APPENDIX B DOT MODEL FOR THE WINE CLUB
| only for RuBoard - do not distribute or recompile |
APPENDIX B DOT MODEL FOR THE WINE CLUB
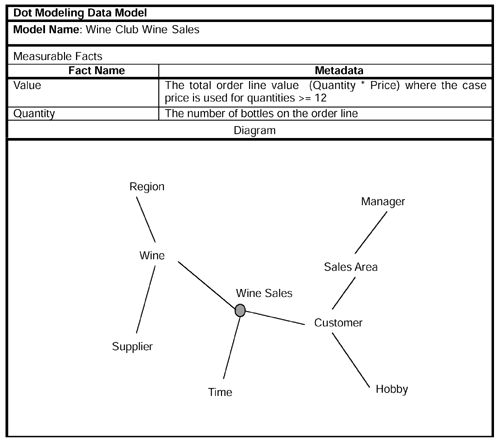
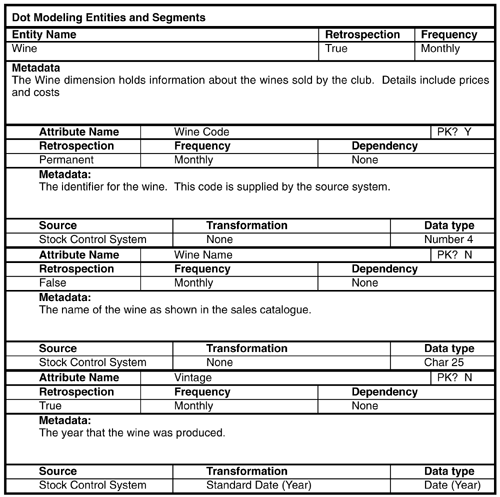
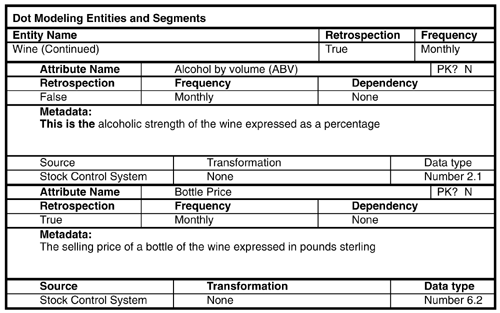
This appendix contains a fuller set of dot model worksheets for the Wine Club case study database. The first worksheets contain the behavioral models. This first worksheet contains the data model for sales of wine.
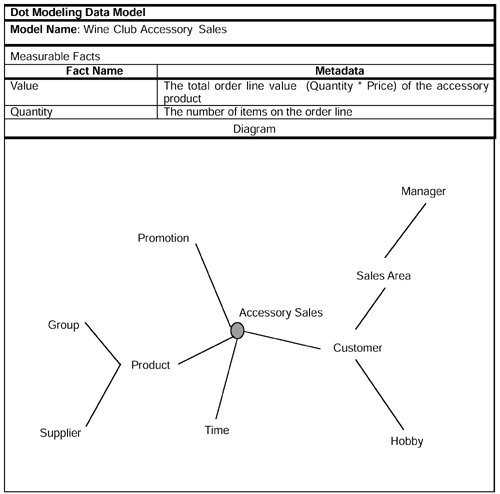
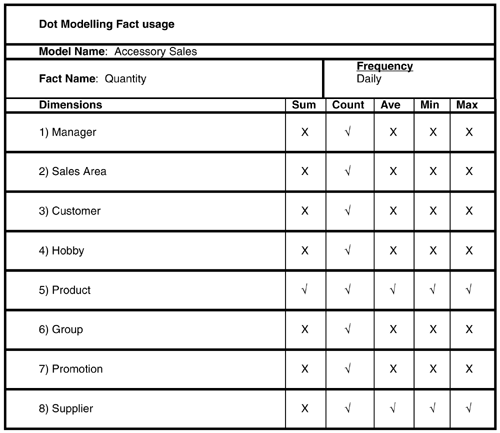
This second dot model shows the customer behavior with respect to the sale of Wine Club accessories. In the main text, the number of dimensions was minimized for the purpose of illustrating the method. Here, we include some additional dimensions.
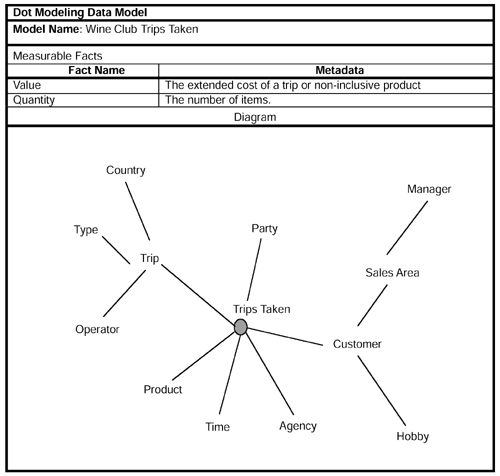
This model contains the customer behavior with respect to trips organized on behalf of the Wine Club. The model contains details about the trip, the tour operator, type of trip (e.g., coach tour) and the area visited (e.g., Burgundy region of France). Also, we record details of the party. The party members may become customer prospects! In addition, there are other products associated with trips, such as personal insurance and noninclusive activities.
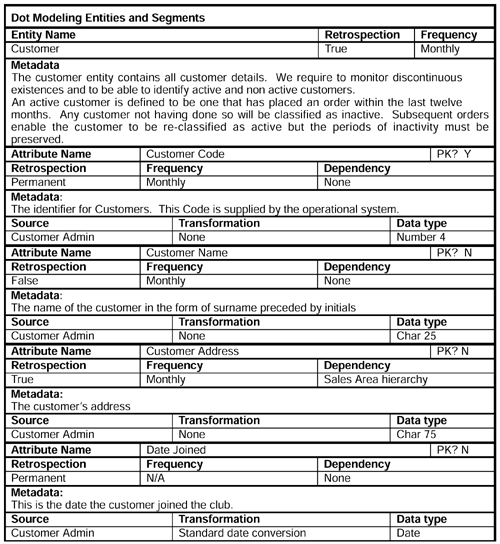
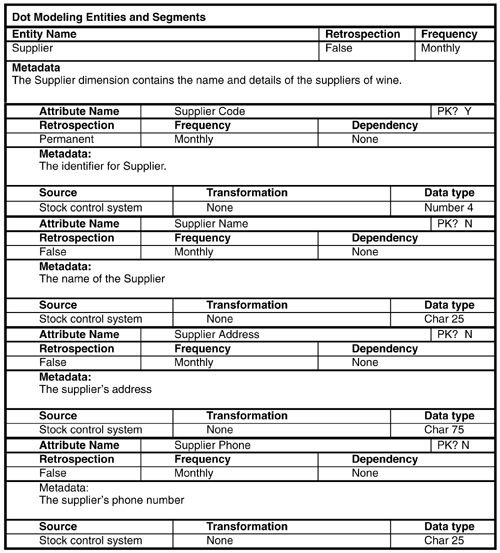
Now we record details of some of the major entities ”customer circumstances, dimensions, and segments that form the nonbehavioral part of the general conceptual model (GCM). We start, obviously, with the customer.
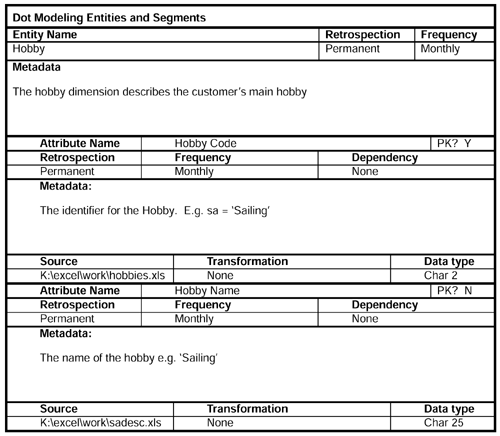
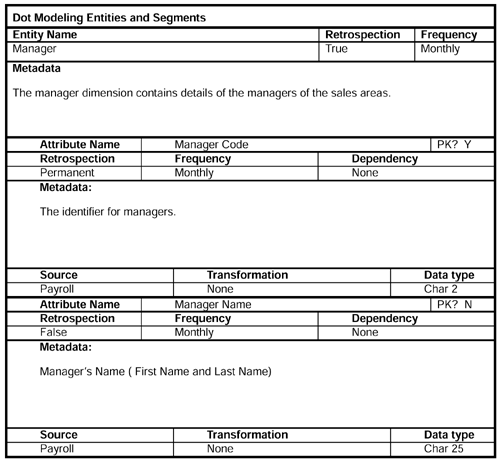
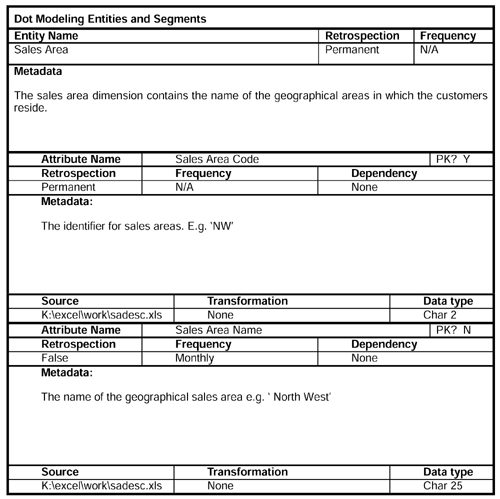
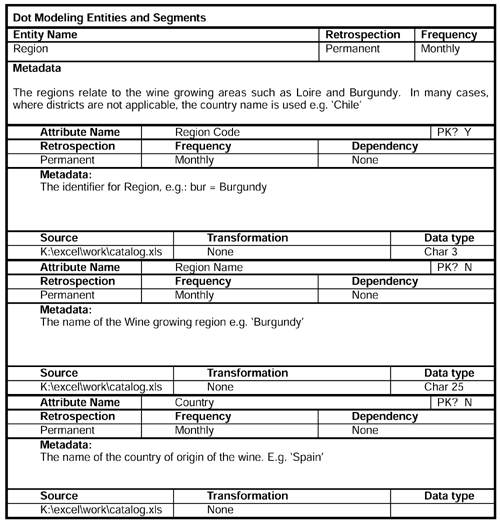
The fact usage worksheet helps us to define by which of the dimensions it is safe to sum the measurable facts. Monetary facts are generally OK, but beware of the issues with quantities . There is risk of adding the quantity of apples to the quantity of oranges, etc.
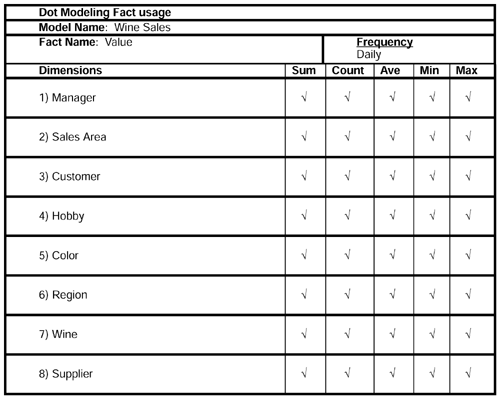
In this example of sales of accessories, the quantities sold can be summed by product, since the product dimension will group by discrete units. But it does not make sense to sum products by, say customer or supplier because combining different units is meaningless. For instance, we might be adding 3 Promotional Sweatshirts to 6 Goblets. The sum of these is 9, but it is nonsensical . Averaging, minimums, and maximums are also usually not very sensible outside of the product domain.
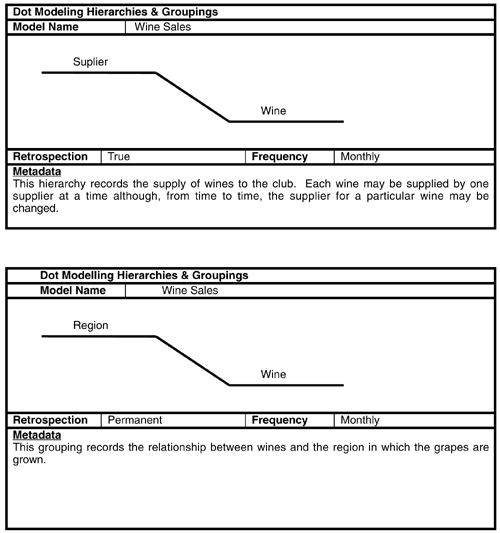
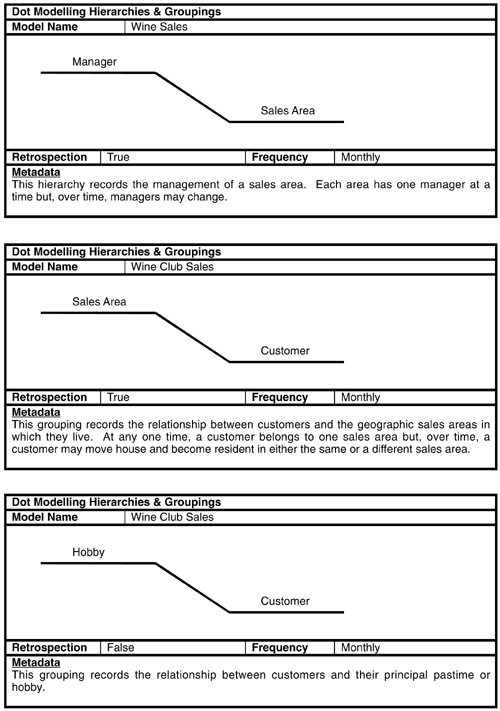
The hierarchies and groupings worksheets record the business meaning of a relationship between two components .
| only for RuBoard - do not distribute or recompile |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 96