CSA Components Overview
| < Day Day Up > |
| CSA uses a distributed architecture consisting of two major components:
The next sections provide an overview of both components. Management ConsoleThe CSA MC runs on top of the Microsoft Windows 2000 Server operating system using either a Microsoft Database Engine (MSDE) by default, which is included in the product installation, or Microsoft SQL 2000 when you need to scale beyond 500 agents. The CSA MC is where all management functions are performed. As part of the CiscoWorks VPN Management Solutions (VMS) network management family of products, the CSA MC has the same look and feel as the other management tools from Cisco, and its configuration interface is accessible via a web browser over a secure encrypted Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) connection. Figure 2-1 provides a typical CSA MC screen you will see upon successfully logging in to the CSA MC application with your web browser. Figure 2-1. Cisco Security Agent Management Console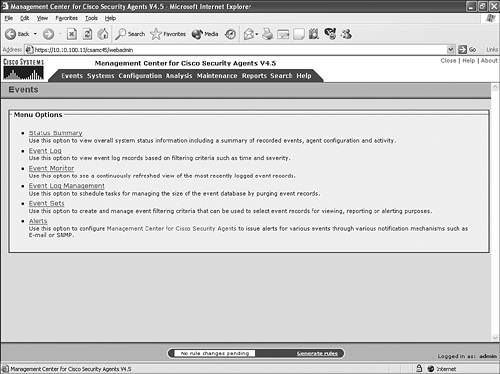 The CSA MC application is where you perform all configuration tasks and tuning of necessary modules, rules, and policies to secure agents. You can also modify host group assignments and attach necessary security policies to groups from this interface. Another major function provided by the MC is the Event Viewer and Reporting tool by which necessary data is presented to the security group such that necessary action can be taken based on event notification. AgentCSA is a software application that installs on end systems. The following are host operating systems supported by the Cisco Security Agent:
The agent monitors the local system for policy violations and protects local resources and data from being compromised. Whenever an attempted policy violation is detected, a message is sent to the MC for centralized reporting purposes. At predetermined time intervals (polling time), the agents report back to the MC server to see whether any policy changes have been made to what is currently running on the local agent. Figure 2-2 shows a view of the CSA user interface that you can access from any agent-protected system in your environment. Figure 2-2. CSA Local User Interface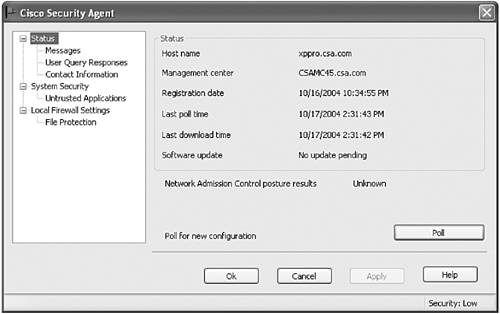 |
| < Day Day Up > |