| Terminal Services is a Windows 2000 service that allows users to remotely access a Windows 2000 desktop and applications, even when using a computer that is not Windows 2000 capable. This allows you to reuse old hardware that cannot support current operating systems and applications. Terminal Services consists of three separate components : -
The Terminal Server The server is where the applications are running. -
The Terminal Services Client The client is responsible for updating the screen, and passing the keyboard and mouse movements to the server -
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) The RDP protocol runs on top of TCP/IP and is responsible for transmitting commands and screen updates between the client and the server. Terminal Services operates by running the applications on the Windows 2000 Server, and transmitting the screen updates and keyboard and mouse actions between the server and the client software. This allows you to use a low- powered computer to run the client software, because all application processing is taking place on the server. When a user logs on to a Terminal Services session, she receives a desktop that looks just like she were sitting in front of a Windows 2000 computer, as shown in Figure 7.24. Figure 7.24. The Windows 2000 Terminal Services user experience. 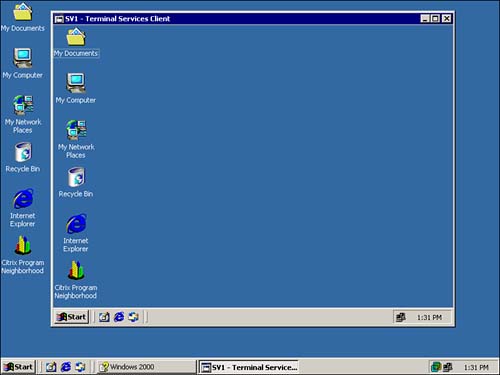 Windows 2000 Terminal service is available in two modes: -
Remote Administration Remote Administration mode allows an administrator to connect remotely to a server, and manage it just like he was sitting in front of the console. Remote Administration mode only supports two concurrent connections, and does not require additional licensing. In addition, only members of the administrators group can connect to a server using Remote Administration mode. -
Application mode In application mode, an unlimited number of connections are supported. However each connection requires a license, called a Terminal Server Client Access License (TSCAL) . A special Terminal Server Licensing Server must be configured to distribute the licenses. There is a grace period of 90 days where the Terminal Server accepts client connections without a valid license. To install Terminal Services -
Select Start, Settings, Control Panel, Add/Remove Programs, Add/Remove Windows Components. -
From the Windows Component Wizard dialog, scroll down and select Terminal Services, as shown in Figure 7.25. If you are installing Terminal Services in Application mode, make sure that you also select Terminal Services Licensing. Click the Next button. Figure 7.25. Selecting Windows 2000 Terminal Services components. 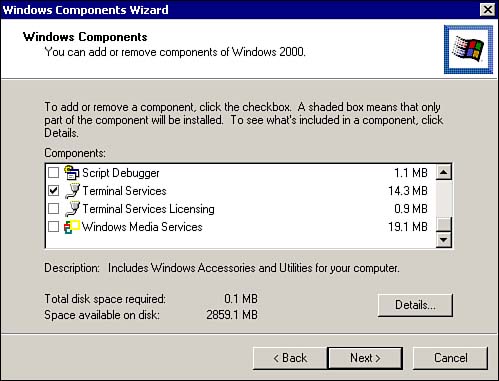 -
This opens the Terminal Services setup dialog as shown in Figure 7.26. From here you can select either Remote or Application Server mode. Click the Next button to continue. Figure 7.26. Selecting the Windows 2000 Terminal Services mode. 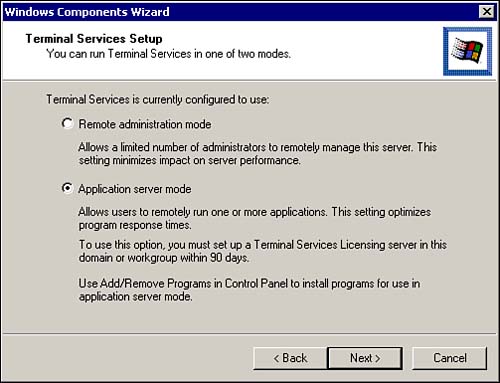 -
When the wizard completes, click the Finish button After the Terminal Services server component is installed, you can install the client software on the remote client computers. The Win32 and Win16 clients are located in the following folder: %systemroot%\system32\ clients \tsclient\. Windows 2000 includes Terminal Server clients for the following platforms: -
32-bit Windows operating systems, including Windows 9x, Me, NT, and 2000 -
Windows for Workgroups running TCP/IP  | Additional clients such as MS-DOS, Unix, Linux, and Macintosh, and additional protocols such as IPX/SPX are supported via a third party add-in from Citrix. |
The Server-side configuration of Terminal Service is managed by two MMCs: -
Terminal Services Configuration This MMC, as seen in Figure 7.27, is used to add and configure network and protocol connections to the Terminal Server, and to configure the connection settings, such as disabling desktop wallpaper and user timeout settings. Figure 7.27. The Terminal Services Configuration MMC. 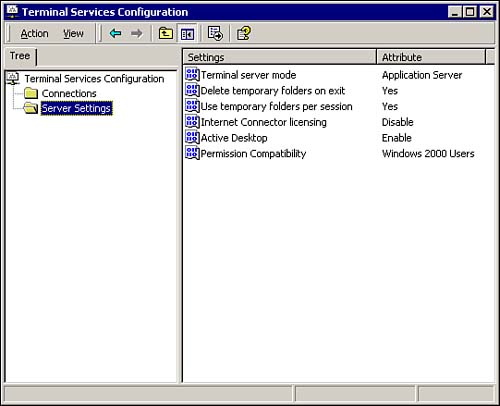 -
Terminal Services Manager This MMC, as shown in Figure 7.28, is used to manage and monitor users, including connecting, disconnecting, remotely controlling users, and resetting user sessions. Figure 7.28. The Terminal Services Manager MMC. 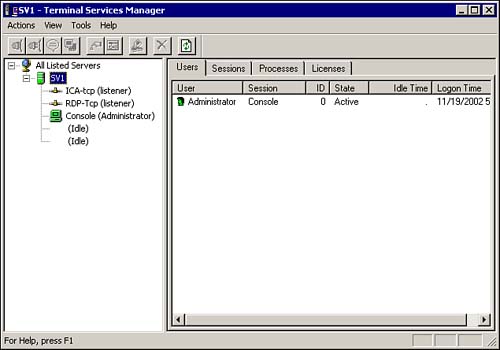 Terminal Services Application Services Mode Unlike the Remote Administrative mode of Terminal Services, in Application Services mode, by default, all users can access a Terminal Services server. This can be controlled from the Terminal Services Profile tab of the users' Properties page in the Active Directory Users and Computers MMC, as shown in Figure 7.29. Figure 7.29. A user's Properties page, showing the Terminal Service Profile tab. 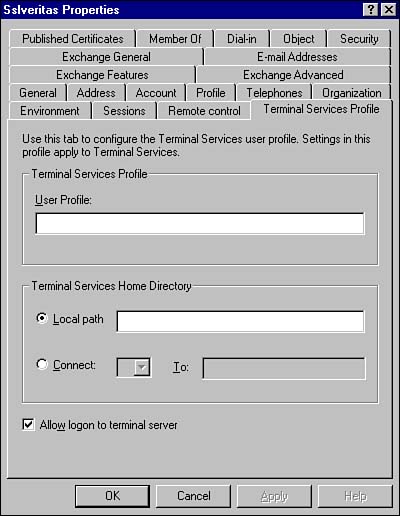 In Application Service mode, as we discussed earlier, each connected user must has a TSCAL, and the licenses must be installed and activated on the Terminal Services Licensing Server. The Licensing Server is installed using the Add/Remove Programs applet, just like other Windows 2000 Services. The licensing rules are as follows : -
Clients have a 90-day grace period so that they can connect to the Terminal Server for testing. After 90 days, the connection is refused . -
Any Windows 2000 computer can connect to the Terminal Services server without requiring the purchase of a TSCAL. -
TSCALs must be purchased for all computers that are not running Windows 2000 that will be connecting to the Terminal Services server. -
If anonymous users will be connecting to the Terminal Services server over the Internet, you must purchase an Internet Connection license.  | When Windows 2000 Terminal Services is running in Application mode, all programs must be installed using the Add/Remove Programs applet in the Control Panel. |
|





