Reducing Project Costs
A budget-constrained project is one in which costs are the most important factor in the project plan. Although you still need to balance schedule requirements and satisfy the project scope, the costs are at the forefront of your decision-making processes as you plan and execute the project.
If your project plan calculates that your total costs are above the allowed budget, you need cost-cutting strategies. Your best approach will involve cutting resources because resources and costs are virtually synonymous in projects. As described in the previous section, when you want to bring in the finish date, you focus on tasks in the critical path . In the same way, when you want to cut costs, you focus on resources to gain the biggest cost savings.
Viewing Project Costs
Review your cost picture first, compare it with your budget, and then make any necessary adjustments. To review total project costs using Project Statistics, do the following:
-
Click Project, Project Information.
-
In the Project Information dialog box, click the Statistics button.
The Project Statistics dialog box appears. The current or scheduled total project cost appears in the Cost column.
You can also see the total project cost in the Project Summary Task when you apply the Cost table, as follows :
-
Display the Gantt Chart or other task sheet.
-
Click View, Table, Cost. The Cost table is applied.
-
Click Tools, Options and then click the View tab.
-
Under Outline Options, select the Show Project Summary Task check box and then click OK.
The project summary task row appears at the top of the task sheet. The total project cost, as currently scheduled, is displayed in the Total Cost field.
Two cost reports can help you analyze project costs, as follows:
Budget report. Click View, Reports. Double-click Costs and then double-click Budget (see Figure 9-12). The Total Cost column is a summary of the resource costs and fixed costs for each task.
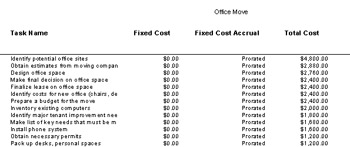
Figure 9-12: Run the Budget report to view costs for each task.
Cash Flow report. Click View, Reports. Double-click Costs and then double-click Cash Flow (see Figure 9-13). This report forecasts the funding needed for each period of time, enabling you to see whether budgeted costs will be exceeded at a particular point.
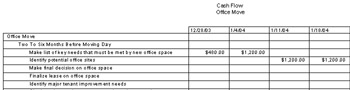
Figure 9-13: Run the Cash Flow report to see cost forecasts by time period.
You can sort a sheet view by costs. To review task or resource costs in order of amount, do the following:
-
Display a task sheet or resource sheet, depending on whether you want to see costs by resource or by task.
-
Click View, Table, Cost.
-
Click Project, Sort, By Cost.
The sheet is sorted by the Total Cost field. To return to the original sort order, click Project, Sort, By ID.
You can filter a sheet view to display only tasks or resources that have costs exceeding a specified amount. To do this, follow these steps:
-
Display a task sheet or resource sheet, depending on whether you want to see costs by resource or by task.
-
Click View, Table, Cost.
-
Click Project, Filtered For, More Filters.
-
In the More Filters dialog box, click Cost Greater Than and then click Apply.
-
In the Cost Greater Than dialog box, enter the amount (see Figure 9-14).
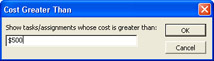
Figure 9-14: To see only those tasks or assignments that have a scheduled cost exceeding a certain amount, enter the amount in this dialog box.To see all tasks or all resources again, click Project, Filtered For, All Tasks or All Resources.
| |
If you investigate your total project costs and discover that you have more budget than costs, you have some decisions to make. Depending on the type of project, the situation, and the amount of extra budget, you can:
-
Reserve the buffer. Use the extra funds as insurance against potential risks.
-
Add resources. Use the money to hire resources and take some of the load off overallocated resources or bring in the finish date.
-
Add scope. Add tasks you were hoping to include, but thought you wouldn't have enough money to do. Build in a higher level of quality. If applicable , increase quantities being produced.
-
Inform your manager or client that you can complete the project well under budget.
| |
Checking Your Cost Assumptions
If you find that your scheduled costs are higher than your budget, first review the individual costs themselves . Check the resource rates as well as fixed costs for tasks and make sure they're accurate.
To check resource rates, review the Resource Sheet with the Entry table applied. With the default fields in the Entry table, you can see each resource's standard rate, overtime rate, and cost per use.
To check fixed costs for tasks, review a task sheet such as the Gantt Chart with the Cost table applied. The Fixed Cost field displays any costs associated with the tasks that are independent of resource costs.
Adjusting the Schedule to Reduce Costs
If many of your resource costs are based on time periods such as an amount per hour or per day, you might be able to cut costs if you can reduce task durations. For example, suppose you have a 2-day fixed-units task assigned to a $100/ hour resource. By default, this resource is assigned to 16 hours of work, for a cost of $1600. If you reduce the duration to1day, the work is reduced to 8 hours, and the cost is reduced to $800.
When you reduce task duration in a fixed-units or fixed-duration task, the amount of work is also reduced. However, if you reduce duration for a fixed-work task, work stays the same and assignment units increase. In this case, resource costs would not be reduced.
| Cross-References | For more information about changing durations, see "Checking and Adjusting Durations" earlier in this chapter. |
Adjusting Assignments to Reduce Costs
Another way to reduce work and therefore cut costs is to reduce work directly. In effect, you're cutting the amount of time that resources are spending on assigned tasks.
The manner in which a work reduction affects your task and resource scheduling depends on the individual task types. When you decrease work in a fixed-units or fixed-work task, duration is reduced. When you decrease work in a fixed-duration task, units are decreased.
To change work amounts for individual resources, display the Task Usage view or Resource Usage view, and edit the Work field for the assignment.
| |
The following are suggestions for reducing resource costs by adjusting assignments:
-
If you have assignments with multiple resources assigned, reduce the work for the more expensive resources and assign the work to less expensive resources. By shuffling work around on an assignment, you won't risk changing duration or units inadvertently.
-
If you have resources with the same skills and availability, replace the more expensive work or material resources with less expensive ones. Although this replacement can introduce some risk into your project, it can also ensure that you're using your expensive resources where you really need them.
-
If you have resources with the same skills and availability, replace slower work or equipment resources with faster ones. If one resource is faster than another, you might save money, even if the faster resource's rate is higher.
-
If you have material resources whose costs are based on assignment units, for example,3tons or 100 yards, decrease the assignment units; that is, use less of the material.
| |
| Note | You can also adjust scope to cut costs. |
| Cross-References | For more information about cutting scope, see "Changing Project Scope" later in this chapter. |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 268