Disk Management Overview
Use the Disk Management snap-in in Windows XP Professional to perform disk-related tasks, such as creating basic and dynamic volumes, formatting them, and assigning drive letters.
You must be a member of the Administrators group to use Disk Management.
To open Disk Management
-
From the Start menu, click Run.
-
In the Open box, type diskmgmt.msc, and then click OK.
| Note | If you upgrade from Microsoft Windows 98, Microsoft Windows 98, Second Edition (SE), or Microsoft Windows Millennium Edition to Windows XP Professional, a message appears when you open Disk Management during the first 30 days after installation. The message indicates that making any changes to your disk configuration, such as creating or deleting partitions or converting them to dynamic, prevents you from uninstalling Windows XP Professional. For more information, see Supporting Installations in this book. |
After you install a new disk, you must choose a partition style and storage type to use on the disk. Your choices vary according to which operating system you are running and whether the computer is an x86 based computer or an Itanium based computer. Table 12-3 describes the storage types and partition styles that are available for each edition of Microsoft Windows XP and Windows 2000.
| Operating System | Storage Types | Partition Styles | ||||
| Basic Volumes | Dynamic Simple, Spanned, and Striped Volumes | Dynamic Mirrored and RAID-5 Volumes | MBR Disks | GPT Disks | ||
| Microsoft Windows XP Home Edition | X | X | ||||
| Windows XP Professional | X | X | X | |||
| Windows XP 64 Bit Edition | X | X | X | X | ||
| Windows 2000 Professional | X | X | X | |||
| Windows 2000 Server family | X | X | X | X |
Windows XP Professional offers two storage types: basic disk and dynamic disk. Basic disks use the same disk structures as those used in Windows Me or earlier, Microsoft Windows NT 4.0, and Microsoft Windows 2000. When using basic disks, you are limited to creating four primary partitions per disk, or three primary partitions and one extended partition with unlimited logical drives. Primary partitions and logical drives on basic disks are known as basic volumes.
Dynamic disks were introduced in Windows 2000 and are supported and enhanced by Windows XP Professional. Dynamic disks provide features that basic disks do not, such as the ability to create volumes that span multiple disks. All volumes on dynamic disks are known as dynamic volumes.
The term partition style refers to the method that Windows XP Professional uses to organize partitions on the disk. All x86-based computers use the partition style known as the master boot record (MBR). The MBR contains a partition table that describes where the partitions are located on the disk. Because MBR is the only partition style available on x86-based computers, you do not need to choose this style; it is used automatically.
Itanium-based computers running the Windows XP 64-Bit Edition use a new partition style called the globally unique identifier (GUID) partition table (GPT). The GPT partition style supports partitions up to 18 exabytes and 128 partitions per disk.
The introduction of GPT makes understanding the partition styles a bit more challenging, but most disk-related tasks are unchanged. You can still use basic disks and dynamic disks as you did in Windows 2000, and these storage types are available on disks that use either partition style.
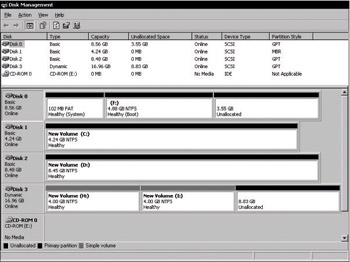
Disk Management differentiates between partition styles by referring to disks that use the master boot record as MBR disks and disks that use the GUID partition table as GPT disks. Figure 12-1 shows how Disk Management displays GPT and MBR disks in an Itanium-based computer.
| Note | You can use Windows XP 64-Bit Edition to manage MBR disks and GPT disks. However, you cannot start Windows XP 64-Bit Edition from an MBR disk.
|
For more information about GPT disks, see Managing GPT Disks in Itanium-based Computers later in this chapter. For sector-level details about MBR and GPT disks, see Troubleshooting Disks and File Systems in this book.
EAN: N/A
Pages: 338