1.1 Current Mass Storage Architectures
| Current architectures (data transfer protocols) have three major problems:
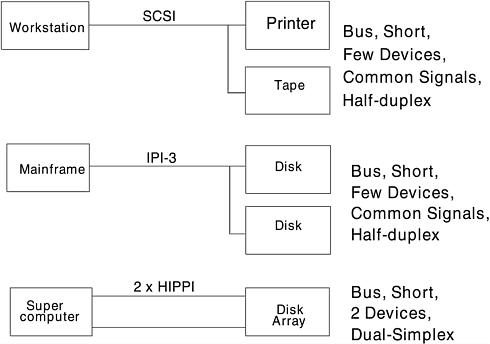
Figure 1-1. Current Limitations For example, the small Computer System Interface (SCSI) parallel interface is restricted to:
In today's modern computer system environments, these restrictions are very limiting to design and confining in space, and it gets worse . The two-byte wide SCSI P-cable limits configurations to 16 devices. The single-ended SCSI protocol is limited to eight IDs or addresses per bus (seven devices and one controller), and wide differential SCSI is limited to 16 IDs per bus (15 devices and one controller) to configure a one-terabyte disk storage unit. A fully redundant disk array would require 30 SCSI IDs (two per bus). These concerns about limited speed, distance, and number of devices caused the industry to start thinking about alternatives. The alternative is Fibre Channel. |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 53