3.6 Special Case IP Addresses
3.6 Special Case IP Addresses
Having described subnetting we now show the seven special case IP addresses in Figure 3.9. In this figure, 0 means a field of all zero bits, -1 means a field of all one bits, and netid, subnetid, and hostid mean the corresponding field that is neither all zero bits nor all one bits. A blank subnet ID column means the address is not subnetted .
Figure 3.9. Special case IP addresses.
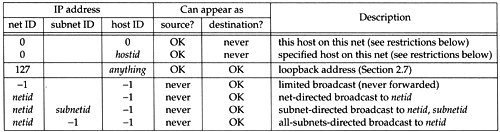
We have divided this table into three sections. The first two entries are special case source addresses, the next one is the special loopback address, and the final four are the broadcast addresses.
The first two entries in the table, with a network ID of 0, can only appear as the source address as part of an initialization procedure when a host is determining its own IP address, for example, when the BOOTP protocol is being used (Chapter 16).
In Section 12.2 we'll examine the four types of broadcast addresses in more detail.
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 378