| Numbers and currencies follow a similar pattern to date/times and DateTime FormatInfo, but without the additional complexity of calendars: Numbers and currencies are formatted using the NumberFormatInfo class. The CultureInfo class has a NumberFormatInfo property called NumberFormat. It is possible to build your own culture-unaware format strings from primitives such as #, the comma, the period, and zero (e.g., "###,###.00"). It is possible to specify culture-aware formats (see Table 6.16) using a format specifier, which draws on information in a NumberFormatInfo object. Table 6.16. Standard Number Format SpecifiersFormat Specifier | Name | Uses NumberFormatInfo |
|---|
c, C | Currency | Yes | d, D | Decimal | No | e, E | Exponential (Scientific) | No | f, F | Fixed point | Yes | g, G | General | No | n, N | Number | Yes | p, P | Percent | Yes | r, R | Round-trip | No | x, X | Hexadecimal | No |
Number types that overload ToString methods accept an IFormatProvider that can be either a NumberFormatInfo or a CultureInfo (from which the NumberFormatInfo is extracted) . The FxCop "Specify IFormatProvider" rule catches number types that overload ToString methods, which are not called with an IFormatProvider.
As we saw with date/times, it should be obvious by now that predicting the myriad cultural differences across the world is very difficult, but to remove any doubt, have a look at the examples in Table 6.17, which show the number 20000.15 formatted for currency in a selection of different cultures. Notice the use of commas and periods to indicate sometimes a thousands separator and a decimal separator, and sometimes vice versa; the positioning of the currency symbol; the positioning of the negative sign; the expression of negatives using parentheses; and the exclusion of decimals altogether. Table 6.17. Examples of Formatted CurrenciesCulture Name | Culture DisplayName | Example Formatted Currency |
|---|
ar-SA | Arabic (Saudi Arabia) | 20,000.15.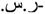 | bg-BG | Bulgarian (Bulgaria) | -20 000,15  | ca-ES | Catalan (Catalan) | -20.000,15 € | zh-CN | Chinese (People's Republic of China) |  -20,000.15 -20,000.15
| zh-HK | Chinese (Hong Kong S.A.R.) | (HK$20,000.15) | da-DK | Danish (Denmark) | kr -20.000,15 | de-DE | German (Germany) | -20.000,15 € | de-AT | German (Austria) | -€ 20.000,15 | en-US | English (United States) | ($20,000.15) | en-GB | English (United Kingdom) | -£20,000.15 | es-AR | Spanish (Argentina) | $-20.000,15 | es-CL | Spanish (Chile) | -$ 20.000,15 | ja-JP | Japanese (Japan) | -¥20,000 | id-ID | Indonesian (Indonesia) | (Rp20.000) |
|
 -20,000.15
-20,000.15