Using Character Map
Windows 2000 uses version 2 of the Unicode character-encoding standard. Unicode is a 16-bit character-encoding system in which each character is stored as 16 bits, or 2 bytes, of computer data. This permits tracking 65,536 different characters. (Traditional character sets are single-byte and can define only 256 characters per set.) To date, about 39,000 of the Unicode character slots have been defined by the Unicode Consortium. These include all the standard Latin alphabetic characters, punctuation marks, diacritics, mathematical and technical symbols, commercial symbols, arrows, dingbats, line-drawing characters, box-drawing characters, characters from 24 non-Latin alphabets, and more.
While Unicode provides for this huge array of characters, the individual fonts on your system probably support only a subset. With the Character Map utility, you can see what's available in each font. Character Map also makes it easy to use the full range of your fonts' character support in your documents. You'll find Character Map invaluable when you need to work with a special-character font (such as Symbol or Wingdings), and when you need accented letters, commercial symbols, and other characters that aren't available on the standard typewriter keys of your keyboard. Character Map's initial display is shown in Figure 13-5.
Figure 13-5. Character Map helps you find and use special characters in any font.
To run Character Map, open the Start menu, point to Programs, Accessories, System Tools, and choose Character Map. (You can also open the Start menu, choose Run, and then type charmap.exe.)
At the top of the window is a box in which you can select any font available on your system. Below the list is a table displaying all the characters available in the selected font. You can't change the size of the Character Map window (other than to minimize it), but you can get an enlarged view of any character by selecting it with the mouse or the keyboard.
To select a character with the mouse, simply click the character. To select a character with the keyboard, press Tab until the highlight is in the character grid. Then use the arrow keys to move the highlight. (Press the Spacebar to see an enlarged version of each character.) Figure 13-6 shows how Character Map looks when the copyright symbol in Times New Roman is selected.
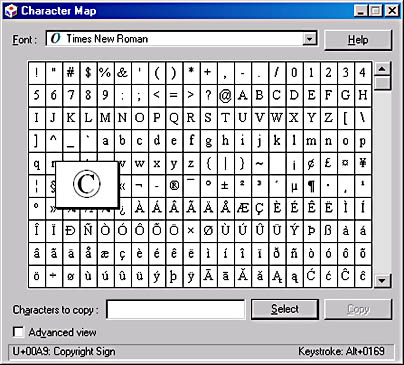
Figure 13-6. To get an enlarged view of any character, simply select it.
In the lower left corner of the Character Map window, you'll find the Unicode code for the selected character (00A9 in the case of the copyright symbol). In the lower right corner, you might find a keystroke combination for the selected character. If so, you can enter that character into most applications by holding down the Alt key, typing the four numbers of the keystroke combination on the numeric keypad, and then releasing the Alt key. Note that you must use the numeric keypad, and that some applications don't accept characters entered in this manner. (In Word you must turn on Num Lock before using the numeric keypad for this purpose.)
Inserting Special Characters into Your Documents
The Alt+key method of entering characters is supported for the sake of compatibility with earlier versions of the operating system. Fortunately, you can insert special characters into your documents in much easier ways. In many applications, you can copy a character from Character Map by using drag and drop. Simply click the character once in Character Map to select it, then drag it to your document, dropping it where you want to insert it.
If your application doesn't support this drag-and-drop maneuver, you can do the following:
- Select the character you want in Character Map.
- Click the Select button.
- Click the Copy button.
- In your application, choose Paste or press Ctrl+V.
You can copy a whole string of characters at once using this method. Select the first character, click Select, select the next, click Select, and so on, until the entire string appears on the Characters To Copy line. Then click the Copy button.
Searching for Characters in Character Map
Characters in Character Map are listed in order of their Unicode values. If the character you need has a relatively low Unicode value, you might be able to scroll right to it. In many cases, though, you'll need to search for it. Character Map provides a variety of ways to locate characters.
Searching by Name
Every Unicode character has a name. For example, a lowercase œ ligature is called Latin Small Ligature oe. A capital Œ ligature is called Latin Capital Ligature Oe. (A ligature combines a frequently used sequence of characters into a single form.) If you know the name of the character you want, you can find it as follows:
- Select the Advanced View check box.
- Type the name of the character on the Search For line.
- Click the Search button.
If you don't know the entire name of the character, type some of it. For example, if you type oe, you'll get both the capital and lowercase œ ligatures. If you type ligature, you'll get all the ligatures available in the current font, and you can select the one you need.
Searching by Unicode Value
To find a character by its Unicode value:
- Select the Advanced View check box.
- Type the four-digit hexadecimal Unicode value into the Go To Unicode box.
For example, to find the Hebrew letter Kaf with Dagesh, you would type FB3B into the Go To Unicode box with a Hebrew font selected, such as Miriam.
SEE ALSO
To install support for multiple languages, see "Installing Language Support and Using Keyboard Layouts."
Searching by Subset
To find MS-DOS characters (characters included in the extended ASCII or OEM character set) or characters from another Unicode subset, follow these steps:
- Select the Advanced View check box.
- Select a subset from the Character Set box.
Searching by Category
Unicode characters are grouped in categories within each font. To search for a character by its category:
- Select the Advanced View check box.
- In the Group By box, choose Unicode Subrange.
- In the Group By window that appears, select the category you're interested in (see Figure 13-7).
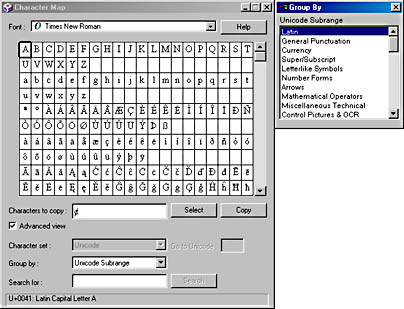
Figure 13-7. To display a list of Unicode categories, choose Unicode Subrange in the Group By box.
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 317