| You can configure alerts to notify you when certain events occur or when certain performance thresholds are reached. You can send these alerts as network messages and as events that are logged in the application event log. You can also configure alerts to start applications and performance logs. To add alerts in Performance Monitor, complete the following steps: -
Right-click Alerts in the left pane of the Performance console, and then choose New Alert Settings. -
In the New Alert Settings dialog box, type a name for the alert, such as Processor Alert or Disk I/O Alert . Then click OK. This opens the dialog box shown in Figure 3-18. Figure 3-18. Use the Disk I-O Alert dialog box to configure counters that trigger alerts. 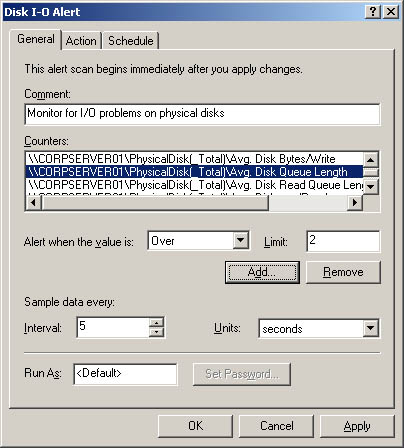 -
In the General tab, type an optional description of the alert. Then click Add to display the Add Counters dialog box. This dialog box is identical to the Add Counters dialog box shown previously in Figure 3-13. -
Use the Add Counters dialog box to add counters that trigger the alert. Click Close when you're finished. -
In the Counters panel, select the first counter and then use the Alert When Value Is ... field to set the occasion when an alert for this counter is triggered. Alerts can be triggered when the counter is over or under a specific value. Select Over or Under, and then set the trigger value. The unit of measurement is whatever makes sense for the currently selected counter(s). For example, to alert if processor time is over 95 percent, you would select Over and then type 95 . Repeat this process to configure other counters you've selected. -
In the Sample Data Every ... field, type in a sample interval and select a time unit in seconds, minutes, hours, or days. The sample interval specifies when new data is collected. For example, if you sample every 10 minutes, the log is updated every 10 minutes. Caution Don't sample too frequently. You'll use system resources and might cause the server to seem unresponsive to user requests .
-
In the Run As field, type the name of the account under which the counter log will run, and then click Set Password. After you type the password for the account and then confirm the password, click OK to close the Set Password dialog box. To run alert logging under the default system account, type <Default> . -
Select the Action tab, shown in Figure 3-19. You can now specify any of the following actions to happen when an alert is triggered: -
Log An Entry In The Application Event Log Creates log entries for alerts -
Send A Network Message To Sends a network message to the computer specified -
Start Performance Data Log Sets a counter log to start when an alert occurs -
Run This Program Sets the complete file path of a program or batch file script to run when the alert occurs Figure 3-19. Set actions that are executed when the alert occurs. 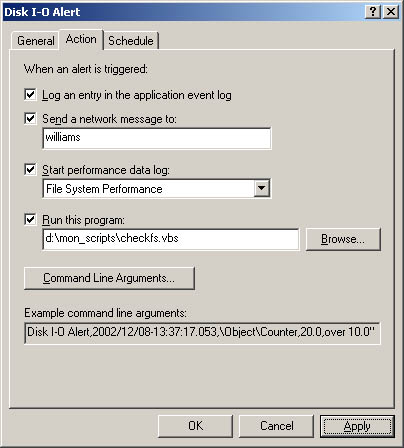 Note Alerts can be configured to run executable programs with the .exe extension and batch files with the .bat or .cmd extension when an alert is triggered. Be sure to type the full path to the program or batch file you want to run. The Run This Program text field will accept only valid file paths. If you enter an invalid file path, you'll see a warning specifying this when you click OK or try to access another tab. To pass arguments to an executable or batch file application, use the options of the Command Line Arguments panel. Normally, arguments are passed as individual strings. However, if you select Single Argument String, the arguments are passed in a comma-separated list within a single string. The Example Command Line Arguments list at the bottom of the tab shows how the arguments would be passed.
-
Choose the Schedule tab, and then specify when alerting starts and stops. For example, you could configure the alerts to start on a Friday evening and stop on Monday morning. Then each time an alert occurs during this period, the specified action(s) are executed. -
You can configure alerts to start manually or automatically at a specific date. Select the appropriate option, and then specify a start date, if necessary. -
You can configure alerts to stop manually or automatically after a specified period of time, such as seven days, or at a specific date and time. -
When you've finished setting the alert schedule, click OK. The alert is then created, and you can manage it in much the same way that you manage counter and trace logs. Real World Figure 3-19 shows the Run This Program field with the path to a Windows script with the .vbs extension as the action to take. If the .vbs script exists in the location specified, this will be accepted as a valid entry. However, when the alert is triggered, the Windows script won't run and an error will be entered in the Application event log. To run a Windows script as an action, you must follow the steps outlined in the section of this chapter entitled "Running Scripts as Actions." | |

