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 354