114.
| [Cover] [Contents] [Index] |
Page 20
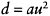 |
(1.16) |
An alternative way to approximate Equation (1.16) is given by:
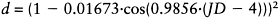 |
(1.17) |
where the term JD denotes the Julian day (e.g. in the case of 5th February, JD=36).
The introduction of the factor d into Equation (1.15) is justified by the following observations. Since at perihelion the magnitude of solar irradiance is greater than that at aphelion, if a sensor obtains the same radiance Lapp at perihelion and aphelion, respectively, the apparent reflectance ρ* at perihelion should be less than that at aphelion. Thus, if the Sun-to-Earth distance is smaller than the average Sun-to-Earth distance, one should use a lower (<1) weighting factor d, and as the Earth is approaching aphelion, a higher value of d should be used.
The final step, that of converting apparent reflectance to ground target reflectance, uses Equation (1.12). We already know the apparent reflectance ρ* from Equation (1.15), while other parameters such as the spherical albedo, S, and the coefficients A and B can be obtained by running either the 5S or the 6S model. An example is given in Table 1.1, which shows part of the output generated by the 5S model. The spherical albedo S and
Table 1.1 Results from the 5S model used for atmospheric correction
|
| Downward | Upward | Total |
| Global gas transmission | 0.961 | 0.965 | 0.932=Tg(θs, θv) |
| Water transmission | 0.988 | 0.989 | 0.980 |
| Ozone transmission | 0.975 | 0.978 | 0.954 |
| CO2 transmission | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| O2 transmission | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.998 |
| NO2 transmission | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| CH4 transmission | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| CO transmission | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Rayleigh scattering transmission | 0.967 | 0.971 | 0.939 |
| Aerosol scattering transmission | 0.953 | 0.962 | 0.917 |
| Total scattering transmission | 0.922 | 0.934 | 0.861=T(θs)T(θv) |
|
| Rayleigh | Aerosols | Total |
| Spherical albedo | 0.048 | 0.087 | 0.123=S |
| Optical depth total | 0.054 | 0.362 | 0.416 |
| Optical depth plane | 0.054 | 0.362 | 0.416 |
| Atmospheric reflectance | 0.019 | 0.017 | 0.037 |
|
|
|
| ρa(θs,θv,φ) |
| Phase function | 0.993 | 0.099 | 0.215 |
| Single scattering albedo | 1.000 | 0.990 | 0.992 |
| [Cover] [Contents] [Index] |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 354