Technical Overview of OSPF
| < Free Open Study > |
Default Routing with EIGRPA default route can be injected into EIGRP in two primary ways:
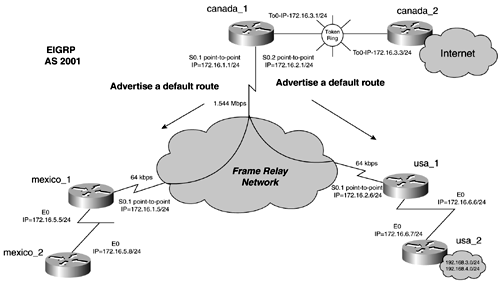
With both ways, the router needs the ip classless global command enabled. With IP classless, the router forwards any packets toward the default route that it does not have a more specific route toward. ip classless is enabled by default in Cisco IOS Software Release 12.0 and later. In Figure 11-11, the canada_1 router advertises a default route to usa_1 and mexico_1. canada_1 does this by creating a static route pointing at a next -hop address of 172.16.3.3 or the canada_2 router. Figure 11-11. EIGRP Default Routing Example 11-27 lists the configuration of the canada_1 router advertising a default static route. Example 11-27 Advertising a Default Static Route with EIGRP on canada_1router eigrp 2001 redistribute static Example 11-28 lists the route table of the mexico_1 router demonstrating how the default route is received. Notice that when the route is advertised, it is an external router because it is redistributed, and it has the * denoting it is the default route. The gateway of last resort also is set. Example 11-28 Route Table of the mexico_1 Routermexico_1# show ip route Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, * - candidate default U - per-user static route, o - ODR T - traffic engineered route Gateway of last resort is 172.16.1.1 to network 0.0.0.0 172.16.0.0/24 is subnetted, 5 subnets C 172.16.5.0 is directly connected, Ethernet0 D 172.16.6.0 [90/2707456] via 172.16.1.1, 00:04:15, Serial0.1 C 172.16.1.0 is directly connected, Serial0.1 D 172.16.2.0 [90/2681856] via 172.16.1.1, 00:04:51, Serial0.1 D 172.16.3.0 [90/2185984] via 172.16.1.1, 00:04:51, Serial0.1 D 192.168.4.0/24 [90/2835456] via 172.16.1.1, 00:04:15, Serial0.1 10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks D 10.1.2.0/30 [90/2313984] via 172.16.1.1, 00:04:51, Serial0.1 D 10.1.1.0/24 [90/2313984] via 172.16.1.1, 00:04:52, Serial0.1 182.16.0.0/24 is subnetted, 2 subnets D 182.16.4.0 [90/2313984] via 172.16.1.1, 00:04:52, Serial0.1 D 182.16.3.0 [90/2313984] via 172.16.1.1, 00:04:52, Serial0.1 D 192.168.3.0/24 [90/2835456] via 172.16.1.1, 00:04:15, Serial0.1 D*EX 0.0.0.0/0 [170/2331136] via 172.16.1.1, 00:00:53, Serial0.1 mexico_1# |
| < Free Open Study > |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 283