7.15. User-Defined Functions DB2 provides built-in functions that allow you to manipulate your data within an SQL statement. For example, the year function can retrieve the year of a timestamp column, as shown here. db2 select year(current timestamp) from sysibm.sysdummy1 1 ----------- 2005
In addition to built-in functions, DB2 allows you to create your own functions. These user-defined functions (UDFs) allow you to simplify database application development by moving some of the logic to the database. A UDF takes zero to many input parameters and returns a value, a row or a table. To create a UDF, use the CREATE FUNCTION statement. UDFs can be classified as follows. Sourced functions: These functions are created on top of DB2 built-in functions. Here's an example. CREATE FUNCTION trim (p_var1 VARCHAR(50)) RETURNS VARCHAR(50) RETURN RTRIM(LTRIM(p_var1))
In this example, RTRIM is a DB2 built-in function that removes all the blanks at the end of a string. LTRIM is a DB2 built-in function that removes all the blanks at the beginning of a string. The UDF trim is created to remove blanks at the beginning and the end of a string by using these two built-in functions. To test the function, you can use the VALUES statement as follows: VALUES (trim(' hello ')
which returns: 1 -------------------------------------------------- hello
SQL functions: These functions are written in SQL PL language. They can return a scalar value, a single row, or a table of data. The following code shows an example of an SQL UDF returning a scalar value: the rounded salary of an employee. CREATE FUNCTION csmmgr.salary_round(p_empno CHAR(6)) RETURNS INTEGER LANGUAGE SQL F1: BEGIN ATOMIC DECLARE v_salary INTEGER; SET v_salary = (SELECT ceiling(salary) FROM employee WHERE empno = p_empno); RETURN v_salary; END
This function takes an employee number as input and returns the salary rounded to the highest integer value. SQL functions can be developed by using the Development Center, as illustrated in Figure 7.29. Figure 7.29. Using the Development Center tool to develop, test, and run the csmmgr.salary_round user-defined function 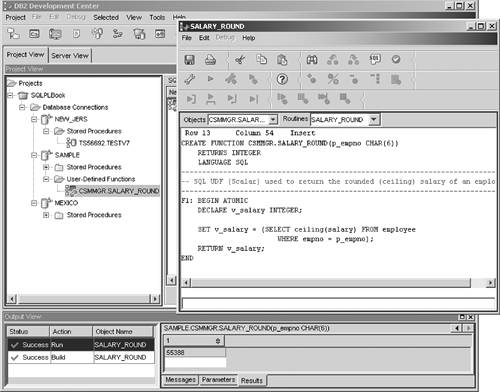
External functions: These functions are defined in the database with references to object code libraries that are written in C, Java, or OLE. Consider this example. CREATE FUNCTION csmmgr.db2killapp(INT) RETURNS INT EXTERNAL NAME 'db2killapplib!db2killapp' LANGUAGE C PARAMETER STYLE SQL NOT FENCED RETURNS NULL ON NULL INPUT NOT DETERMINISTIC NO SQL NO EXTERNAL ACTION
This statement registers the UDF csmmgr.db2killapp to DB2. It is an external function written in C. The C executable code is stored in the db2killapplib library, which is stored under the sqllib\function subdirectory.
|
