Binary Numbers
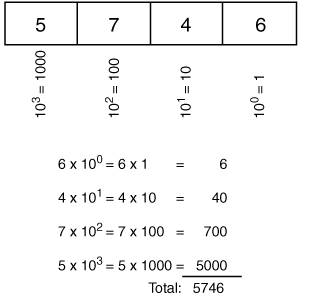
Decimal NumbersWe first analyze the decimal numbers that we are familiar with. Decimal numbers are known as base 10 numbers. Within all numbering systems, the symbols used as digits range from 0 up to one less than the base; thus, within decimal numbers, the following ten unique symbols are used as digits: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 When multiples of these symbols are combined to create a decimal number, each digit in the number is weighted based on its position within the number. The weights used are all powers of 10 (which is what base 10 means). The rightmost digit, which is the least significant, has a weight of 100 (1). The next digit has a weight of 101 (10). The next has a weight of 102 (100), and so on. For example, consider the decimal number 5746. Figure C-1 illustrates how this number is interpreted. Figure C-1. Interpreting a Decimal Number Figure C-1 describes the following points:
We read this number as "five thousand seven hundred and forty-six." The next section provides a similar analysis of binary numbers. |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 156
- Step 1.2 Install SSH Windows Clients to Access Remote Machines Securely
- Step 3.2 Use PuTTY / plink as a Command Line Replacement for telnet / rlogin
- Step 3.3 Use WinSCP as a Graphical Replacement for FTP and RCP
- Step 4.4 How to Generate a Key Using PuTTY
- Step 4.7 Using Public Key Authentication for Automated File Transfers